Giorgio Stefanoni
Weakly-supervised Contextualization of Knowledge Graph Facts
Jul 08, 2018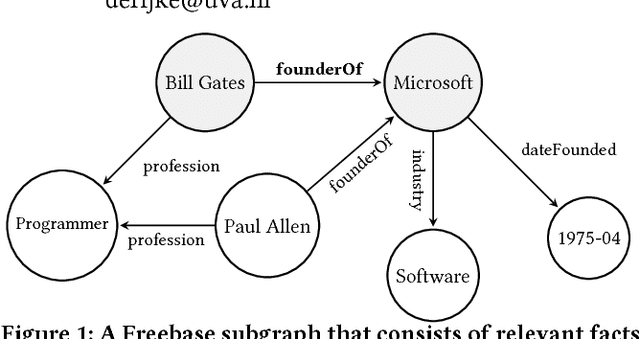
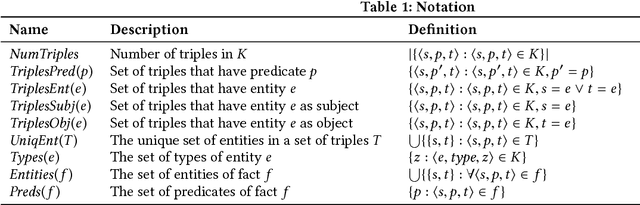
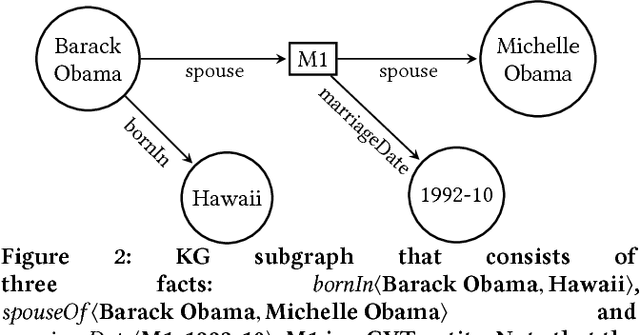
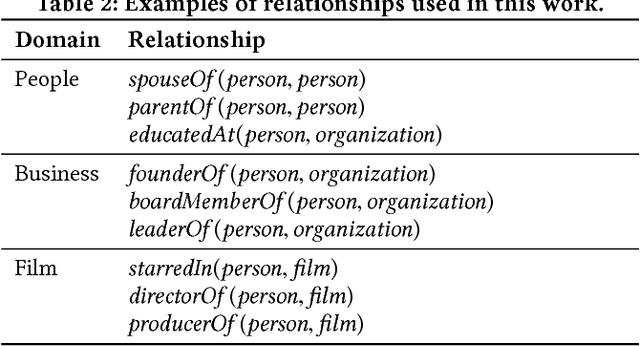
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) model facts about the world, they consist of nodes (entities such as companies and people) that are connected by edges (relations such as founderOf). Facts encoded in KGs are frequently used by search applications to augment result pages. When presenting a KG fact to the user, providing other facts that are pertinent to that main fact can enrich the user experience and support exploratory information needs. KG fact contextualization is the task of augmenting a given KG fact with additional and useful KG facts. The task is challenging because of the large size of KGs, discovering other relevant facts even in a small neighborhood of the given fact results in an enormous amount of candidates. We introduce a neural fact contextualization method (NFCM) to address the KG fact contextualization task. NFCM first generates a set of candidate facts in the neighborhood of a given fact and then ranks the candidate facts using a supervised learning to rank model. The ranking model combines features that we automatically learn from data and that represent the query-candidate facts with a set of hand-crafted features we devised or adjusted for this task. In order to obtain the annotations required to train the learning to rank model at scale, we generate training data automatically using distant supervision on a large entity-tagged text corpus. We show that ranking functions learned on this data are effective at contextualizing KG facts. Evaluation using human assessors shows that it significantly outperforms several competitive baselines.
Answering Conjunctive Queries over $\mathcal{EL}$ Knowledge Bases with Transitive and Reflexive Roles
May 13, 2015
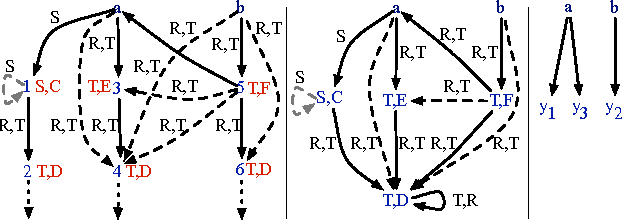

Abstract:Answering conjunctive queries (CQs) over $\mathcal{EL}$ knowledge bases (KBs) with complex role inclusions is PSPACE-hard and in PSPACE in certain cases; however, if complex role inclusions are restricted to role transitivity, the tight upper complexity bound has so far been unknown. Furthermore, the existing algorithms cannot handle reflexive roles, and they are not practicable. Finally, the problem is tractable for acyclic CQs and $\mathcal{ELH}$, and NP-complete for unrestricted CQs and $\mathcal{ELHO}$ KBs. In this paper we complete the complexity landscape of CQ answering for several important cases. In particular, we present a practicable NP algorithm for answering CQs over $\mathcal{ELHO}^s$ KBs---a logic containing all of OWL 2 EL, but with complex role inclusions restricted to role transitivity. Our preliminary evaluation suggests that the algorithm can be suitable for practical use. Moreover, we show that, even for a restricted class of so-called arborescent acyclic queries, CQ answering over $\mathcal{EL}$ KBs becomes NP-hard in the presence of either transitive or reflexive roles. Finally, we show that answering arborescent CQs over $\mathcal{ELHO}$ KBs is tractable, whereas answering acyclic CQs is NP-hard.
Reasoning about Explanations for Negative Query Answers in DL-Lite
Feb 04, 2014

Abstract:In order to meet usability requirements, most logic-based applications provide explanation facilities for reasoning services. This holds also for Description Logics, where research has focused on the explanation of both TBox reasoning and, more recently, query answering. Besides explaining the presence of a tuple in a query answer, it is important to explain also why a given tuple is missing. We address the latter problem for instance and conjunctive query answering over DL-Lite ontologies by adopting abductive reasoning; that is, we look for additions to the ABox that force a given tuple to be in the result. As reasoning tasks we consider existence and recognition of an explanation, and relevance and necessity of a given assertion for an explanation. We characterize the computational complexity of these problems for arbitrary, subset minimal, and cardinality minimal explanations.
Introducing Nominals to the Combined Query Answering Approaches for EL
Apr 01, 2013



Abstract:So-called combined approaches answer a conjunctive query over a description logic ontology in three steps: first, they materialise certain consequences of the ontology and the data; second, they evaluate the query over the data; and third, they filter the result of the second phase to eliminate unsound answers. Such approaches were developed for various members of the DL-Lite and the EL families of languages, but none of them can handle ontologies containing nominals. In our work, we bridge this gap and present a combined query answering approach for ELHO---a logic that contains all features of the OWL 2 EL standard apart from transitive roles and complex role inclusions. This extension is nontrivial because nominals require equality reasoning, which introduces complexity into the first and the third step. Our empirical evaluation suggests that our technique is suitable for practical application, and so it provides a practical basis for conjunctive query answering in a large fragment of OWL 2 EL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge