Hantae Kim
Guiding Frame-Level CTC Alignments Using Self-knowledge Distillation
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Transformer encoder with connectionist temporal classification (CTC) framework is widely used for automatic speech recognition (ASR). However, knowledge distillation (KD) for ASR displays a problem of disagreement between teacher-student models in frame-level alignment which ultimately hinders it from improving the student model's performance. In order to resolve this problem, this paper introduces a self-knowledge distillation (SKD) method that guides the frame-level alignment during the training time. In contrast to the conventional method using separate teacher and student models, this study introduces a simple and effective method sharing encoder layers and applying the sub-model as the student model. Overall, our approach is effective in improving both the resource efficiency as well as performance. We also conducted an experimental analysis of the spike timings to illustrate that the proposed method improves performance by reducing the alignment disagreement.
Specializing Multi-domain NMT via Penalizing Low Mutual Information
Oct 24, 2022



Abstract:Multi-domain Neural Machine Translation (NMT) trains a single model with multiple domains. It is appealing because of its efficacy in handling multiple domains within one model. An ideal multi-domain NMT should learn distinctive domain characteristics simultaneously, however, grasping the domain peculiarity is a non-trivial task. In this paper, we investigate domain-specific information through the lens of mutual information (MI) and propose a new objective that penalizes low MI to become higher. Our method achieved the state-of-the-art performance among the current competitive multi-domain NMT models. Also, we empirically show our objective promotes low MI to be higher resulting in domain-specialized multi-domain NMT.
DaLC: Domain Adaptation Learning Curve Prediction for Neural Machine Translation
Apr 20, 2022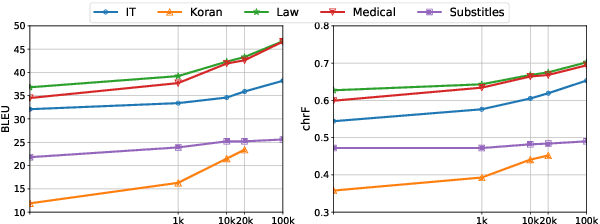



Abstract:Domain Adaptation (DA) of Neural Machine Translation (NMT) model often relies on a pre-trained general NMT model which is adapted to the new domain on a sample of in-domain parallel data. Without parallel data, there is no way to estimate the potential benefit of DA, nor the amount of parallel samples it would require. It is however a desirable functionality that could help MT practitioners to make an informed decision before investing resources in dataset creation. We propose a Domain adaptation Learning Curve prediction (DaLC) model that predicts prospective DA performance based on in-domain monolingual samples in the source language. Our model relies on the NMT encoder representations combined with various instance and corpus-level features. We demonstrate that instance-level is better able to distinguish between different domains compared to corpus-level frameworks proposed in previous studies. Finally, we perform in-depth analyses of the results highlighting the limitations of our approach, and provide directions for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge