Georgios Kouros
Spec-Gloss Surfels and Normal-Diffuse Priors for Relightable Glossy Objects
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Accurate reconstruction and relighting of glossy objects remain a longstanding challenge, as object shape, material properties, and illumination are inherently difficult to disentangle. Existing neural rendering approaches often rely on simplified BRDF models or parameterizations that couple diffuse and specular components, which restricts faithful material recovery and limits relighting fidelity. We propose a relightable framework that integrates a microfacet BRDF with the specular-glossiness parameterization into 2D Gaussian Splatting with deferred shading. This formulation enables more physically consistent material decomposition, while diffusion-based priors for surface normals and diffuse color guide early-stage optimization and mitigate ambiguity. A coarse-to-fine optimization of the environment map accelerates convergence and preserves high-dynamic-range specular reflections. Extensive experiments on complex, glossy scenes demonstrate that our method achieves high-quality geometry and material reconstruction, delivering substantially more realistic and consistent relighting under novel illumination compared to existing Gaussian splatting methods.
RGS-DR: Reflective Gaussian Surfels with Deferred Rendering for Shiny Objects
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:We introduce RGS-DR, a novel inverse rendering method for reconstructing and rendering glossy and reflective objects with support for flexible relighting and scene editing. Unlike existing methods (e.g., NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting), which struggle with view-dependent effects, RGS-DR utilizes a 2D Gaussian surfel representation to accurately estimate geometry and surface normals, an essential property for high-quality inverse rendering. Our approach explicitly models geometric and material properties through learnable primitives rasterized into a deferred shading pipeline, effectively reducing rendering artifacts and preserving sharp reflections. By employing a multi-level cube mipmap, RGS-DR accurately approximates environment lighting integrals, facilitating high-quality reconstruction and relighting. A residual pass with spherical-mipmap-based directional encoding further refines the appearance modeling. Experiments demonstrate that RGS-DR achieves high-quality reconstruction and rendering quality for shiny objects, often outperforming reconstruction-exclusive state-of-the-art methods incapable of relighting.
Unveiling the Ambiguity in Neural Inverse Rendering: A Parameter Compensation Analysis
Apr 19, 2024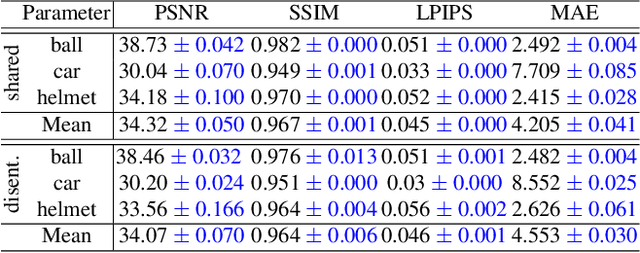

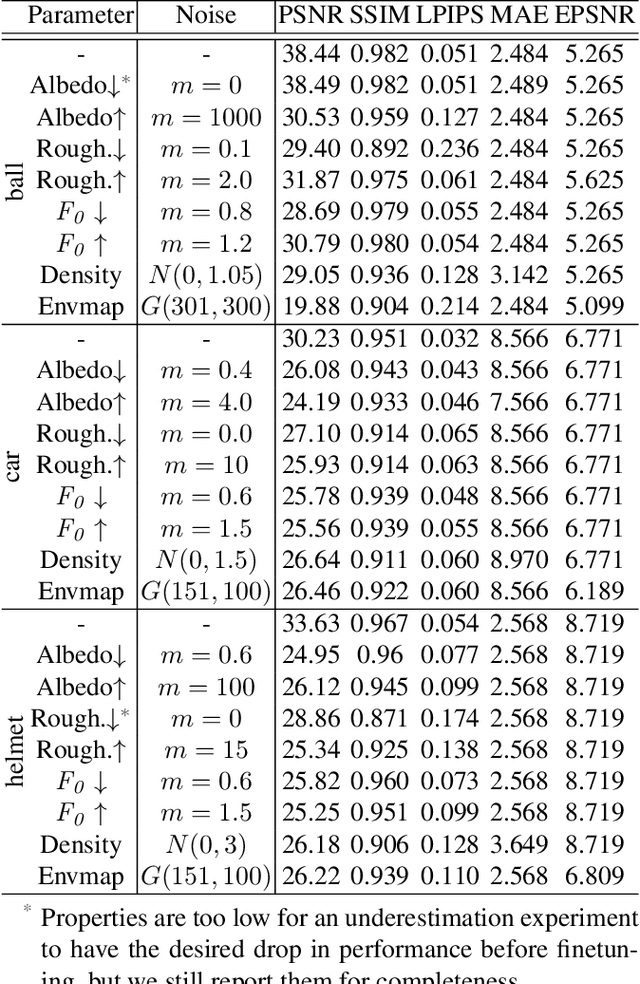
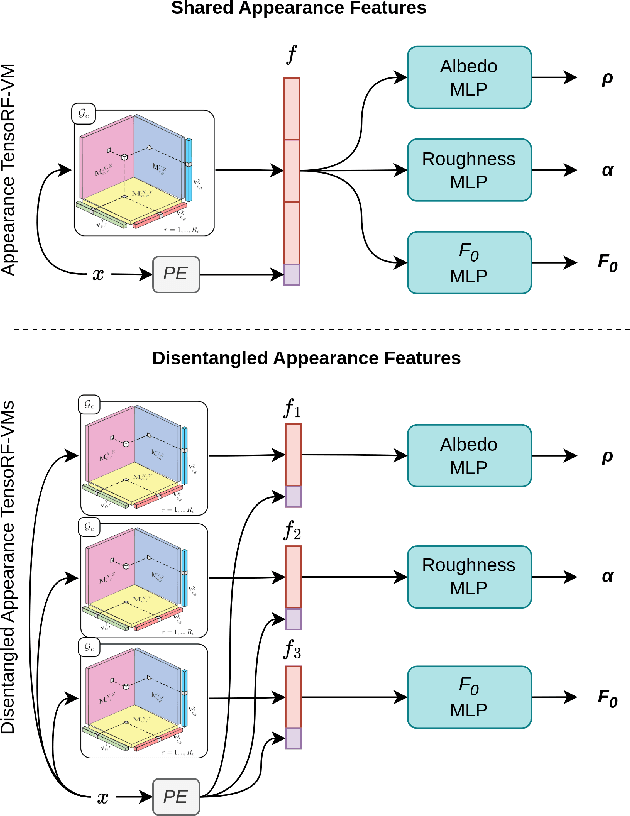
Abstract:Inverse rendering aims to reconstruct the scene properties of objects solely from multiview images. However, it is an ill-posed problem prone to producing ambiguous estimations deviating from physically accurate representations. In this paper, we utilize Neural Microfacet Fields (NMF), a state-of-the-art neural inverse rendering method to illustrate the inherent ambiguity. We propose an evaluation framework to assess the degree of compensation or interaction between the estimated scene properties, aiming to explore the mechanisms behind this ill-posed problem and potential mitigation strategies. Specifically, we introduce artificial perturbations to one scene property and examine how adjusting another property can compensate for these perturbations. To facilitate such experiments, we introduce a disentangled NMF where material properties are independent. The experimental findings underscore the intrinsic ambiguity present in neural inverse rendering and highlight the importance of providing additional guidance through geometry, material, and illumination priors.
TeTriRF: Temporal Tri-Plane Radiance Fields for Efficient Free-Viewpoint Video
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) revolutionize the realm of visual media by providing photorealistic Free-Viewpoint Video (FVV) experiences, offering viewers unparalleled immersion and interactivity. However, the technology's significant storage requirements and the computational complexity involved in generation and rendering currently limit its broader application. To close this gap, this paper presents Temporal Tri-Plane Radiance Fields (TeTriRF), a novel technology that significantly reduces the storage size for Free-Viewpoint Video (FVV) while maintaining low-cost generation and rendering. TeTriRF introduces a hybrid representation with tri-planes and voxel grids to support scaling up to long-duration sequences and scenes with complex motions or rapid changes. We propose a group training scheme tailored to achieving high training efficiency and yielding temporally consistent, low-entropy scene representations. Leveraging these properties of the representations, we introduce a compression pipeline with off-the-shelf video codecs, achieving an order of magnitude less storage size compared to the state-of-the-art. Our experiments demonstrate that TeTriRF can achieve competitive quality with a higher compression rate.
Ref-DVGO: Reflection-Aware Direct Voxel Grid Optimization for an Improved Quality-Efficiency Trade-Off in Reflective Scene Reconstruction
Aug 21, 2023



Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have revolutionized the field of novel view synthesis, demonstrating remarkable performance. However, the modeling and rendering of reflective objects remain challenging problems. Recent methods have shown significant improvements over the baselines in handling reflective scenes, albeit at the expense of efficiency. In this work, we aim to strike a balance between efficiency and quality. To this end, we investigate an implicit-explicit approach based on conventional volume rendering to enhance the reconstruction quality and accelerate the training and rendering processes. We adopt an efficient density-based grid representation and reparameterize the reflected radiance in our pipeline. Our proposed reflection-aware approach achieves a competitive quality efficiency trade-off compared to competing methods. Based on our experimental results, we propose and discuss hypotheses regarding the factors influencing the results of density-based methods for reconstructing reflective objects. The source code is available at https://github.com/gkouros/ref-dvgo.
Category-Level Pose Retrieval with Contrastive Features Learnt with Occlusion Augmentation
Aug 16, 2022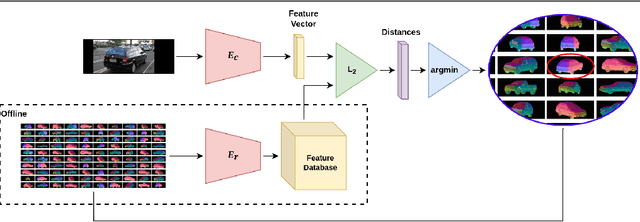
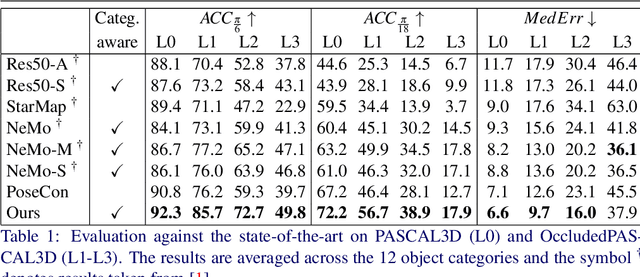
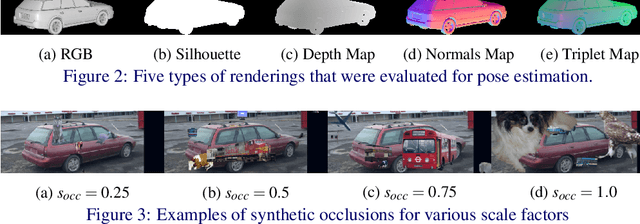
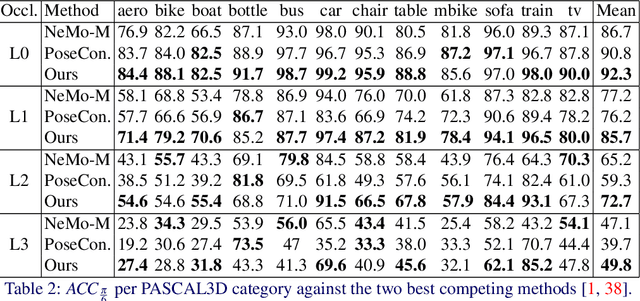
Abstract:Pose estimation is usually tackled as either a bin classification problem or as a regression problem. In both cases, the idea is to directly predict the pose of an object. This is a non-trivial task because of appearance variations of similar poses and similarities between different poses. Instead, we follow the key idea that it is easier to compare two poses than to estimate them. Render-and-compare approaches have been employed to that end, however, they tend to be unstable, computationally expensive, and slow for real-time applications. We propose doing category-level pose estimation by learning an alignment metric using a contrastive loss with a dynamic margin and a continuous pose-label space. For efficient inference, we use a simple real-time image retrieval scheme with a reference set of renderings projected to an embedding space. To achieve robustness to real-world conditions, we employ synthetic occlusions, bounding box perturbations, and appearance augmentations. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on PASCAL3D and OccludedPASCAL3D, as well as high-quality results on KITTI3D.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge