Garry Nolan
MMIL: A novel algorithm for disease associated cell type discovery
Jun 12, 2024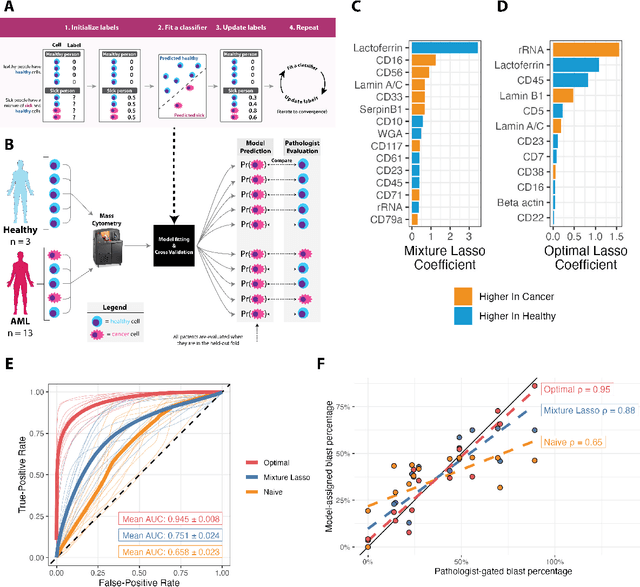
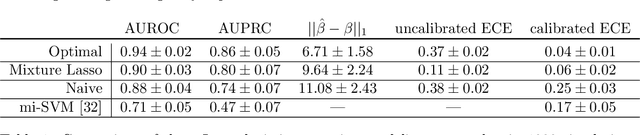
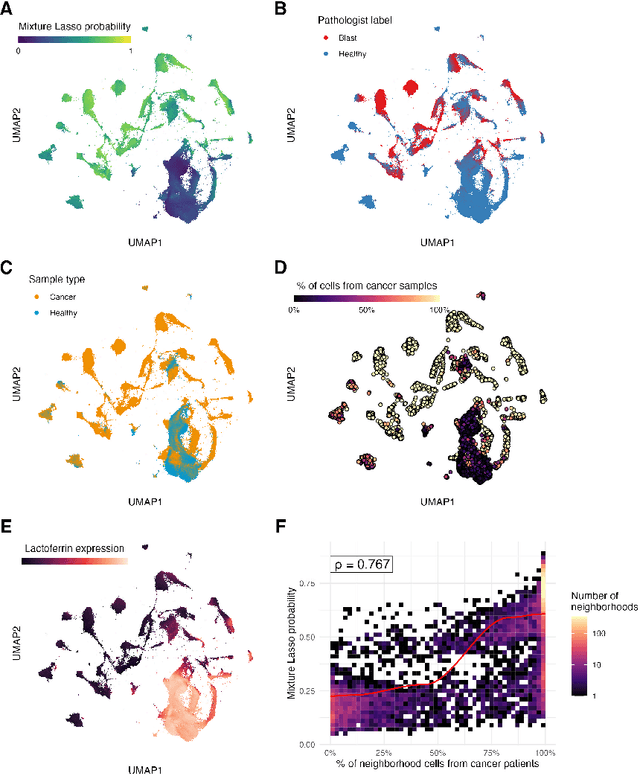
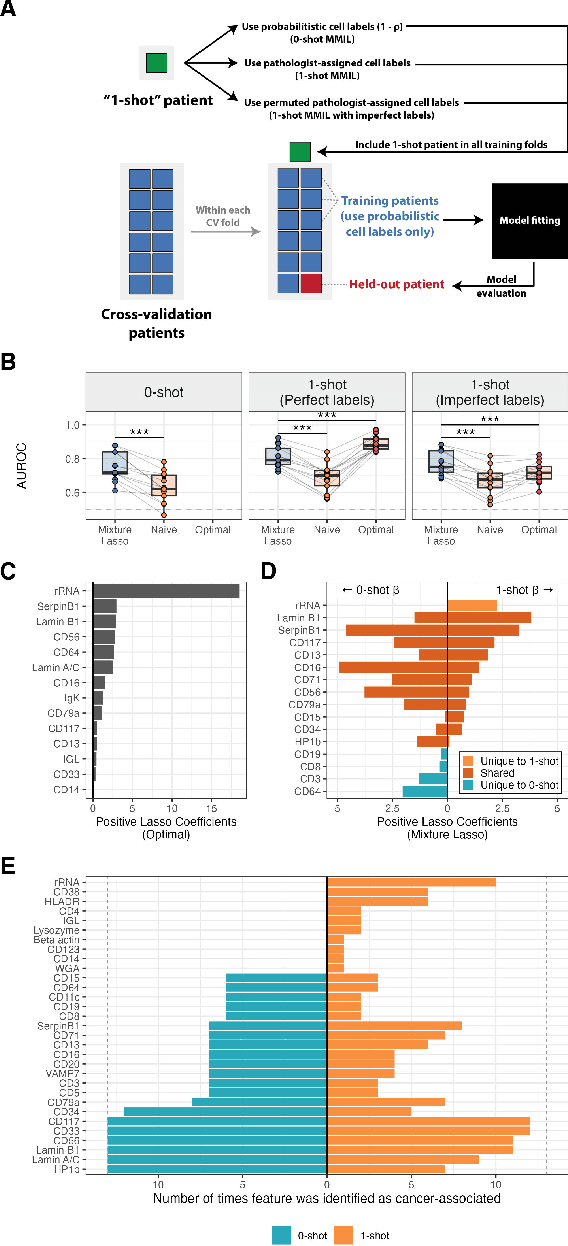
Abstract:Single-cell datasets often lack individual cell labels, making it challenging to identify cells associated with disease. To address this, we introduce Mixture Modeling for Multiple Instance Learning (MMIL), an expectation maximization method that enables the training and calibration of cell-level classifiers using patient-level labels. Our approach can be used to train e.g. lasso logistic regression models, gradient boosted trees, and neural networks. When applied to clinically-annotated, primary patient samples in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), our method accurately identifies cancer cells, generalizes across tissues and treatment timepoints, and selects biologically relevant features. In addition, MMIL is capable of incorporating cell labels into model training when they are known, providing a powerful framework for leveraging both labeled and unlabeled data simultaneously. Mixture Modeling for MIL offers a novel approach for cell classification, with significant potential to advance disease understanding and management, especially in scenarios with unknown gold-standard labels and high dimensionality.
MITI Minimum Information guidelines for highly multiplexed tissue images
Aug 21, 2021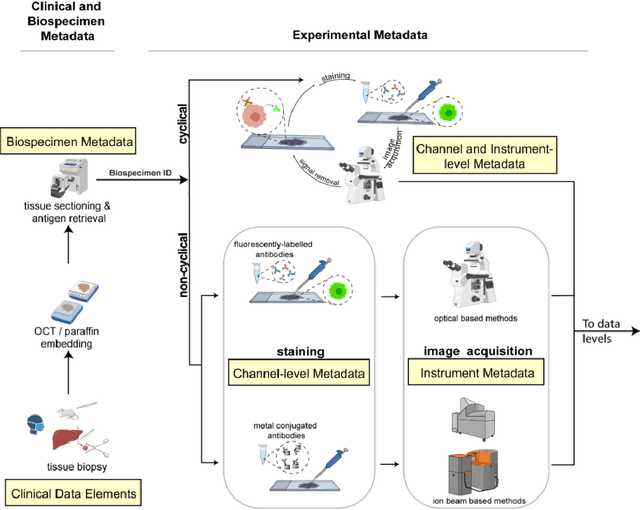
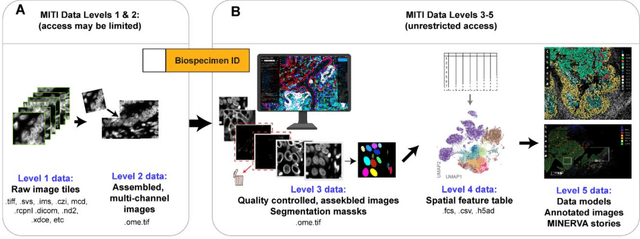
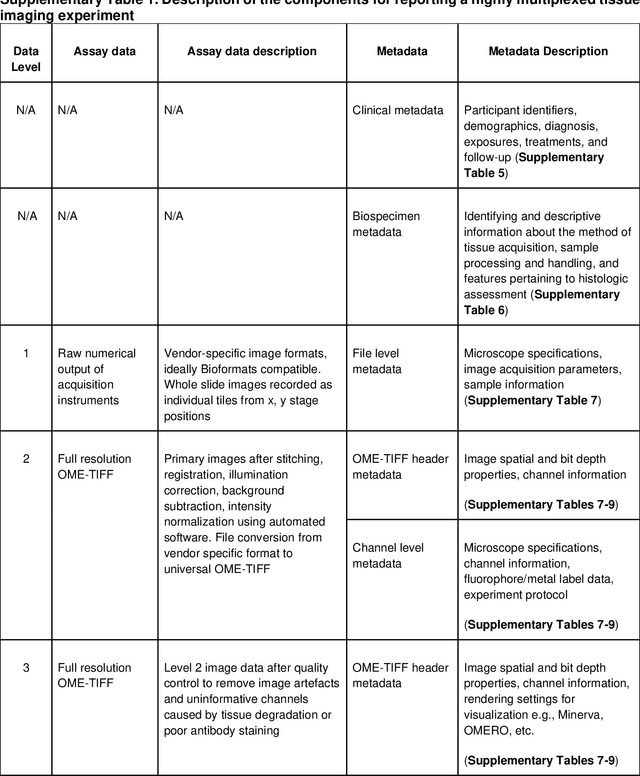
Abstract:The imminent release of atlases combining highly multiplexed tissue imaging with single cell sequencing and other omics data from human tissues and tumors creates an urgent need for data and metadata standards compliant with emerging and traditional approaches to histology. We describe the development of a Minimum Information about highly multiplexed Tissue Imaging (MITI) standard that draws on best practices from genomics and microscopy of cultured cells and model organisms.
Joint Modeling and Registration of Cell Populations in Cohorts of High-Dimensional Flow Cytometric Data
May 31, 2013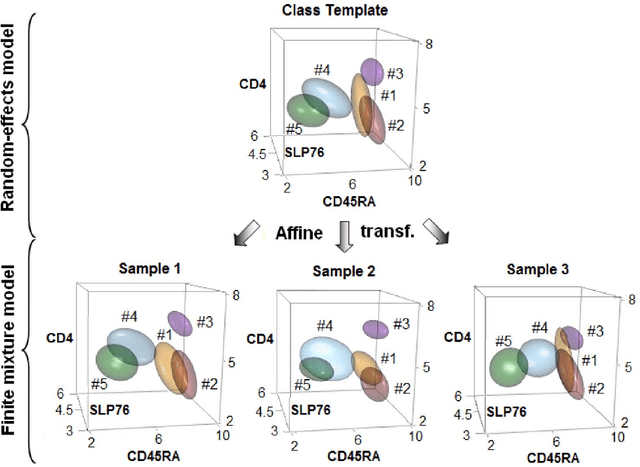
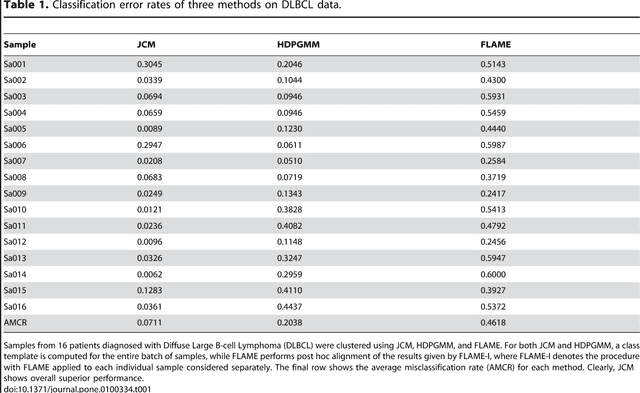
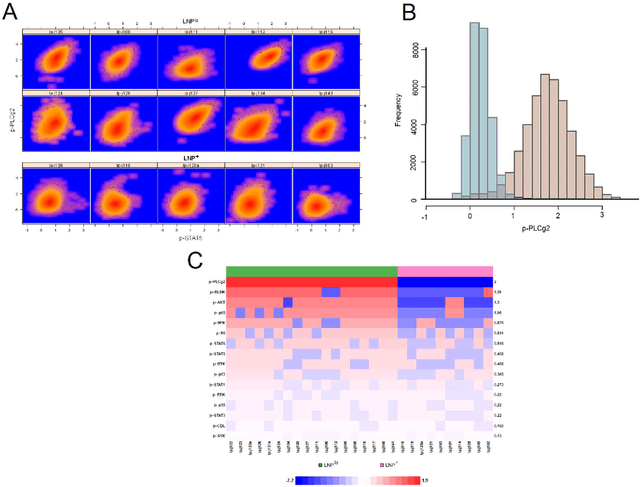
Abstract:In systems biomedicine, an experimenter encounters different potential sources of variation in data such as individual samples, multiple experimental conditions, and multi-variable network-level responses. In multiparametric cytometry, which is often used for analyzing patient samples, such issues are critical. While computational methods can identify cell populations in individual samples, without the ability to automatically match them across samples, it is difficult to compare and characterize the populations in typical experiments, such as those responding to various stimulations or distinctive of particular patients or time-points, especially when there are many samples. Joint Clustering and Matching (JCM) is a multi-level framework for simultaneous modeling and registration of populations across a cohort. JCM models every population with a robust multivariate probability distribution. Simultaneously, JCM fits a random-effects model to construct an overall batch template -- used for registering populations across samples, and classifying new samples. By tackling systems-level variation, JCM supports practical biomedical applications involving large cohorts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge