Fangzhou Xu
Hierarchical Structured Neural Network for Retrieval
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:Embedding Based Retrieval (EBR) is a crucial component of the retrieval stage in (Ads) Recommendation System that utilizes Two Tower or Siamese Networks to learn embeddings for both users and items (ads). It then employs an Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search (ANN) to efficiently retrieve the most relevant ads for a specific user. Despite the recent rise to popularity in the industry, they have a couple of limitations. Firstly, Two Tower model architecture uses a single dot product interaction which despite their efficiency fail to capture the data distribution in practice. Secondly, the centroid representation and cluster assignment, which are components of ANN, occur after the training process has been completed. As a result, they do not take into account the optimization criteria used for retrieval model. In this paper, we present Hierarchical Structured Neural Network (HSNN), a deployed jointly optimized hierarchical clustering and neural network model that can take advantage of sophisticated interactions and model architectures that are more common in the ranking stages while maintaining a sub-linear inference cost. We achieve 6.5% improvement in offline evaluation and also demonstrate 1.22% online gains through A/B experiments. HSNN has been successfully deployed into the Ads Recommendation system and is currently handling major portion of the traffic. The paper shares our experience in developing this system, dealing with challenges like freshness, volatility, cold start recommendations, cluster collapse and lessons deploying the model in a large scale retrieval production system.
BusTr: Predicting Bus Travel Times from Real-Time Traffic
Jul 02, 2020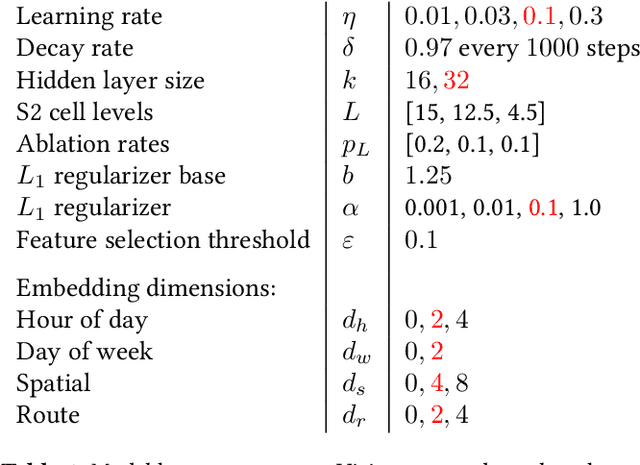
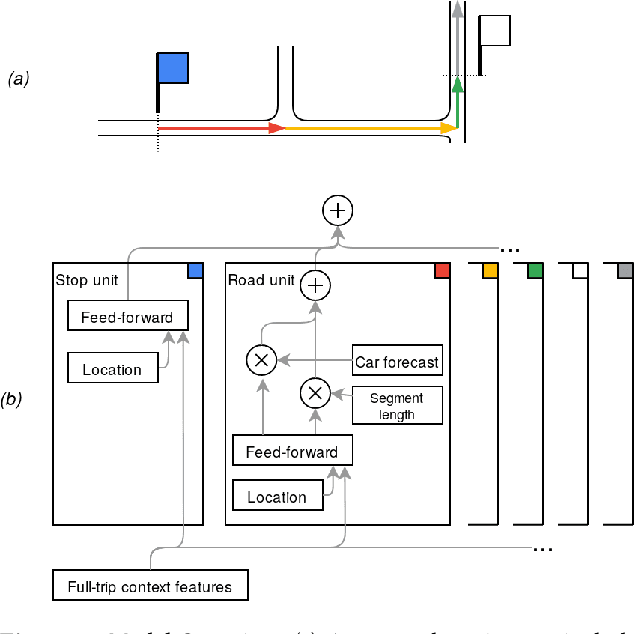
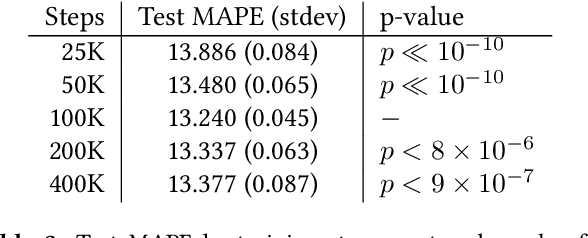
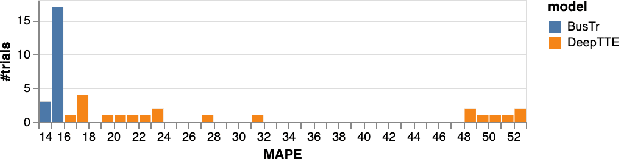
Abstract:We present BusTr, a machine-learned model for translating road traffic forecasts into predictions of bus delays, used by Google Maps to serve the majority of the world's public transit systems where no official real-time bus tracking is provided. We demonstrate that our neural sequence model improves over DeepTTE, the state-of-the-art baseline, both in performance (-30% MAPE) and training stability. We also demonstrate significant generalization gains over simpler models, evaluated on longitudinal data to cope with a constantly evolving world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge