Hanqi Zhao
A Hitchhiker's Guide to Poisson Gradient Estimation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Poisson-distributed latent variable models are widely used in computational neuroscience, but differentiating through discrete stochastic samples remains challenging. Two approaches address this: Exponential Arrival Time (EAT) simulation and Gumbel-SoftMax (GSM) relaxation. We provide the first systematic comparison of these methods, along with practical guidance for practitioners. Our main technical contribution is a modification to the EAT method that theoretically guarantees an unbiased first moment (exactly matching the firing rate), and reduces second-moment bias. We evaluate these methods on their distributional fidelity, gradient quality, and performance on two tasks: (1) variational autoencoders with Poisson latents, and (2) partially observable generalized linear models, where latent neural connectivity must be inferred from observed spike trains. Across all metrics, our modified EAT method exhibits better overall performance (often comparable to exact gradients), and substantially higher robustness to hyperparameter choices. Together, our results clarify the trade-offs between these methods and offer concrete recommendations for practitioners working with Poisson latent variable models.
HDPlanner: Advancing Autonomous Deployments in Unknown Environments through Hierarchical Decision Networks
Aug 07, 2024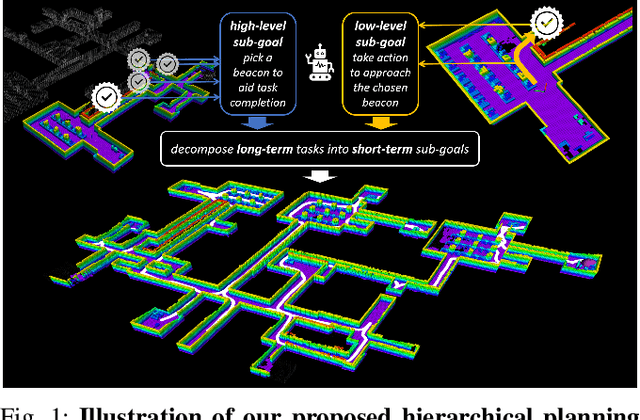
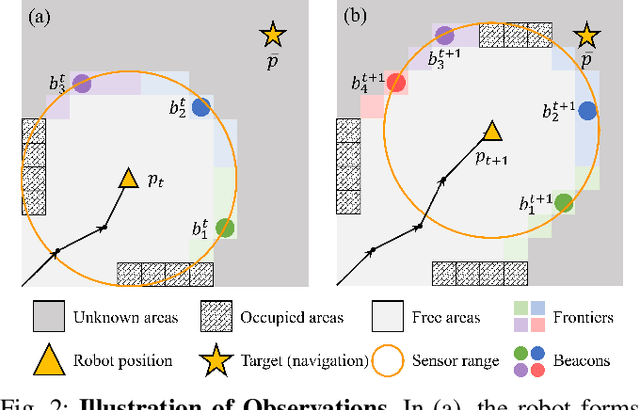
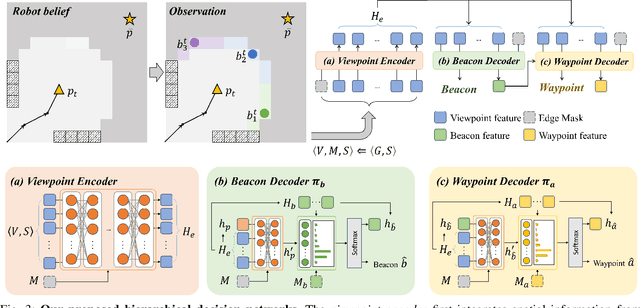
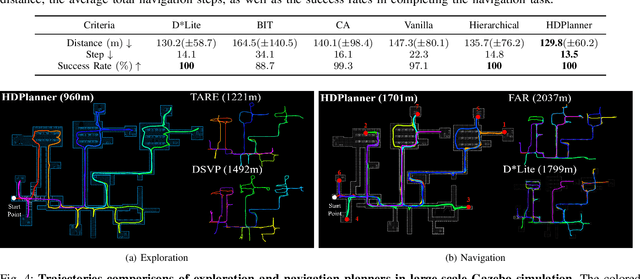
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce HDPlanner, a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) based framework designed to tackle two core and challenging tasks for mobile robots: autonomous exploration and navigation, where the robot must optimize its trajectory adaptively to achieve the task objective through continuous interactions in unknown environments. Specifically, HDPlanner relies on novel hierarchical attention networks to empower the robot to reason about its belief across multiple spatial scales and sequence collaborative decisions, where our networks decompose long-term objectives into short-term informative task assignments and informative path plannings. We further propose a contrastive learning-based joint optimization to enhance the robustness of HDPlanner. We empirically demonstrate that HDPlanner significantly outperforms state-of-the-art conventional and learning-based baselines on an extensive set of simulations, including hundreds of test maps and large-scale, complex Gazebo environments. Notably, HDPlanner achieves real-time planning with travel distances reduced by up to 35.7% compared to exploration benchmarks and by up to 16.5% than navigation benchmarks. Furthermore, we validate our approach on hardware, where it generates high-quality, adaptive trajectories in both indoor and outdoor environments, highlighting its real-world applicability without additional training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge