Haomiao Jiang
Cube: A Roblox View of 3D Intelligence
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models trained on vast amounts of data have demonstrated remarkable reasoning and generation capabilities in the domains of text, images, audio and video. Our goal at Roblox is to build such a foundation model for 3D intelligence, a model that can support developers in producing all aspects of a Roblox experience, from generating 3D objects and scenes to rigging characters for animation to producing programmatic scripts describing object behaviors. We discuss three key design requirements for such a 3D foundation model and then present our first step towards building such a model. We expect that 3D geometric shapes will be a core data type and describe our solution for 3D shape tokenizer. We show how our tokenization scheme can be used in applications for text-to-shape generation, shape-to-text generation and text-to-scene generation. We demonstrate how these applications can collaborate with existing large language models (LLMs) to perform scene analysis and reasoning. We conclude with a discussion outlining our path to building a fully unified foundation model for 3D intelligence.
SmoothCache: A Universal Inference Acceleration Technique for Diffusion Transformers
Nov 15, 2024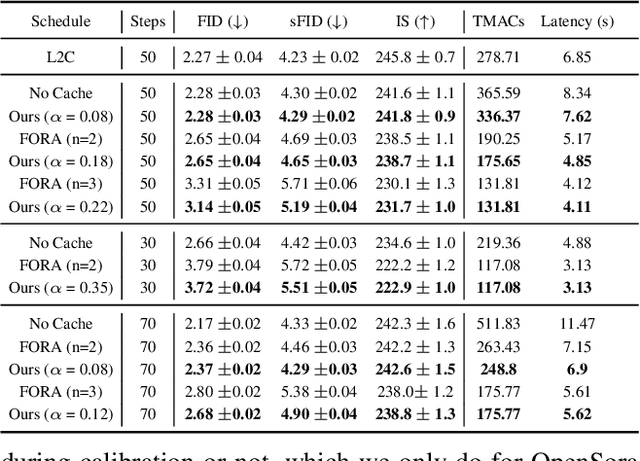
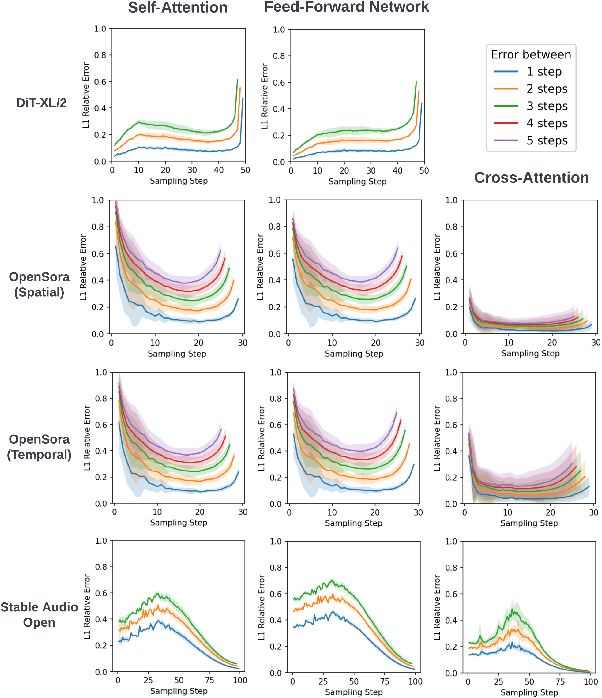
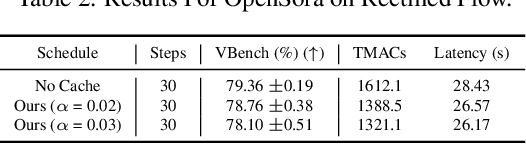
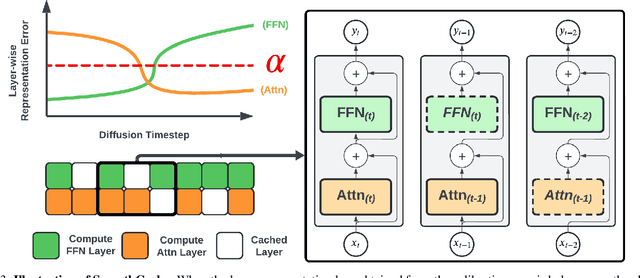
Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiT) have emerged as powerful generative models for various tasks, including image, video, and speech synthesis. However, their inference process remains computationally expensive due to the repeated evaluation of resource-intensive attention and feed-forward modules. To address this, we introduce SmoothCache, a model-agnostic inference acceleration technique for DiT architectures. SmoothCache leverages the observed high similarity between layer outputs across adjacent diffusion timesteps. By analyzing layer-wise representation errors from a small calibration set, SmoothCache adaptively caches and reuses key features during inference. Our experiments demonstrate that SmoothCache achieves 8% to 71% speed up while maintaining or even improving generation quality across diverse modalities. We showcase its effectiveness on DiT-XL for image generation, Open-Sora for text-to-video, and Stable Audio Open for text-to-audio, highlighting its potential to enable real-time applications and broaden the accessibility of powerful DiT models.
Learning the image processing pipeline
May 30, 2016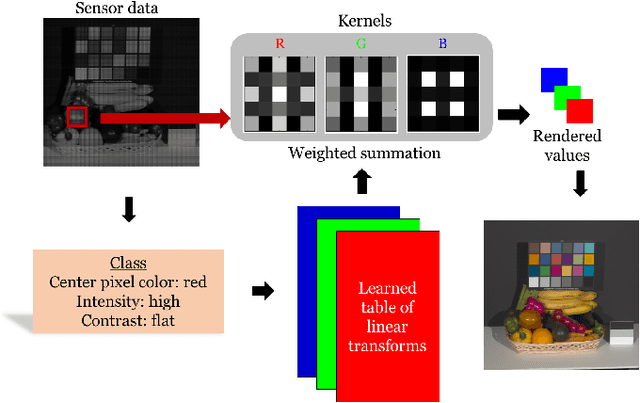
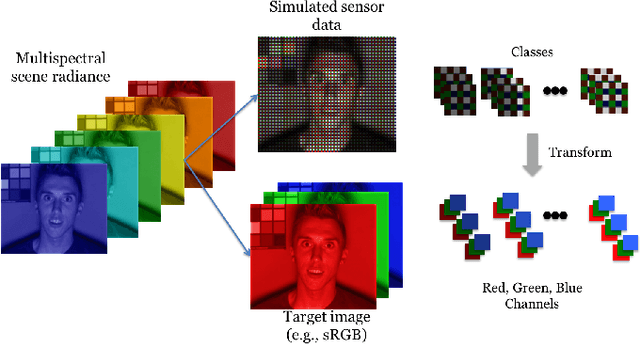
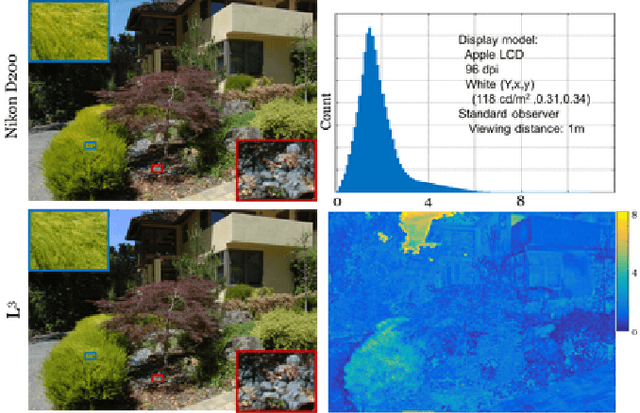

Abstract:Many creative ideas are being proposed for image sensor designs, and these may be useful in applications ranging from consumer photography to computer vision. To understand and evaluate each new design, we must create a corresponding image processing pipeline that transforms the sensor data into a form that is appropriate for the application. The need to design and optimize these pipelines is time-consuming and costly. We explain a method that combines machine learning and image systems simulation that automates the pipeline design. The approach is based on a new way of thinking of the image processing pipeline as a large collection of local linear filters. We illustrate how the method has been used to design pipelines for novel sensor architectures in consumer photography applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge