Fang Tang
Strategizing Equitable Transit Evacuations: A Data-Driven Reinforcement Learning Approach
Dec 08, 2024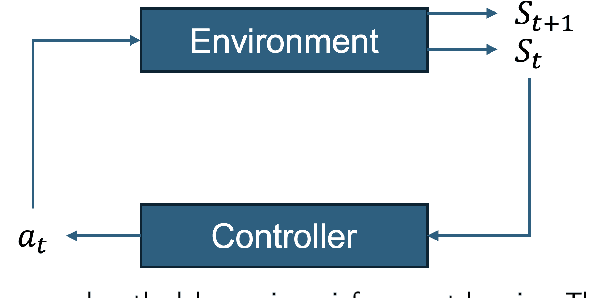

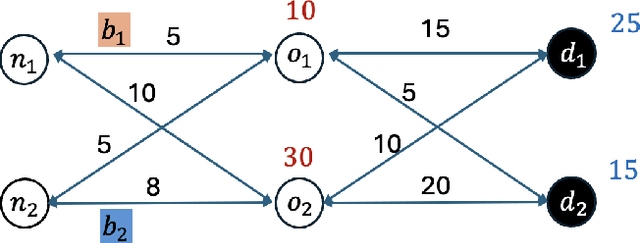
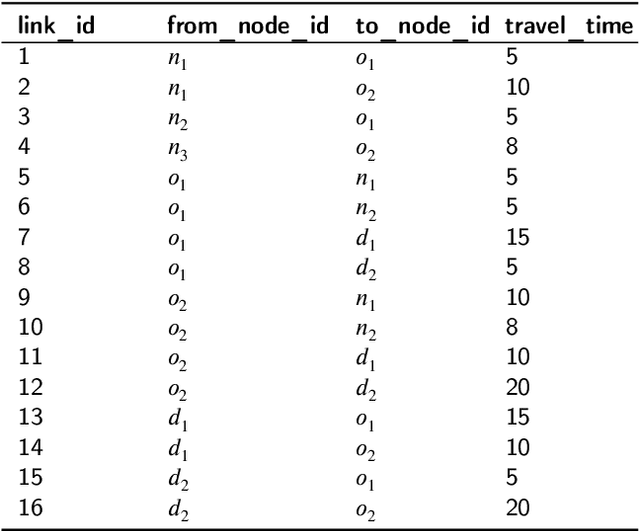
Abstract:As natural disasters become increasingly frequent, the need for efficient and equitable evacuation planning has become more critical. This paper proposes a data-driven, reinforcement learning-based framework to optimize bus-based evacuations with an emphasis on improving both efficiency and equity. We model the evacuation problem as a Markov Decision Process solved by reinforcement learning, using real-time transit data from General Transit Feed Specification and transportation networks extracted from OpenStreetMap. The reinforcement learning agent dynamically reroutes buses from their scheduled location to minimize total passengers' evacuation time while prioritizing equity-priority communities. Simulations on the San Francisco Bay Area transportation network indicate that the proposed framework achieves significant improvements in both evacuation efficiency and equitable service distribution compared to traditional rule-based and random strategies. These results highlight the potential of reinforcement learning to enhance system performance and urban resilience during emergency evacuations, offering a scalable solution for real-world applications in intelligent transportation systems.
Deep Adaptive Network: An Efficient Deep Neural Network with Sparse Binary Connections
Apr 21, 2016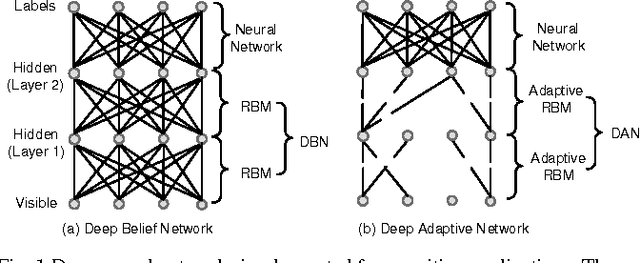
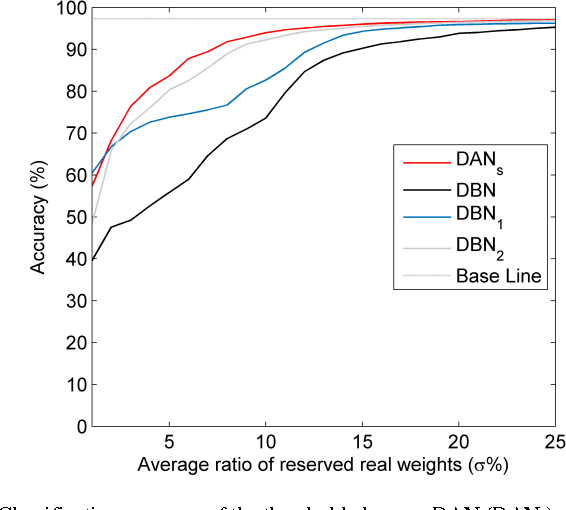
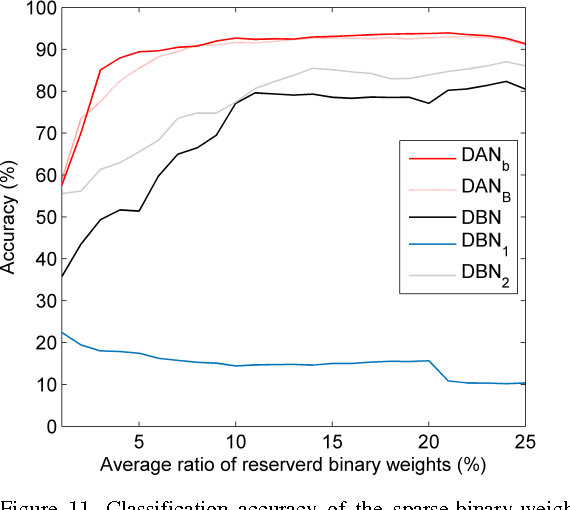
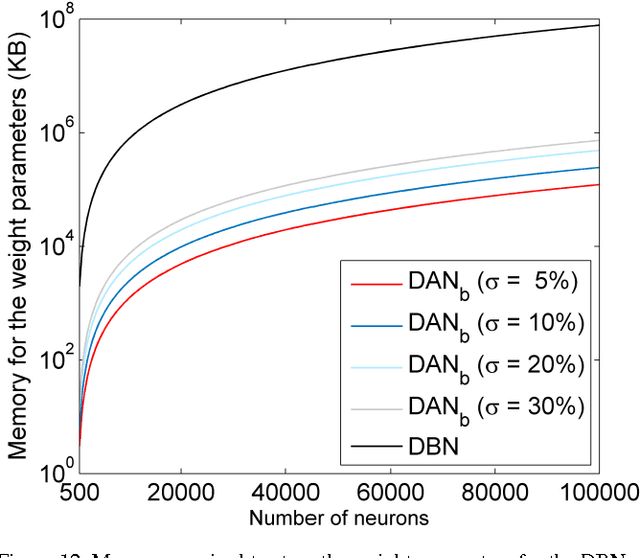
Abstract:Deep neural networks are state-of-the-art models for understanding the content of images, video and raw input data. However, implementing a deep neural network in embedded systems is a challenging task, because a typical deep neural network, such as a Deep Belief Network using 128x128 images as input, could exhaust Giga bytes of memory and result in bandwidth and computing bottleneck. To address this challenge, this paper presents a hardware-oriented deep learning algorithm, named as the Deep Adaptive Network, which attempts to exploit the sparsity in the neural connections. The proposed method adaptively reduces the weights associated with negligible features to zero, leading to sparse feedforward network architecture. Furthermore, since the small proportion of important weights are significantly larger than zero, they can be robustly thresholded and represented using single-bit integers (-1 and +1), leading to implementations of deep neural networks with sparse and binary connections. Our experiments showed that, for the application of recognizing MNIST handwritten digits, the features extracted by a two-layer Deep Adaptive Network with about 25% reserved important connections achieved 97.2% classification accuracy, which was almost the same with the standard Deep Belief Network (97.3%). Furthermore, for efficient hardware implementations, the sparse-and-binary-weighted deep neural network could save about 99.3% memory and 99.9% computation units without significant loss of classification accuracy for pattern recognition applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge