Gi Pyo Nam
V-NAW: Video-based Noise-aware Adaptive Weighting for Facial Expression Recognition
Mar 20, 2025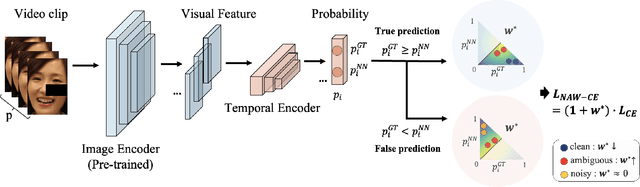
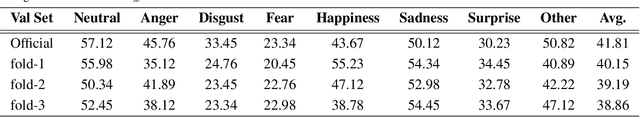
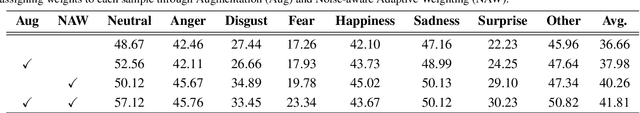
Abstract:Facial Expression Recognition (FER) plays a crucial role in human affective analysis and has been widely applied in computer vision tasks such as human-computer interaction and psychological assessment. The 8th Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-Wild (ABAW) Challenge aims to assess human emotions using the video-based Aff-Wild2 dataset. This challenge includes various tasks, including the video-based EXPR recognition track, which is our primary focus. In this paper, we demonstrate that addressing label ambiguity and class imbalance, which are known to cause performance degradation, can lead to meaningful performance improvements. Specifically, we propose Video-based Noise-aware Adaptive Weighting (V-NAW), which adaptively assigns importance to each frame in a clip to address label ambiguity and effectively capture temporal variations in facial expressions. Furthermore, we introduce a simple and effective augmentation strategy to reduce redundancy between consecutive frames, which is a primary cause of overfitting. Through extensive experiments, we validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating significant improvements in video-based FER performance.
IG-FIQA: Improving Face Image Quality Assessment through Intra-class Variance Guidance robust to Inaccurate Pseudo-Labels
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:In the realm of face image quality assesment (FIQA), method based on sample relative classification have shown impressive performance. However, the quality scores used as pseudo-labels assigned from images of classes with low intra-class variance could be unrelated to the actual quality in this method. To address this issue, we present IG-FIQA, a novel approach to guide FIQA training, introducing a weight parameter to alleviate the adverse impact of these classes. This method involves estimating sample intra-class variance at each iteration during training, ensuring minimal computational overhead and straightforward implementation. Furthermore, this paper proposes an on-the-fly data augmentation methodology for improved generalization performance in FIQA. On various benchmark datasets, our proposed method, IG-FIQA, achieved novel state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance.
VIGFace: Virtual Identity Generation Model for Face Image Synthesis
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning-based face recognition continues to face challenges due to its reliance on huge datasets obtained from web crawling, which can be costly to gather and raise significant real-world privacy concerns. To address this issue, we propose VIGFace, a novel framework capable of generating synthetic facial images. Initially, we train the face recognition model using a real face dataset and create a feature space for both real and virtual IDs where virtual prototypes are orthogonal to other prototypes. Subsequently, we generate synthetic images by using the diffusion model based on the feature space. Our proposed framework provides two significant benefits. Firstly, it allows for creating virtual facial images without concerns about portrait rights, guaranteeing that the generated virtual face images are clearly differentiated from existing individuals. Secondly, it serves as an effective augmentation method by incorporating real existing images. Further experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our framework, achieving state-of-the-art results from both perspectives without any external data.
K-FACE: A Large-Scale KIST Face Database in Consideration with Unconstrained Environments
Mar 03, 2021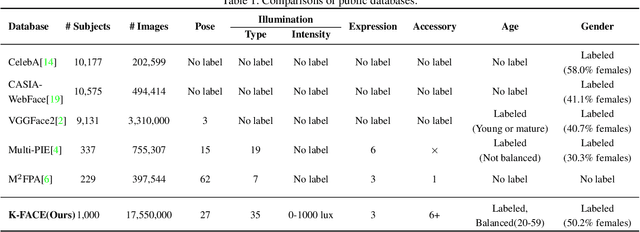
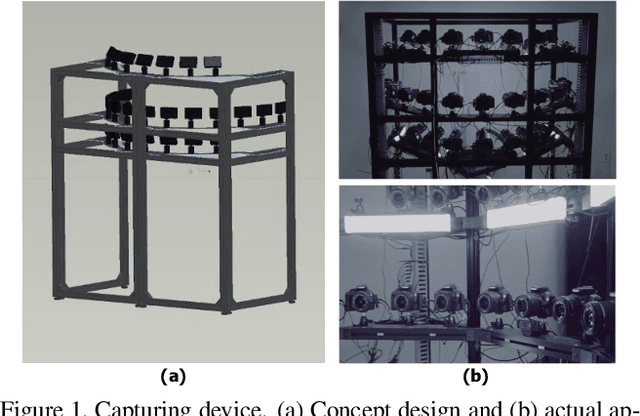
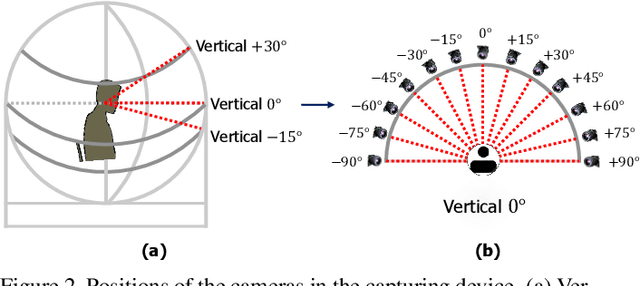
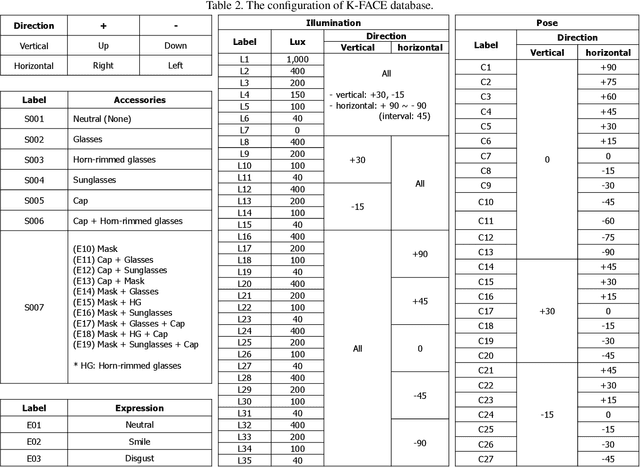
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a new large-scale face database from KIST, denoted as K-FACE, and describe a novel capturing device specifically designed to obtain the data. The K-FACE database contains more than 1 million high-quality images of 1,000 subjects selected by considering the ratio of gender and age groups. It includes a variety of attributes, including 27 poses, 35 lighting conditions, three expressions, and occlusions by the combination of five types of accessories. As the K-FACE database is systematically constructed through a hemispherical capturing system with elaborate lighting control and multiple cameras, it is possible to accurately analyze the effects of factors that cause performance degradation, such as poses, lighting changes, and accessories. We consider not only the balance of external environmental factors, such as pose and lighting, but also the balance of personal characteristics such as gender and age group. The gender ratio is the same, while the age groups of subjects are uniformly distributed from the 20s to 50s for both genders. The K-FACE database can be extensively utilized in various vision tasks, such as face recognition, face frontalization, illumination normalization, face age estimation, and three-dimensional face model generation. We expect systematic diversity and uniformity of the K-FACE database to promote these research fields.
A 3D model-based approach for fitting masks to faces in the wild
Mar 01, 2021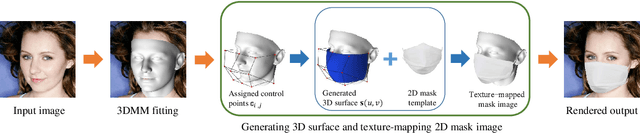
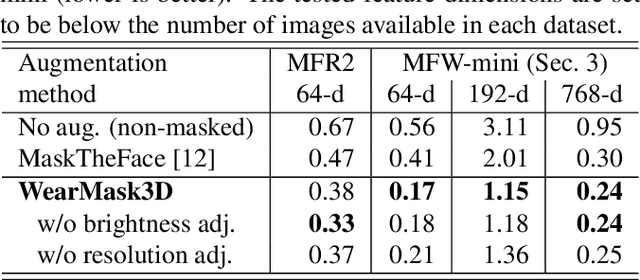

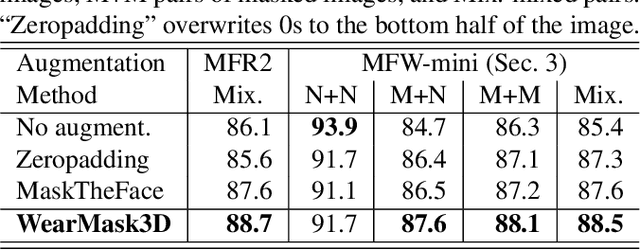
Abstract:Face recognition research now requires a large number of labelled masked face images in the era of this unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic. Unfortunately, the rapid spread of the virus has left us little time to prepare for such dataset in the wild. To circumvent this issue, we present a 3D model-based approach called WearMask3D for augmenting face images of various poses to the masked face counterparts. Our method proceeds by first fitting a 3D morphable model on the input image, second overlaying the mask surface onto the face model and warping the respective mask texture, and last projecting the 3D mask back to 2D. The mask texture is adapted based on the brightness and resolution of the input image. By working in 3D, our method can produce more natural masked faces of diverse poses from a single mask texture. To compare precisely between different augmentation approaches, we have constructed a dataset comprising masked and unmasked faces with labels called MFW-mini. Experimental results demonstrate WearMask3D, which will be made publicly available, produces more realistic masked images, and utilizing these images for training leads to improved recognition accuracy of masked faces compared to the state-of-the-art.
The Unconstrained Ear Recognition Challenge 2019 - ArXiv Version With Appendix
Mar 14, 2019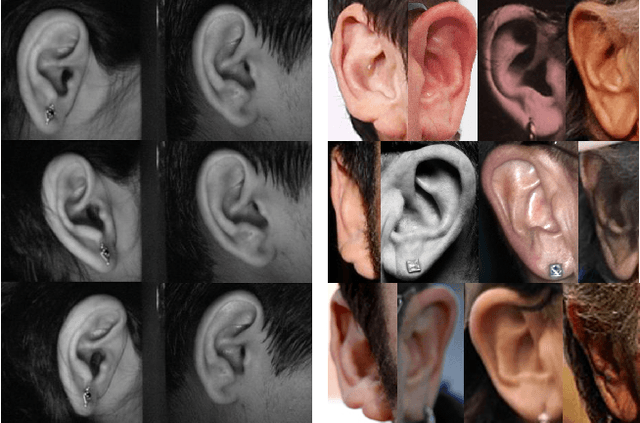
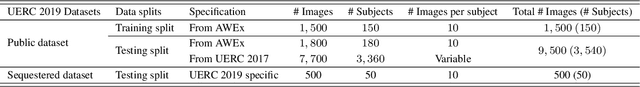
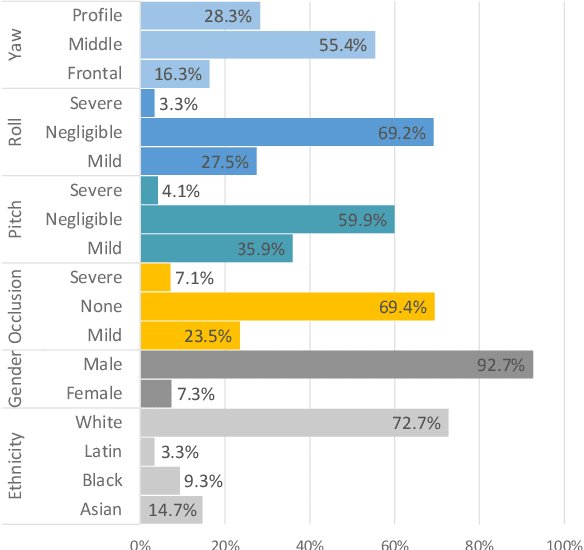
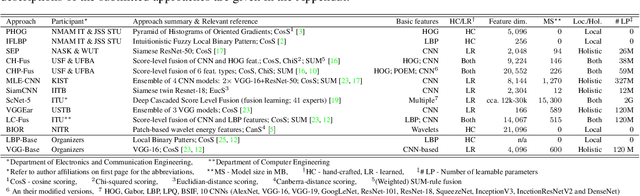
Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the 2019 Unconstrained Ear Recognition Challenge (UERC), the second in a series of group benchmarking efforts centered around the problem of person recognition from ear images captured in uncontrolled settings. The goal of the challenge is to assess the performance of existing ear recognition techniques on a challenging large-scale ear dataset and to analyze performance of the technology from various viewpoints, such as generalization abilities to unseen data characteristics, sensitivity to rotations, occlusions and image resolution and performance bias on sub-groups of subjects, selected based on demographic criteria, i.e. gender and ethnicity. Research groups from 12 institutions entered the competition and submitted a total of 13 recognition approaches ranging from descriptor-based methods to deep-learning models. The majority of submissions focused on ensemble based methods combining either representations from multiple deep models or hand-crafted with learned image descriptors. Our analysis shows that methods incorporating deep learning models clearly outperform techniques relying solely on hand-crafted descriptors, even though both groups of techniques exhibit similar behaviour when it comes to robustness to various covariates, such presence of occlusions, changes in (head) pose, or variability in image resolution. The results of the challenge also show that there has been considerable progress since the first UERC in 2017, but that there is still ample room for further research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge