Francesco Martinuzzi
Transformers vs. Recurrent Models for Estimating Forest Gross Primary Production
Nov 14, 2025



Abstract:Monitoring the spatiotemporal dynamics of forest CO$_2$ uptake (Gross Primary Production, GPP), remains a central challenge in terrestrial ecosystem research. While Eddy Covariance (EC) towers provide high-frequency estimates, their limited spatial coverage constrains large-scale assessments. Remote sensing offers a scalable alternative, yet most approaches rely on single-sensor spectral indices and statistical models that are often unable to capture the complex temporal dynamics of GPP. Recent advances in deep learning (DL) and data fusion offer new opportunities to better represent the temporal dynamics of vegetation processes, but comparative evaluations of state-of-the-art DL models for multimodal GPP prediction remain scarce. Here, we explore the performance of two representative models for predicting GPP: 1) GPT-2, a transformer architecture, and 2) Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), a recurrent neural network, using multivariate inputs. Overall, both achieve similar accuracy. But, while LSTM performs better overall, GPT-2 excels during extreme events. Analysis of temporal context length further reveals that LSTM attains similar accuracy using substantially shorter input windows than GPT-2, highlighting an accuracy-efficiency trade-off between the two architectures. Feature importance analysis reveals radiation as the dominant predictor, followed by Sentinel-2, MODIS land surface temperature, and Sentinel-1 contributions. Our results demonstrate how model architecture, context length, and multimodal inputs jointly determine performance in GPP prediction, guiding future developments of DL frameworks for monitoring terrestrial carbon dynamics.
Minimal Deterministic Echo State Networks Outperform Random Reservoirs in Learning Chaotic Dynamics
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Machine learning (ML) is widely used to model chaotic systems. Among ML approaches, echo state networks (ESNs) have received considerable attention due to their simple construction and fast training. However, ESN performance is highly sensitive to hyperparameter choices and to its random initialization. In this work, we demonstrate that ESNs constructed using deterministic rules and simple topologies (MESNs) outperform standard ESNs in the task of chaotic attractor reconstruction. We use a dataset of more than 90 chaotic systems to benchmark 10 different minimal deterministic reservoir initializations. We find that MESNs obtain up to a 41% reduction in error compared to standard ESNs. Furthermore, we show that the MESNs are more robust, exhibiting less inter-run variation, and have the ability to reuse hyperparameters across different systems. Our results illustrate how structured simplicity in ESN design can outperform stochastic complexity in learning chaotic dynamics.
Earth System Data Cubes: Avenues for advancing Earth system research
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in Earth system science have been marked by the exponential increase in the availability of diverse, multivariate datasets characterised by moderate to high spatio-temporal resolutions. Earth System Data Cubes (ESDCs) have emerged as one suitable solution for transforming this flood of data into a simple yet robust data structure. ESDCs achieve this by organising data into an analysis-ready format aligned with a spatio-temporal grid, facilitating user-friendly analysis and diminishing the need for extensive technical data processing knowledge. Despite these significant benefits, the completion of the entire ESDC life cycle remains a challenging task. Obstacles are not only of a technical nature but also relate to domain-specific problems in Earth system research. There exist barriers to realising the full potential of data collections in light of novel cloud-based technologies, particularly in curating data tailored for specific application domains. These include transforming data to conform to a spatio-temporal grid with minimum distortions and managing complexities such as spatio-temporal autocorrelation issues. Addressing these challenges is pivotal for the effective application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) approaches. Furthermore, adhering to open science principles for data dissemination, reproducibility, visualisation, and reuse is crucial for fostering sustainable research. Overcoming these challenges offers a substantial opportunity to advance data-driven Earth system research, unlocking the full potential of an integrated, multidimensional view of Earth system processes. This is particularly true when such research is coupled with innovative research paradigms and technological progress.
A Sensitivity Analysis of Cellular Automata and Heterogeneous Topology Networks: Partially-Local Cellular Automata and Homogeneous Homogeneous Random Boolean Networks
Jul 25, 2024Abstract:Elementary Cellular Automata (ECA) are a well-studied computational universe that is, despite its simple configurations, capable of impressive computational variety. Harvesting this computation in a useful way has historically shown itself to be difficult, but if combined with reservoir computing (RC), this becomes much more feasible. Furthermore, RC and ECA enable energy-efficient AI, making the combination a promising concept for Edge AI. In this work, we contrast ECA to substrates of Partially-Local CA (PLCA) and Homogeneous Homogeneous Random Boolean Networks (HHRBN). They are, in comparison, the topological heterogeneous counterparts of ECA. This represents a step from ECA towards more biological-plausible substrates. We analyse these substrates by testing on an RC benchmark (5-bit memory), using Temporal Derrida plots to estimate the sensitivity and assess the defect collapse rate. We find that, counterintuitively, disordered topology does not necessarily mean disordered computation. There are countering computational "forces" of topology imperfections leading to a higher collapse rate (order) and yet, if accounted for, an increased sensitivity to the initial condition. These observations together suggest a shrinking critical range.
AI for Extreme Event Modeling and Understanding: Methodologies and Challenges
Jun 28, 2024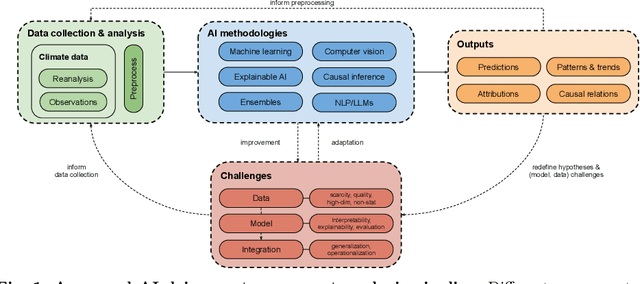

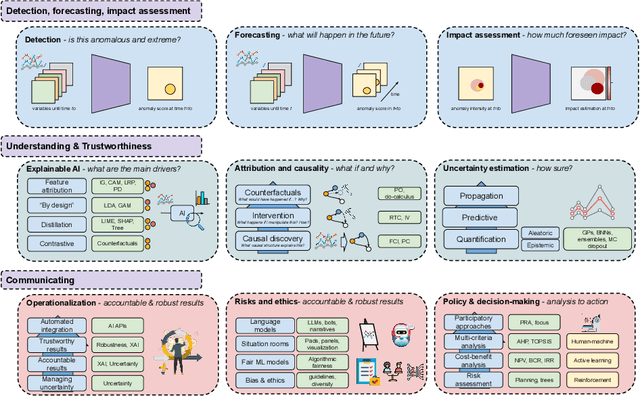

Abstract:In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has deeply impacted various fields, including Earth system sciences. Here, AI improved weather forecasting, model emulation, parameter estimation, and the prediction of extreme events. However, the latter comes with specific challenges, such as developing accurate predictors from noisy, heterogeneous and limited annotated data. This paper reviews how AI is being used to analyze extreme events (like floods, droughts, wildfires and heatwaves), highlighting the importance of creating accurate, transparent, and reliable AI models. We discuss the hurdles of dealing with limited data, integrating information in real-time, deploying models, and making them understandable, all crucial for gaining the trust of stakeholders and meeting regulatory needs. We provide an overview of how AI can help identify and explain extreme events more effectively, improving disaster response and communication. We emphasize the need for collaboration across different fields to create AI solutions that are practical, understandable, and trustworthy for analyzing and predicting extreme events. Such collaborative efforts aim to enhance disaster readiness and disaster risk reduction.
DeepExtremeCubes: Integrating Earth system spatio-temporal data for impact assessment of climate extremes
Jun 26, 2024


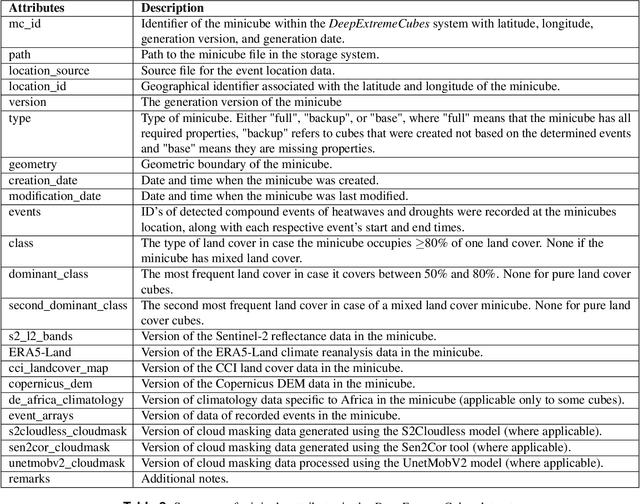
Abstract:With climate extremes' rising frequency and intensity, robust analytical tools are crucial to predict their impacts on terrestrial ecosystems. Machine learning techniques show promise but require well-structured, high-quality, and curated analysis-ready datasets. Earth observation datasets comprehensively monitor ecosystem dynamics and responses to climatic extremes, yet the data complexity can challenge the effectiveness of machine learning models. Despite recent progress in deep learning to ecosystem monitoring, there is a need for datasets specifically designed to analyse compound heatwave and drought extreme impact. Here, we introduce the DeepExtremeCubes database, tailored to map around these extremes, focusing on persistent natural vegetation. It comprises over 40,000 spatially sampled small data cubes (i.e. minicubes) globally, with a spatial coverage of 2.5 by 2.5 km. Each minicube includes (i) Sentinel-2 L2A images, (ii) ERA5-Land variables and generated extreme event cube covering 2016 to 2022, and (iii) ancillary land cover and topography maps. The paper aims to (1) streamline data accessibility, structuring, pre-processing, and enhance scientific reproducibility, and (2) facilitate biosphere dynamics forecasting in response to compound extremes.
Recurrent Neural Networks for Modelling Gross Primary Production
Apr 19, 2024


Abstract:Accurate quantification of Gross Primary Production (GPP) is crucial for understanding terrestrial carbon dynamics. It represents the largest atmosphere-to-land CO$_2$ flux, especially significant for forests. Eddy Covariance (EC) measurements are widely used for ecosystem-scale GPP quantification but are globally sparse. In areas lacking local EC measurements, remote sensing (RS) data are typically utilised to estimate GPP after statistically relating them to in-situ data. Deep learning offers novel perspectives, and the potential of recurrent neural network architectures for estimating daily GPP remains underexplored. This study presents a comparative analysis of three architectures: Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs), and Long-Short Term Memory (LSTMs). Our findings reveal comparable performance across all models for full-year and growing season predictions. Notably, LSTMs outperform in predicting climate-induced GPP extremes. Furthermore, our analysis highlights the importance of incorporating radiation and RS inputs (optical, temperature, and radar) for accurate GPP predictions, particularly during climate extremes.
ReservoirComputing.jl: An Efficient and Modular Library for Reservoir Computing Models
Apr 08, 2022


Abstract:We introduce ReservoirComputing.jl, an open source Julia library for reservoir computing models. The software offers a great number of algorithms presented in the literature, and allows to expand on them with both internal and external tools in a simple way. The implementation is highly modular, fast and comes with a comprehensive documentation, which includes reproduced experiments from literature. The code and documentation are hosted on Github under an MIT license https://github.com/SciML/ReservoirComputing.jl.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge