Nobuhiro Kaji
Chat Detection in an Intelligent Assistant: Combining Task-oriented and Non-task-oriented Spoken Dialogue Systems
Jul 24, 2018
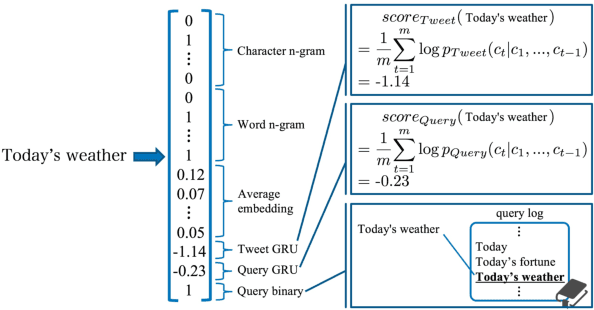

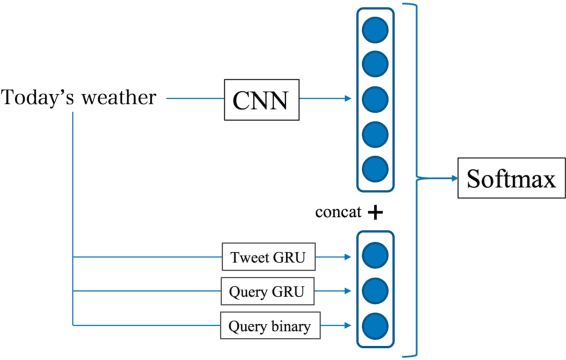
Abstract:Recently emerged intelligent assistants on smartphones and home electronics (e.g., Siri and Alexa) can be seen as novel hybrids of domain-specific task-oriented spoken dialogue systems and open-domain non-task-oriented ones. To realize such hybrid dialogue systems, this paper investigates determining whether or not a user is going to have a chat with the system. To address the lack of benchmark datasets for this task, we construct a new dataset consisting of 15; 160 utterances collected from the real log data of a commercial intelligent assistant (and will release the dataset to facilitate future research activity). In addition, we investigate using tweets and Web search queries for handling open-domain user utterances, which characterize the task of chat detection. Experiments demonstrated that, while simple supervised methods are effective, the use of the tweets and search queries further improves the F1-score from 86.21 to 87.53.
Predicting Causes of Reformulation in Intelligent Assistants
Jul 13, 2017



Abstract:Intelligent assistants (IAs) such as Siri and Cortana conversationally interact with users and execute a wide range of actions (e.g., searching the Web, setting alarms, and chatting). IAs can support these actions through the combination of various components such as automatic speech recognition, natural language understanding, and language generation. However, the complexity of these components hinders developers from determining which component causes an error. To remove this hindrance, we focus on reformulation, which is a useful signal of user dissatisfaction, and propose a method to predict the reformulation causes. We evaluate the method using the user logs of a commercial IA. The experimental results have demonstrated that features designed to detect the error of a specific component improve the performance of reformulation cause detection.
Incremental Skip-gram Model with Negative Sampling
Apr 15, 2017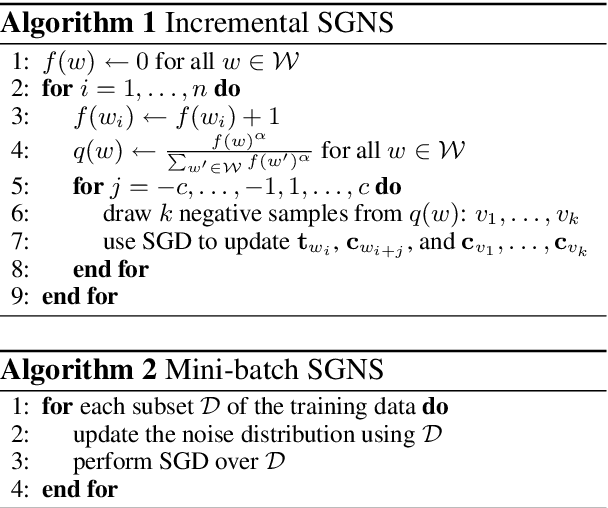

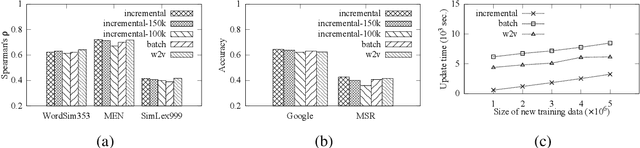
Abstract:This paper explores an incremental training strategy for the skip-gram model with negative sampling (SGNS) from both empirical and theoretical perspectives. Existing methods of neural word embeddings, including SGNS, are multi-pass algorithms and thus cannot perform incremental model update. To address this problem, we present a simple incremental extension of SGNS and provide a thorough theoretical analysis to demonstrate its validity. Empirical experiments demonstrated the correctness of the theoretical analysis as well as the practical usefulness of the incremental algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge