Heidi Schambra
Quantifying Impairment and Disease Severity Using AI Models Trained on Healthy Subjects
Nov 21, 2023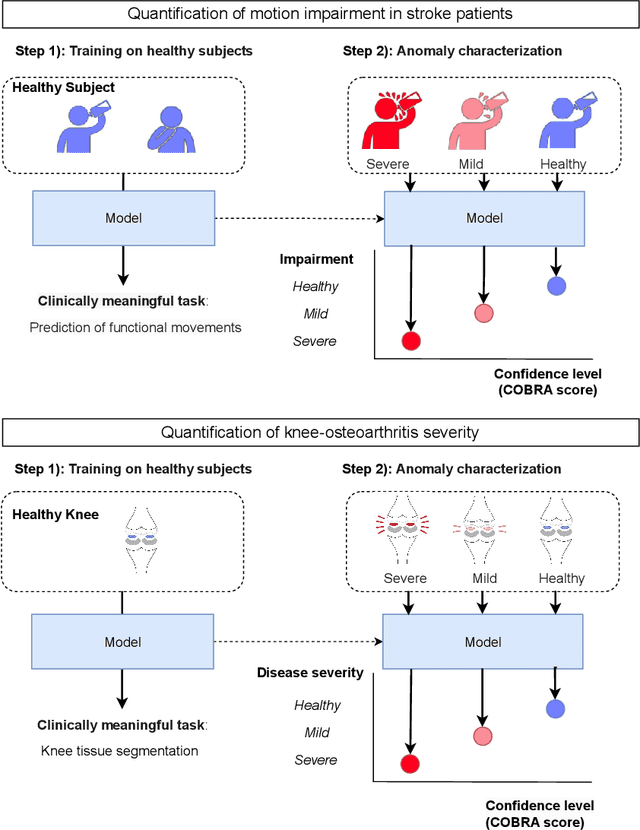
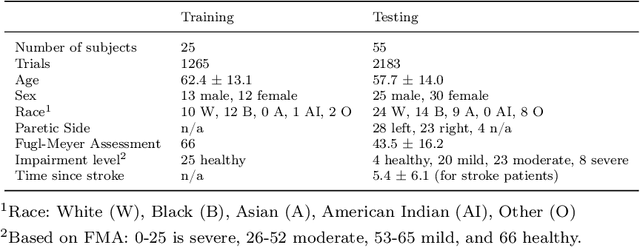
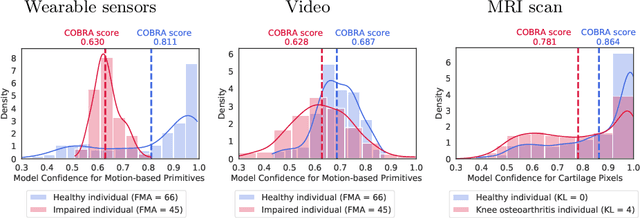
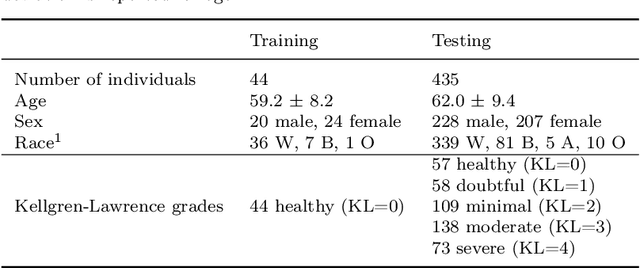
Abstract:Automatic assessment of impairment and disease severity is a key challenge in data-driven medicine. We propose a novel framework to address this challenge, which leverages AI models trained exclusively on healthy individuals. The COnfidence-Based chaRacterization of Anomalies (COBRA) score exploits the decrease in confidence of these models when presented with impaired or diseased patients to quantify their deviation from the healthy population. We applied the COBRA score to address a key limitation of current clinical evaluation of upper-body impairment in stroke patients. The gold-standard Fugl-Meyer Assessment (FMA) requires in-person administration by a trained assessor for 30-45 minutes, which restricts monitoring frequency and precludes physicians from adapting rehabilitation protocols to the progress of each patient. The COBRA score, computed automatically in under one minute, is shown to be strongly correlated with the FMA on an independent test cohort for two different data modalities: wearable sensors ($\rho = 0.845$, 95% CI [0.743,0.908]) and video ($\rho = 0.746$, 95% C.I [0.594, 0.847]). To demonstrate the generalizability of the approach to other conditions, the COBRA score was also applied to quantify severity of knee osteoarthritis from magnetic-resonance imaging scans, again achieving significant correlation with an independent clinical assessment ($\rho = 0.644$, 95% C.I [0.585,0.696]).
PrimSeq: a deep learning-based pipeline to quantitate rehabilitation training
Dec 22, 2021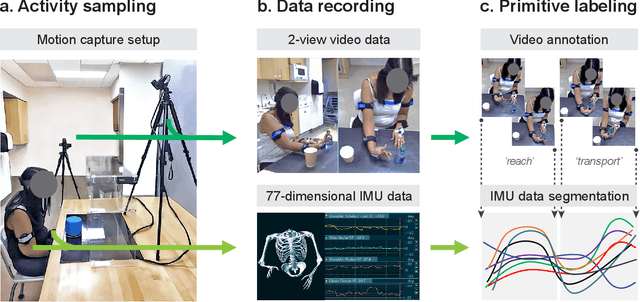
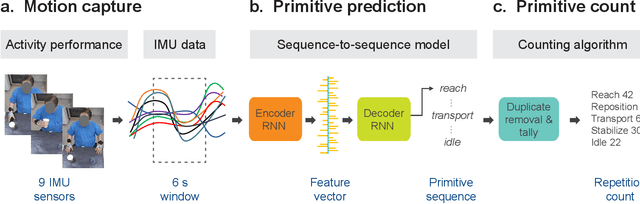
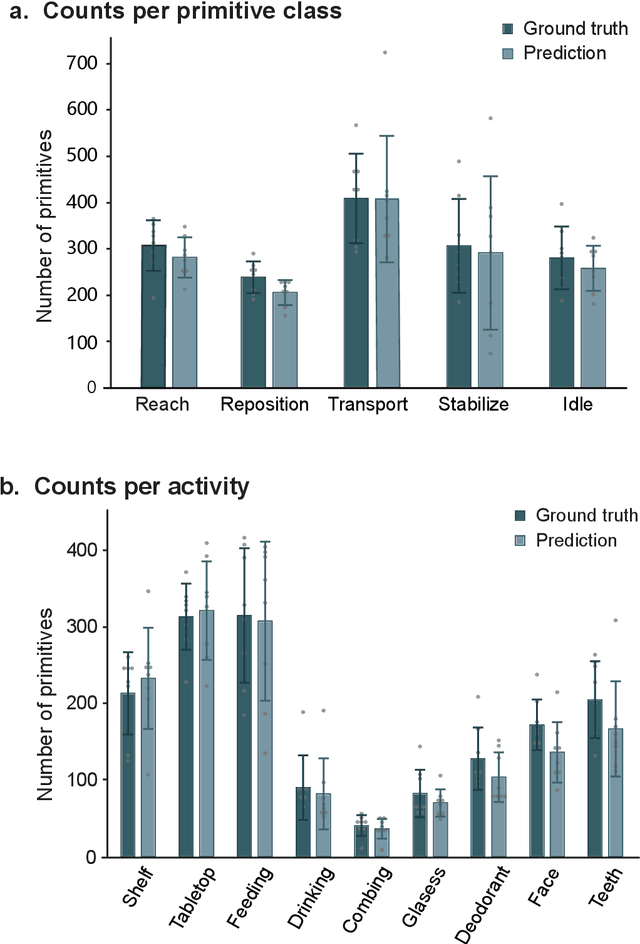
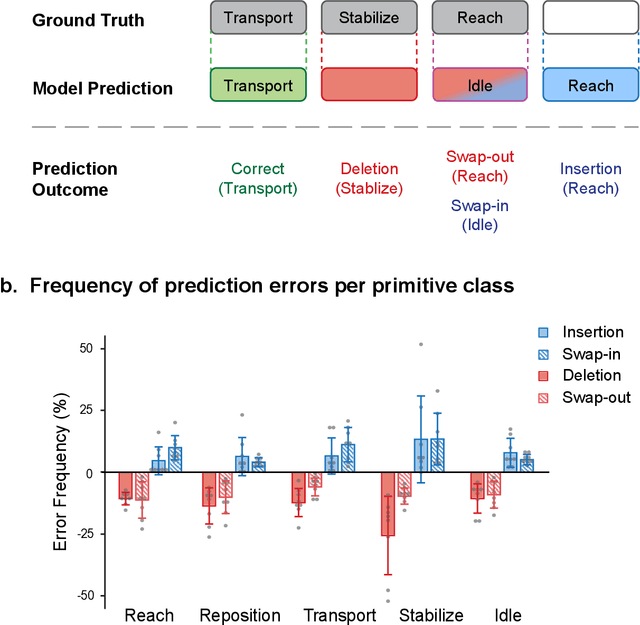
Abstract:Stroke rehabilitation seeks to increase neuroplasticity through the repeated practice of functional motions, but may have minimal impact on recovery because of insufficient repetitions. The optimal training content and quantity are currently unknown because no practical tools exist to measure them. Here, we present PrimSeq, a pipeline to classify and count functional motions trained in stroke rehabilitation. Our approach integrates wearable sensors to capture upper-body motion, a deep learning model to predict motion sequences, and an algorithm to tally motions. The trained model accurately decomposes rehabilitation activities into component functional motions, outperforming competitive machine learning methods. PrimSeq furthermore quantifies these motions at a fraction of the time and labor costs of human experts. We demonstrate the capabilities of PrimSeq in previously unseen stroke patients with a range of upper extremity motor impairment. We expect that these advances will support the rigorous measurement required for quantitative dosing trials in stroke rehabilitation.
Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling for Action Identification at High Temporal Resolution
Nov 03, 2021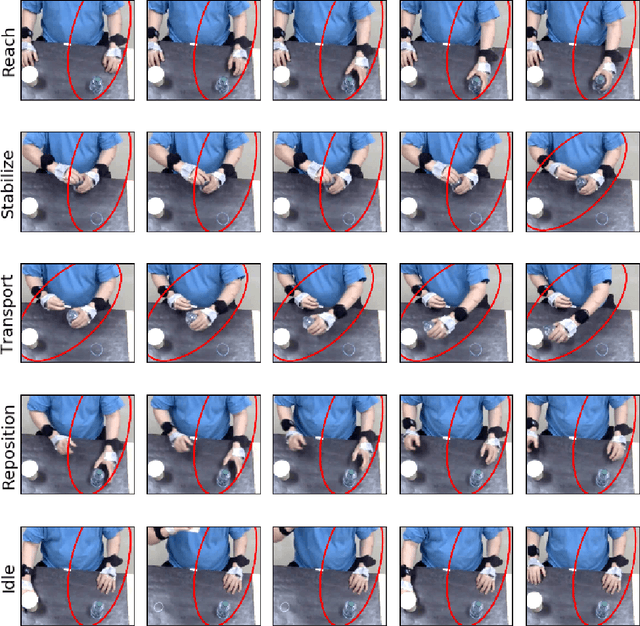
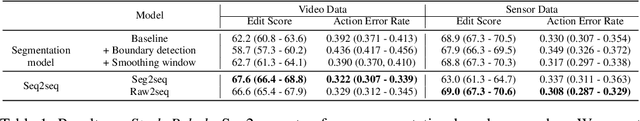
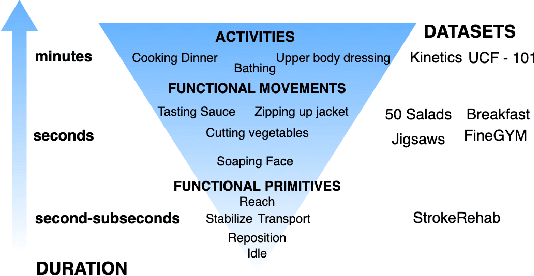
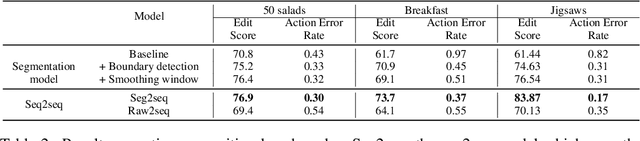
Abstract:Automatic action identification from video and kinematic data is an important machine learning problem with applications ranging from robotics to smart health. Most existing works focus on identifying coarse actions such as running, climbing, or cutting a vegetable, which have relatively long durations. This is an important limitation for applications that require the identification of subtle motions at high temporal resolution. For example, in stroke recovery, quantifying rehabilitation dose requires differentiating motions with sub-second durations. Our goal is to bridge this gap. To this end, we introduce a large-scale, multimodal dataset, StrokeRehab, as a new action-recognition benchmark that includes subtle short-duration actions labeled at a high temporal resolution. These short-duration actions are called functional primitives, and consist of reaches, transports, repositions, stabilizations, and idles. The dataset consists of high-quality Inertial Measurement Unit sensors and video data of 41 stroke-impaired patients performing activities of daily living like feeding, brushing teeth, etc. We show that current state-of-the-art models based on segmentation produce noisy predictions when applied to these data, which often leads to overcounting of actions. To address this, we propose a novel approach for high-resolution action identification, inspired by speech-recognition techniques, which is based on a sequence-to-sequence model that directly predicts the sequence of actions. This approach outperforms current state-of-the-art methods on the StrokeRehab dataset, as well as on the standard benchmark datasets 50Salads, Breakfast, and Jigsaws.
Towards data-driven stroke rehabilitation via wearable sensors and deep learning
Apr 22, 2020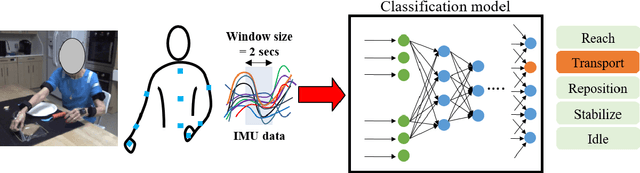
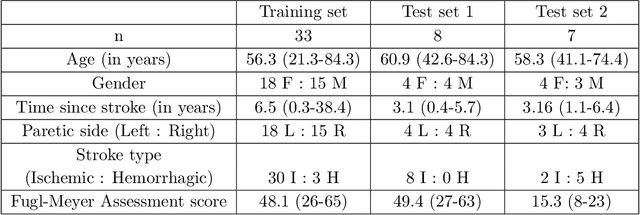
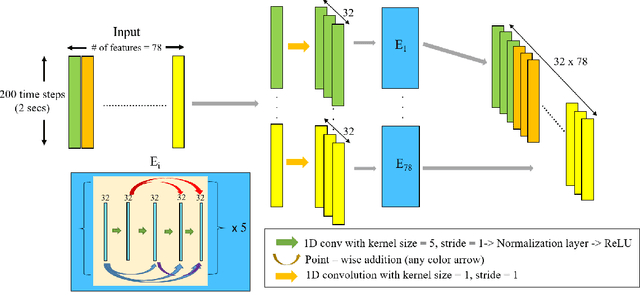
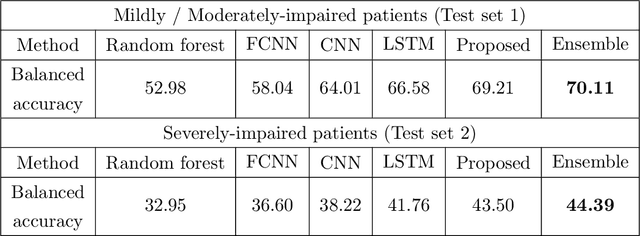
Abstract:Recovery after stroke is often incomplete, but rehabilitation training may potentiate recovery by engaging endogenous neuroplasticity. In preclinical models of stroke, high doses of rehabilitation training are required to restore functional movement to the affected limbs of animals. In humans, however, the necessary dose of training to potentiate recovery is not known. This ignorance stems from the lack of objective, pragmatic approaches for measuring training doses in rehabilitation activities. Here, to develop a measurement approach, we took the critical first step of automatically identifying functional primitives, the basic building block of activities. Forty-eight individuals with chronic stroke performed a variety of rehabilitation activities while wearing inertial measurement units (IMUs) to capture upper body motion. Primitives were identified by human labelers, who labeled and segmented the associated IMU data. We performed automatic classification of these primitives using machine learning. We designed a convolutional neural network model that outperformed existing methods. The model includes an initial module to compute separate embeddings of different physical quantities in the sensor data. In addition, it replaces batch normalization (which performs normalization based on statistics computed from the training data) with instance normalization (which uses statistics computed from the test data). This increases robustness to possible distributional shifts when applying the method to new patients. With this approach, we attained an average classification accuracy of 70%. Thus, using a combination of IMU-based motion capture and deep learning, we were able to identify primitives automatically. This approach builds towards objectively-measured rehabilitation training, enabling the identification and counting of functional primitives that accrues to a training dose.
Be Like Water: Robustness to Extraneous Variables Via Adaptive Feature Normalization
Feb 25, 2020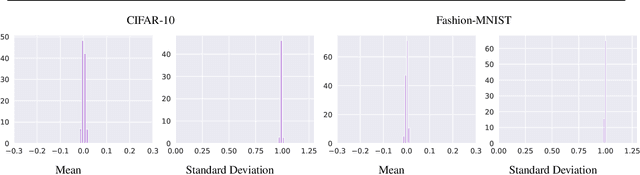
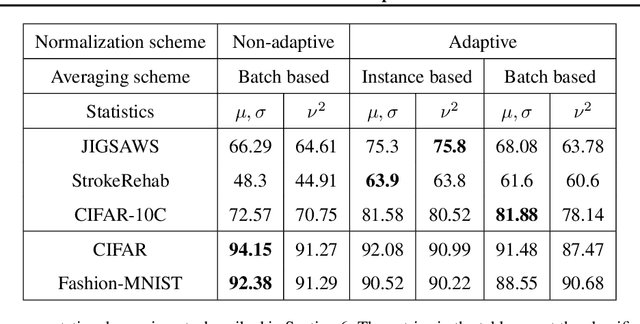
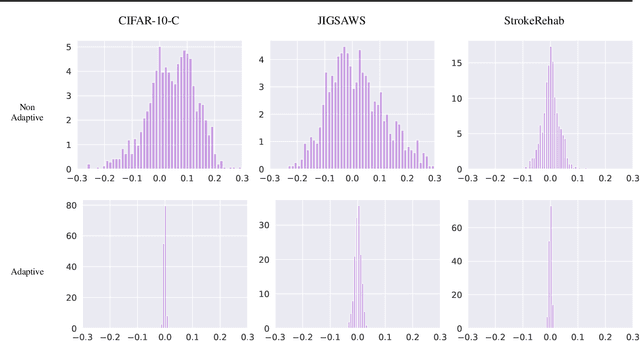
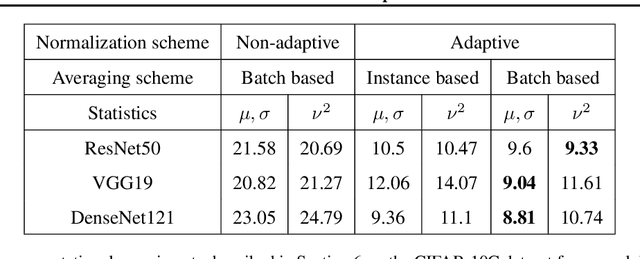
Abstract:Extraneous variables are variables that are irrelevant for a certain task, but heavily affect the distribution of the available data. In this work, we show that the presence of such variables can degrade the performance of deep-learning models. We study three datasets where there is a strong influence of known extraneous variables: classification of upper-body movements in stroke patients, annotation of surgical activities, and recognition of corrupted images. Models trained with batch normalization learn features that are highly dependent on the extraneous variables. In batch normalization, the statistics used to normalize the features are learned from the training set and fixed at test time, which produces a mismatch in the presence of varying extraneous variables. We demonstrate that estimating the feature statistics adaptively during inference, as in instance normalization, addresses this issue, producing normalized features that are more robust to changes in the extraneous variables. This results in a significant gain in performance for different network architectures and choices of feature statistics.
Pragmatic classification of movement primitives for stroke rehabilitation
Mar 11, 2019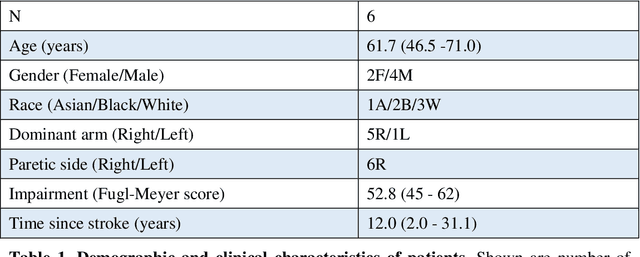
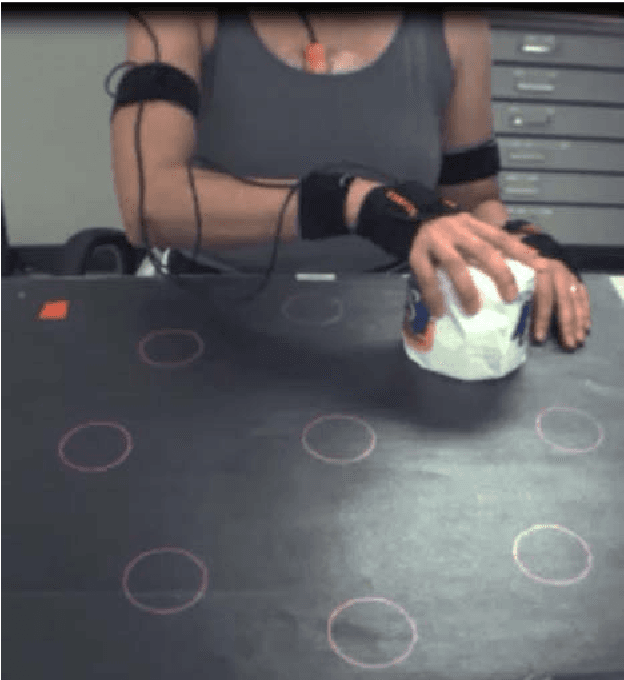

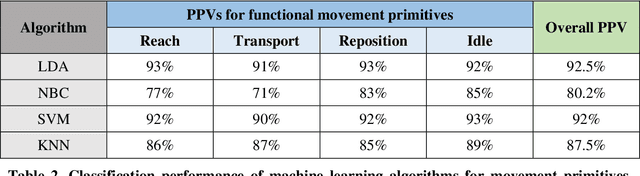
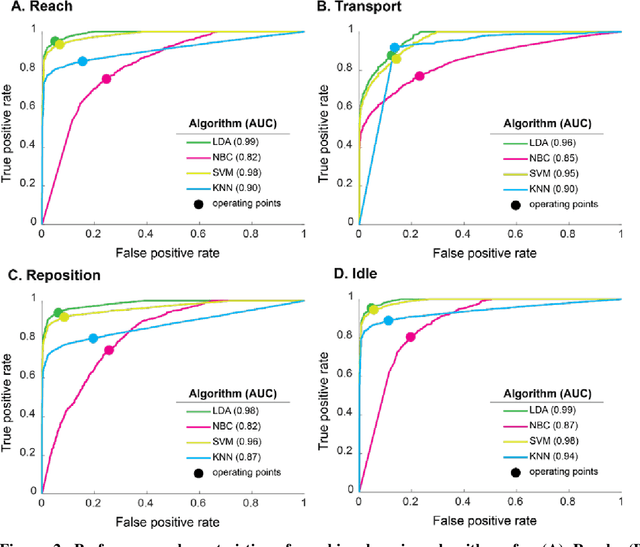
Abstract:Rehabilitation training is the primary intervention to improve motor recovery after stroke, but a tool to measure functional training does not currently exist. To bridge this gap, we previously developed an approach to classify functional movement primitives using wearable sensors and a machine learning (ML) algorithm. We found that this approach had encouraging classification performance but had computational and practical limitations, such as training time, sensor cost, and magnetic drift. Here, we sought to refine this approach and determine the algorithm, sensor configurations, and data requirements needed to maximize computational and practical performance. Motion data had been previously collected from 6 stroke patients wearing 11 inertial measurement units (IMUs) as they moved objects on a target array. To identify optimal ML performance, we evaluated 4 algorithms that are commonly used in activity recognition (linear discriminant analysis (LDA), na\"ive Bayes, support vector machine, and k-nearest neighbors). We compared their classification accuracy, computational complexity, and tuning requirements. To identify optimal sensor configuration, we progressively sampled fewer sensors and compared classification accuracy. To identify optimal data requirements, we compared accuracy using data from IMUs versus accelerometers. We found that LDA had the highest classification accuracy (92%) of the algorithms tested. It also was the most pragmatic, with low training and testing times and modest tuning requirements. We found that 7 sensors on the paretic arm and back resulted in the best accuracy. Using this array, accelerometers had a lower accuracy (84%). We refined strategies to accurately and pragmatically quantify functional movement primitives in stroke patients. We propose that this optimized ML-sensor approach could be a means to quantify training dose after stroke.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge