Giuseppe Romano
Multifidelity deep neural operators for efficient learning of partial differential equations with application to fast inverse design of nanoscale heat transport
Apr 14, 2022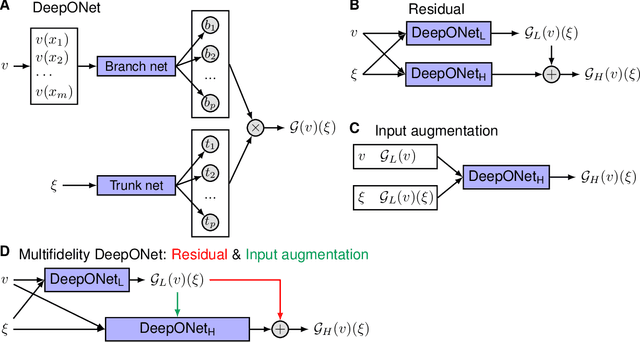
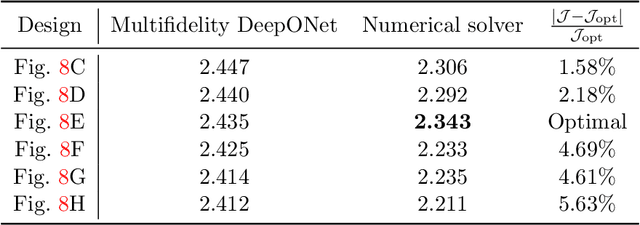
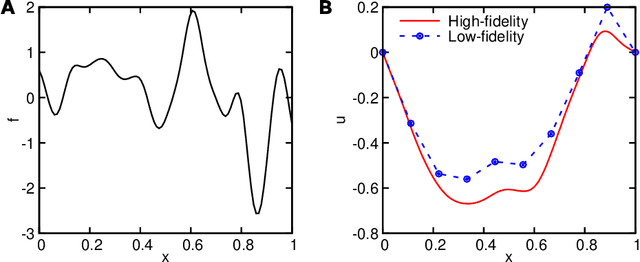
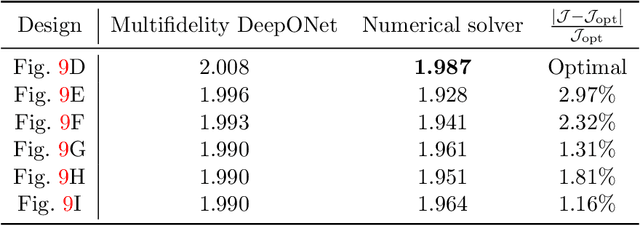
Abstract:Deep neural operators can learn operators mapping between infinite-dimensional function spaces via deep neural networks and have become an emerging paradigm of scientific machine learning. However, training neural operators usually requires a large amount of high-fidelity data, which is often difficult to obtain in real engineering problems. Here, we address this challenge by using multifidelity learning, i.e., learning from multifidelity datasets. We develop a multifidelity neural operator based on a deep operator network (DeepONet). A multifidelity DeepONet includes two standard DeepONets coupled by residual learning and input augmentation. Multifidelity DeepONet significantly reduces the required amount of high-fidelity data and achieves one order of magnitude smaller error when using the same amount of high-fidelity data. We apply a multifidelity DeepONet to learn the phonon Boltzmann transport equation (BTE), a framework to compute nanoscale heat transport. By combining a trained multifidelity DeepONet with genetic algorithm or topology optimization, we demonstrate a fast solver for the inverse design of BTE problems.
Fast classification of small X-ray diffraction datasets using data augmentation and deep neural networks
Nov 20, 2018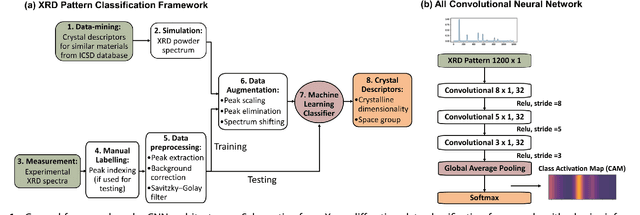
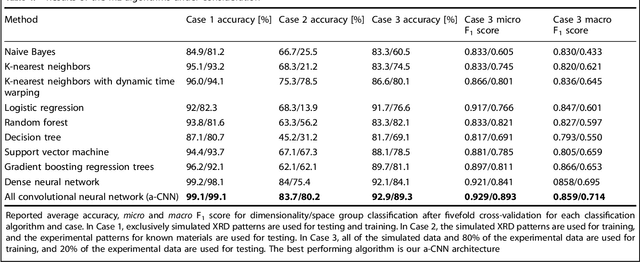
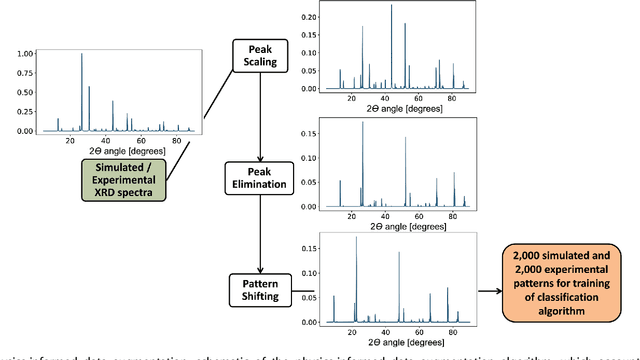
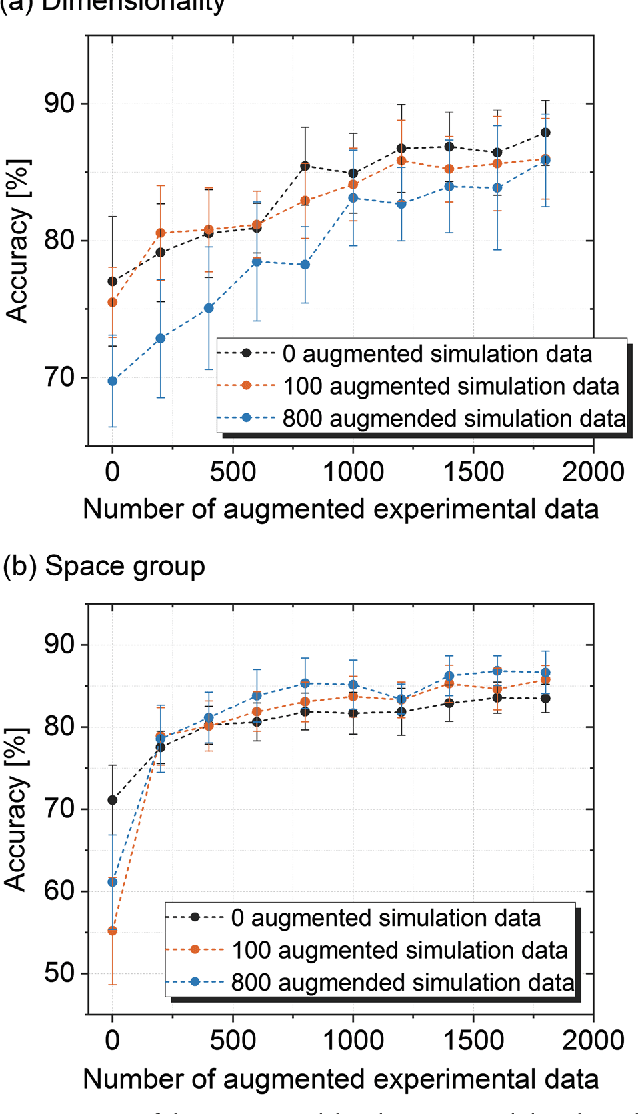
Abstract:X-ray diffraction (XRD) for crystal structure characterization is among the most time-consuming and complex steps in the development cycle of novel materials. We propose a machine-learning-enabled approach to predict crystallographic dimensionality and space group from a limited number of experimental thin-film XRD patterns. We overcome the sparse-data problem intrinsic to novel materials development by coupling a supervised machine-learning approach with a physics-based data augmentation strategy . Using this approach, XRD spectrum acquisition and analysis occurs under 5.5 minutes, with accuracy comparable to human expert labeling. We simulate experimental powder diffraction patterns from crystallographic information contained in the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database (ICSD). We train a classification algorithm using a combination of labeled simulated and experimental augmented datasets, which account for thin-film characteristics and measurement noise. As a test case, 88 metal-halide thin films spanning 3 dimensionalities and 7 space-groups are synthesized and classified. The accuracies and throughputs of multiple machine-learning techniques are evaluated, along with the effect of augmented dataset size. The most accurate classification algorithm is found to be a feed-forward deep neural network. The calculated accuracies for dimensionality and space-group classification are comparable to ground-truth labelling by a human expert, approximately 90\% and 85\%, respectively. Additionally, we systematically evaluate the maximum XRD spectrum step size (data acquisition rate) before loss of predictive accuracy occurs, and determine it to be \ang{0.16} $2\theta $, which enables an XRD spectrum to be obtained and analyzed in 5 minutes or less.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge