Fulin Luo
DLIMD: Dictionary Learning based Image-domain Material Decomposition for spectral CT
May 24, 2019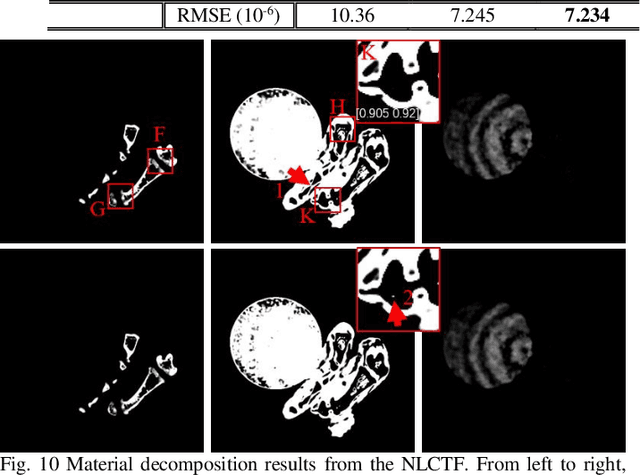
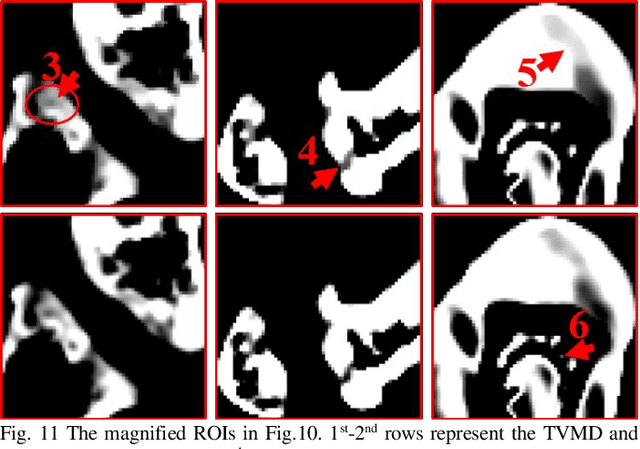

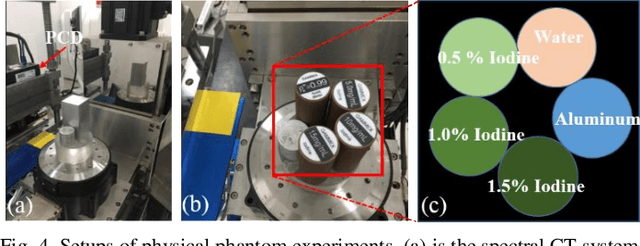
Abstract:The potential huge advantage of spectral computed tomography (CT) is its capability to provide accuracy material identification and quantitative tissue information. This can benefit clinical applications, such as brain angiography, early tumor recognition, etc. To achieve more accurate material components with higher material image quality, we develop a dictionary learning based image-domain material decomposition (DLIMD) for spectral CT in this paper. First, we reconstruct spectral CT image from projections and calculate material coefficients matrix by selecting uniform regions of basis materials from image reconstruction results. Second, we employ the direct inversion (DI) method to obtain initial material decomposition results, and a set of image patches are extracted from the mode-1 unfolding of normalized material image tensor to train a united dictionary by the K-SVD technique. Third, the trained dictionary is employed to explore the similarities from decomposed material images by constructing the DLIMD model. Fourth, more constraints (i.e., volume conservation and the bounds of each pixel within material maps) are further integrated into the model to improve the accuracy of material decomposition. Finally, both physical phantom and preclinical experiments are employed to evaluate the performance of the proposed DLIMD in material decomposition accuracy, material image edge preservation and feature recovery.
Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Imagery Based on Spatial-spectral Manifold Learning
Dec 22, 2018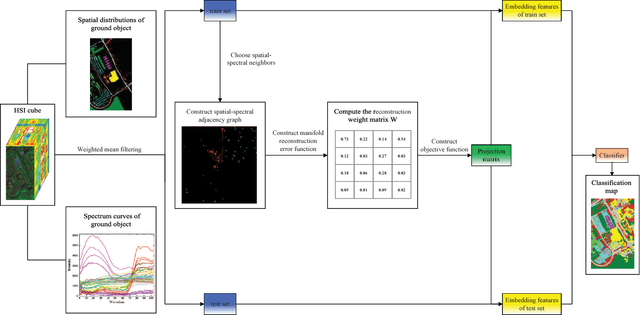
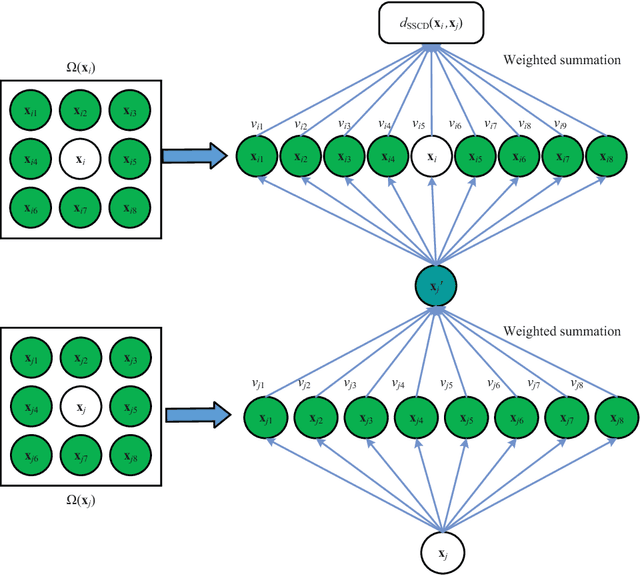


Abstract:The graph embedding (GE) methods have been widely applied for dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral imagery (HSI). However, a major challenge of GE is how to choose proper neighbors for graph construction and explore the spatial information of HSI data. In this paper, we proposed an unsupervised dimensionality reduction algorithm termed spatial-spectral manifold reconstruction preserving embedding (SSMRPE) for HSI classification. At first, a weighted mean filter (WMF) is employed to preprocess the image, which aims to reduce the influence of background noise. According to the spatial consistency property of HSI, the SSMRPE method utilizes a new spatial-spectral combined distance (SSCD) to fuse the spatial structure and spectral information for selecting effective spatial-spectral neighbors of HSI pixels. Then, it explores the spatial relationship between each point and its neighbors to adjusts the reconstruction weights for improving the efficiency of manifold reconstruction. As a result, the proposed method can extract the discriminant features and subsequently improve the classification performance of HSI. The experimental results on PaviaU and Salinas hyperspectral datasets indicate that SSMRPE can achieve better classification accuracies in comparison with some state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge