Go Kamoda
Can Language Models Handle a Non-Gregorian Calendar?
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Temporal reasoning and knowledge are essential capabilities for language models (LMs). While much prior work has analyzed and improved temporal reasoning in LMs, most studies have focused solely on the Gregorian calendar. However, many non-Gregorian systems, such as the Japanese, Hijri, and Hebrew calendars, are in active use and reflect culturally grounded conceptions of time. If and how well current LMs can accurately handle such non-Gregorian calendars has not been evaluated so far. Here, we present a systematic evaluation of how well open-source LMs handle one such non-Gregorian system: the Japanese calendar. For our evaluation, we create datasets for four tasks that require both temporal knowledge and temporal reasoning. Evaluating a range of English-centric and Japanese-centric LMs, we find that some models can perform calendar conversions, but even Japanese-centric models struggle with Japanese-calendar arithmetic and with maintaining consistency across calendars. Our results highlight the importance of developing LMs that are better equipped for culture-specific calendar understanding.
SoftMatcha: A Soft and Fast Pattern Matcher for Billion-Scale Corpus Searches
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Researchers and practitioners in natural language processing and computational linguistics frequently observe and analyze the real language usage in large-scale corpora. For that purpose, they often employ off-the-shelf pattern-matching tools, such as grep, and keyword-in-context concordancers, which is widely used in corpus linguistics for gathering examples. Nonetheless, these existing techniques rely on surface-level string matching, and thus they suffer from the major limitation of not being able to handle orthographic variations and paraphrasing -- notable and common phenomena in any natural language. In addition, existing continuous approaches such as dense vector search tend to be overly coarse, often retrieving texts that are unrelated but share similar topics. Given these challenges, we propose a novel algorithm that achieves \emph{soft} (or semantic) yet efficient pattern matching by relaxing a surface-level matching with word embeddings. Our algorithm is highly scalable with respect to the size of the corpus text utilizing inverted indexes. We have prepared an efficient implementation, and we provide an accessible web tool. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed method (i) can execute searches on billion-scale corpora in less than a second, which is comparable in speed to surface-level string matching and dense vector search; (ii) can extract harmful instances that semantically match queries from a large set of English and Japanese Wikipedia articles; and (iii) can be effectively applied to corpus-linguistic analyses of Latin, a language with highly diverse inflections.
Weight-based Analysis of Detokenization in Language Models: Understanding the First Stage of Inference Without Inference
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:According to the stages-of-inference hypothesis, early layers of language models map their subword-tokenized input, which does not necessarily correspond to a linguistically meaningful segmentation, to more meaningful representations that form the model's ``inner vocabulary''. Prior analysis of this detokenization stage has predominantly relied on probing and interventions such as path patching, which involve selecting particular inputs, choosing a subset of components that will be patched, and then observing changes in model behavior. Here, we show that several important aspects of the detokenization stage can be understood purely by analyzing model weights, without performing any model inference steps. Specifically, we introduce an analytical decomposition of first-layer attention in GPT-2. Our decomposition yields interpretable terms that quantify the relative contributions of position-related, token-related, and mixed effects. By focusing on terms in this decomposition, we discover weight-based explanations of attention bias toward close tokens and attention for detokenization.
The Curse of Popularity: Popular Entities have Catastrophic Side Effects when Deleting Knowledge from Language Models
Jun 10, 2024
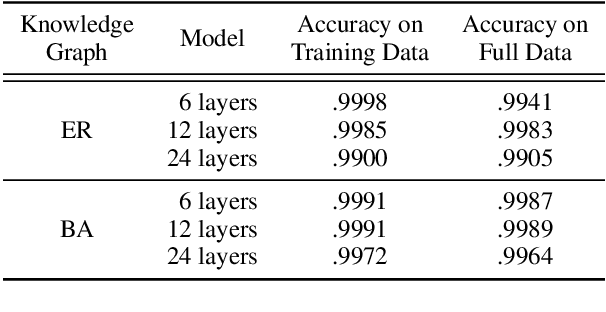
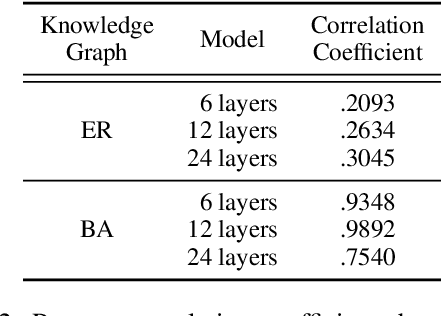
Abstract:Language models (LMs) encode world knowledge in their internal parameters through training. However, LMs may learn personal and confidential information from the training data, leading to privacy concerns such as data leakage. Therefore, research on knowledge deletion from LMs is essential. This study focuses on the knowledge stored in LMs and analyzes the relationship between the side effects of knowledge deletion and the entities related to the knowledge. Our findings reveal that deleting knowledge related to popular entities can have catastrophic side effects. Furthermore, this research is the first to analyze knowledge deletion in models trained on synthetic knowledge graphs, indicating a new direction for controlled experiments.
Test-time Augmentation for Factual Probing
Oct 26, 2023



Abstract:Factual probing is a method that uses prompts to test if a language model "knows" certain world knowledge facts. A problem in factual probing is that small changes to the prompt can lead to large changes in model output. Previous work aimed to alleviate this problem by optimizing prompts via text mining or fine-tuning. However, such approaches are relation-specific and do not generalize to unseen relation types. Here, we propose to use test-time augmentation (TTA) as a relation-agnostic method for reducing sensitivity to prompt variations by automatically augmenting and ensembling prompts at test time. Experiments show improved model calibration, i.e., with TTA, model confidence better reflects prediction accuracy. Improvements in prediction accuracy are observed for some models, but for other models, TTA leads to degradation. Error analysis identifies the difficulty of producing high-quality prompt variations as the main challenge for TTA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge