Haiou Liu
Optimization-Guided Diffusion for Interactive Scene Generation
Dec 11, 2025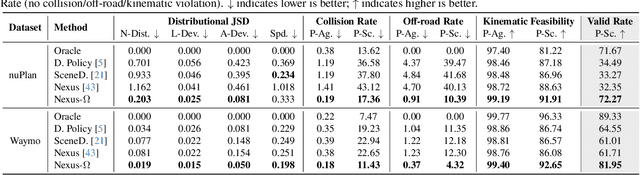
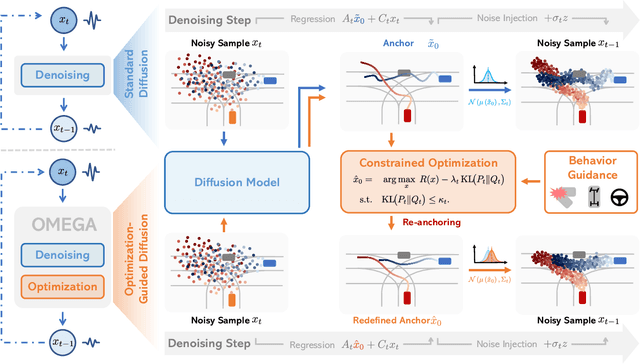
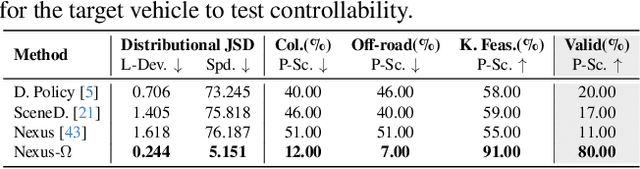
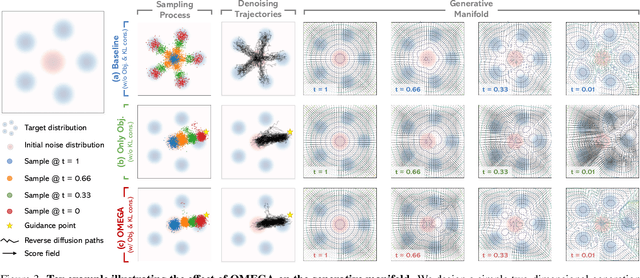
Abstract:Realistic and diverse multi-agent driving scenes are crucial for evaluating autonomous vehicles, but safety-critical events which are essential for this task are rare and underrepresented in driving datasets. Data-driven scene generation offers a low-cost alternative by synthesizing complex traffic behaviors from existing driving logs. However, existing models often lack controllability or yield samples that violate physical or social constraints, limiting their usability. We present OMEGA, an optimization-guided, training-free framework that enforces structural consistency and interaction awareness during diffusion-based sampling from a scene generation model. OMEGA re-anchors each reverse diffusion step via constrained optimization, steering the generation towards physically plausible and behaviorally coherent trajectories. Building on this framework, we formulate ego-attacker interactions as a game-theoretic optimization in the distribution space, approximating Nash equilibria to generate realistic, safety-critical adversarial scenarios. Experiments on nuPlan and Waymo show that OMEGA improves generation realism, consistency, and controllability, increasing the ratio of physically and behaviorally valid scenes from 32.35% to 72.27% for free exploration capabilities, and from 11% to 80% for controllability-focused generation. Our approach can also generate $5\times$ more near-collision frames with a time-to-collision under three seconds while maintaining the overall scene realism.
A Hierarchical Multi-Vehicle Coordinated Motion Planning Method based on Interactive Spatio-Temporal Corridors
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:Multi-vehicle coordinated motion planning has always been challenged to safely and efficiently resolve conflicts under non-holonomic dynamic constraints. Constructing spatial-temporal corridors for multi-vehicle can decouple the high-dimensional conflicts and further reduce the difficulty of obtaining feasible trajectories. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel hierarchical method based on interactive spatio-temporal corridors (ISTCs). In the first layer, based on the initial guidance trajectories, Mixed Integer Quadratic Programming is designed to construct ISTCs capable of resolving conflicts in generic multi-vehicle scenarios. And then in the second layer, Non-Linear Programming is settled to generate in-corridor trajectories that satisfy the vehicle dynamics. By introducing ISTCs, the multi-vehicle coordinated motion planning problem is able to be decoupled into single-vehicle trajectory optimization problems, which greatly decentralizes the computational pressure and has great potential for real-world applications. Besides, the proposed method searches for feasible solutions in the 3-D $(x,y,t)$ configuration space, preserving more possibilities than the traditional velocity-path decoupling method. Simulated experiments in unsignalized intersection and challenging dense scenarios have been conduced to verify the feasibility and adaptability of the proposed framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge