Hanning Yuan
Meta Dynamic Graph for Traffic Flow Prediction
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Traffic flow prediction is a typical spatio-temporal prediction problem and has a wide range of applications. The core challenge lies in modeling the underlying complex spatio-temporal dependencies. Various methods have been proposed, and recent studies show that the modeling of dynamics is useful to meet the core challenge. While handling spatial dependencies and temporal dependencies using separate base model structures may hinder the modeling of spatio-temporal correlations, the modeling of dynamics can bridge this gap. Incorporating spatio-temporal heterogeneity also advances the main goal, since it can extend the parameter space and allow more flexibility. Despite these advances, two limitations persist: 1) the modeling of dynamics is often limited to the dynamics of spatial topology (e.g., adjacency matrix changes), which, however, can be extended to a broader scope; 2) the modeling of heterogeneity is often separated for spatial and temporal dimensions, but this gap can also be bridged by the modeling of dynamics. To address the above limitations, we propose a novel framework for traffic prediction, called Meta Dynamic Graph (MetaDG). MetaDG leverages dynamic graph structures of node representations to explicitly model spatio-temporal dynamics. This generates both dynamic adjacency matrices and meta-parameters, extending dynamic modeling beyond topology while unifying the capture of spatio-temporal heterogeneity into a single dimension. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets validate the effectiveness of MetaDG.
DWCL: Dual-Weighted Contrastive Learning for Multi-View Clustering
Nov 26, 2024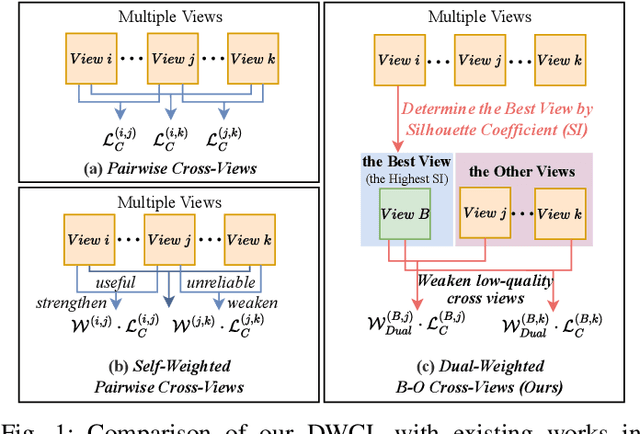
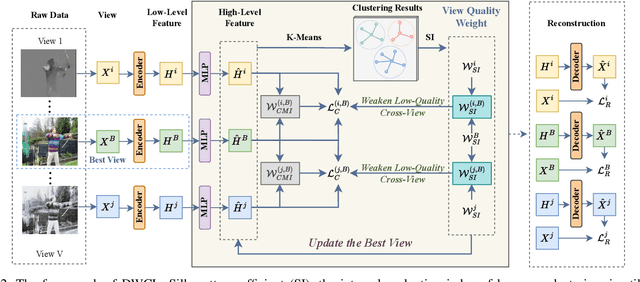
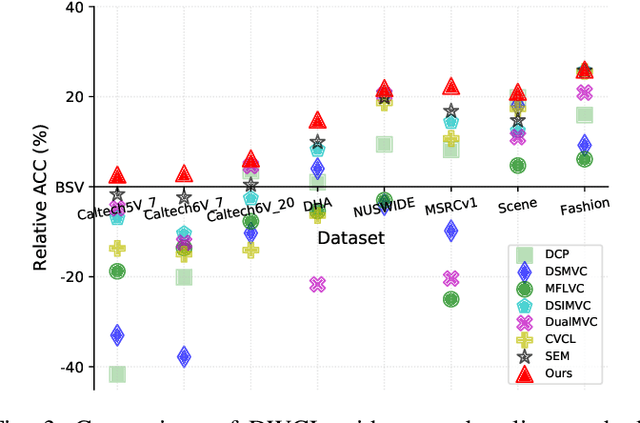
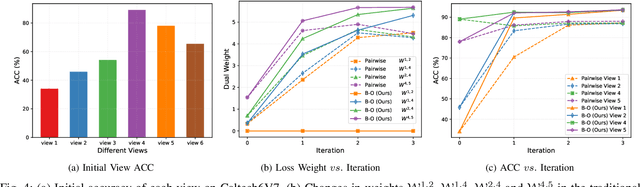
Abstract:Multi-view contrastive clustering (MVCC) has gained significant attention for generating consistent clustering structures from multiple views through contrastive learning. However, most existing MVCC methods create cross-views by combining any two views, leading to a high volume of unreliable pairs. Furthermore, these approaches often overlook discrepancies in multi-view representations, resulting in representation degeneration. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel model called Dual-Weighted Contrastive Learning (DWCL) for Multi-View Clustering. Specifically, to reduce the impact of unreliable cross-views, we introduce an innovative Best-Other (B-O) contrastive mechanism that enhances the representation of individual views at a low computational cost. Furthermore, we develop a dual weighting strategy that combines a view quality weight, reflecting the quality of each view, with a view discrepancy weight. This approach effectively mitigates representation degeneration by downplaying cross-views that are both low in quality and high in discrepancy. We theoretically validate the efficiency of the B-O contrastive mechanism and the effectiveness of the dual weighting strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DWCL outperforms previous methods across eight multi-view datasets, showcasing superior performance and robustness in MVCC. Specifically, our method achieves absolute accuracy improvements of 5.4\% and 5.6\% compared to state-of-the-art methods on the Caltech6V7 and MSRCv1 datasets, respectively.
Deep Contrastive Multi-view Clustering under Semantic Feature Guidance
Mar 09, 2024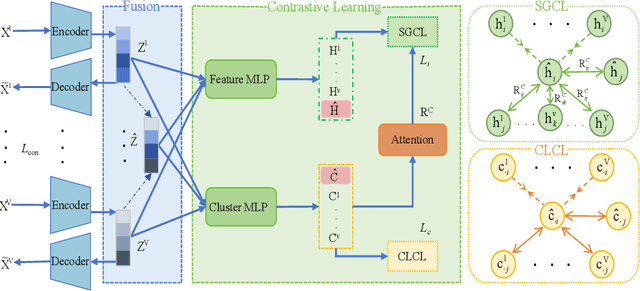
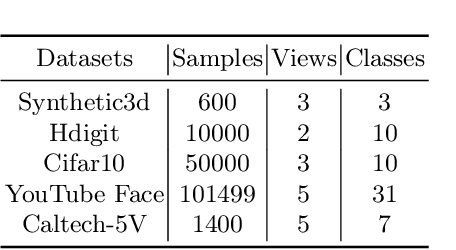
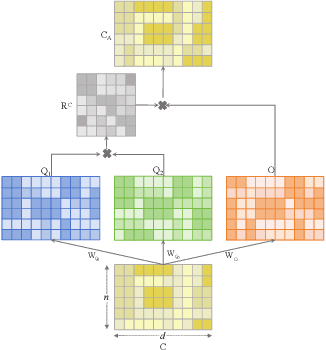
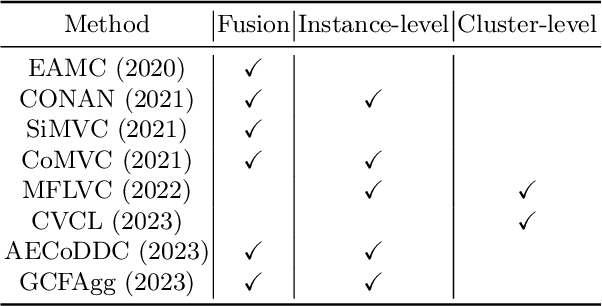
Abstract:Contrastive learning has achieved promising performance in the field of multi-view clustering recently. However, the positive and negative sample construction mechanisms ignoring semantic consistency lead to false negative pairs, limiting the performance of existing algorithms from further improvement. To solve this problem, we propose a multi-view clustering framework named Deep Contrastive Multi-view Clustering under Semantic feature guidance (DCMCS) to alleviate the influence of false negative pairs. Specifically, view-specific features are firstly extracted from raw features and fused to obtain fusion view features according to view importance. To mitigate the interference of view-private information, specific view and fusion view semantic features are learned by cluster-level contrastive learning and concatenated to measure the semantic similarity of instances. By minimizing instance-level contrastive loss weighted by semantic similarity, DCMCS adaptively weakens contrastive leaning between false negative pairs. Experimental results on several public datasets demonstrate the proposed framework outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge