Hayato Kobayashi
Diamonds in the Rough: Generating Fluent Sentences from Early-Stage Drafts for Academic Writing Assistance
Oct 21, 2019
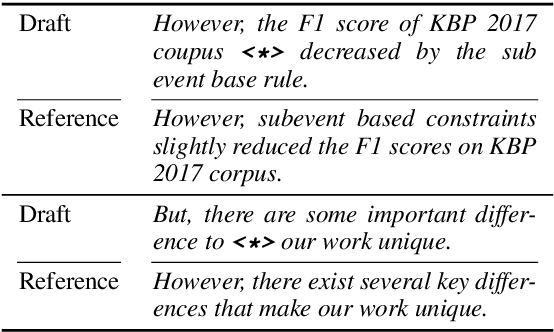

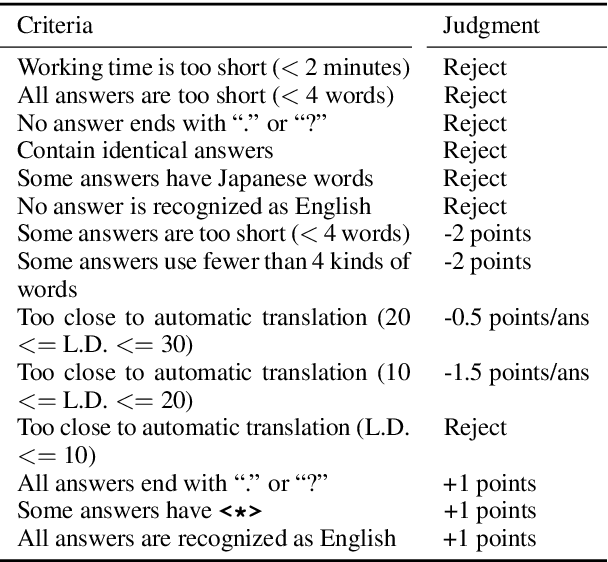
Abstract:The writing process consists of several stages such as drafting, revising, editing, and proofreading. Studies on writing assistance, such as grammatical error correction (GEC), have mainly focused on sentence editing and proofreading, where surface-level issues such as typographical, spelling, or grammatical errors should be corrected. We broaden this focus to include the earlier revising stage, where sentences require adjustment to the information included or major rewriting and propose Sentence-level Revision (SentRev) as a new writing assistance task. Well-performing systems in this task can help inexperienced authors by producing fluent, complete sentences given their rough, incomplete drafts. We build a new freely available crowdsourced evaluation dataset consisting of incomplete sentences authored by non-native writers paired with their final versions extracted from published academic papers for developing and evaluating SentRev models. We also establish baseline performance on SentRev using our newly built evaluation dataset.
Cross-domain Recommendation via Deep Domain Adaptation
Mar 08, 2018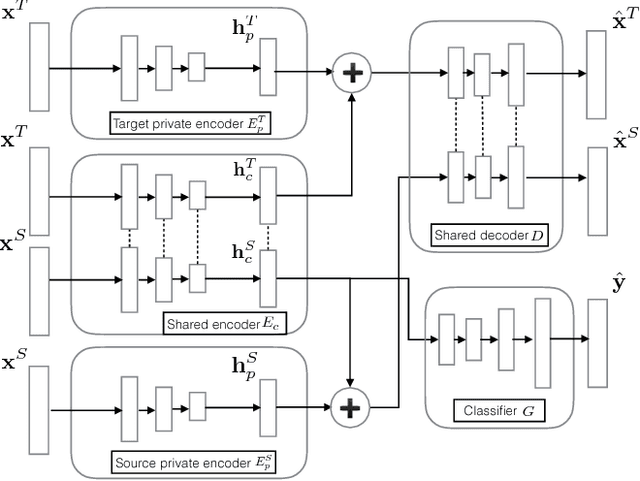
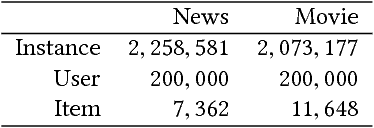
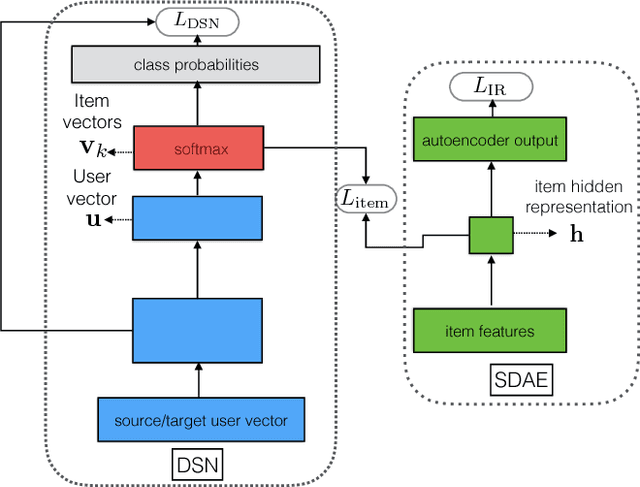
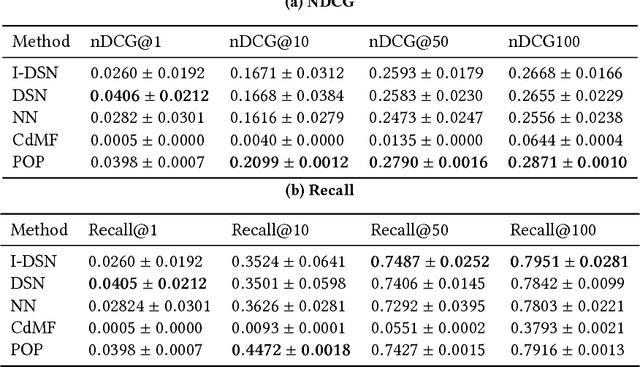
Abstract:The behavior of users in certain services could be a clue that can be used to infer their preferences and may be used to make recommendations for other services they have never used. However, the cross-domain relationships between items and user consumption patterns are not simple, especially when there are few or no common users and items across domains. To address this problem, we propose a content-based cross-domain recommendation method for cold-start users that does not require user- and item- overlap. We formulate recommendation as extreme multi-class classification where labels (items) corresponding to the users are predicted. With this formulation, the problem is reduced to a domain adaptation setting, in which a classifier trained in the source domain is adapted to the target domain. For this, we construct a neural network that combines an architecture for domain adaptation, Domain Separation Network, with a denoising autoencoder for item representation. We assess the performance of our approach in experiments on a pair of data sets collected from movie and news services of Yahoo! JAPAN and show that our approach outperforms several baseline methods including a cross-domain collaborative filtering method.
Incremental Skip-gram Model with Negative Sampling
Apr 15, 2017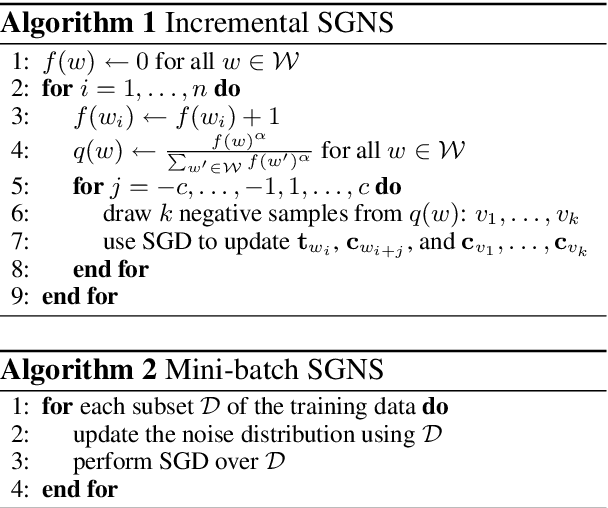

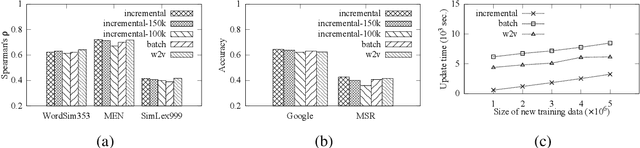
Abstract:This paper explores an incremental training strategy for the skip-gram model with negative sampling (SGNS) from both empirical and theoretical perspectives. Existing methods of neural word embeddings, including SGNS, are multi-pass algorithms and thus cannot perform incremental model update. To address this problem, we present a simple incremental extension of SGNS and provide a thorough theoretical analysis to demonstrate its validity. Empirical experiments demonstrated the correctness of the theoretical analysis as well as the practical usefulness of the incremental algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge