Enza Messina
Gromov-Wasserstein and optimal transport: from assignment problems to probabilistic numeric
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:The assignment problem, a cornerstone of operations research, seeks an optimal one-to-one mapping between agents and tasks to minimize total cost. This work traces its evolution from classical formulations and algorithms to modern optimal transport (OT) theory, positioning the Quadratic Assignment Problem (QAP) and related structural matching tasks within this framework. We connect the linear assignment problem to Monge's transport problem, Kantorovich's relaxation, and Wasserstein distances, then extend to cases where source and target lie in different metric-measure spaces requiring Gromov-Wasserstein (GW) distances. GW formulations, including the fused GW variant that integrates structural and feature information, naturally address QAP-like problems by optimizing alignment based on both intra-domain distances and cross-domain attributes. Applications include graph matching, keypoint correspondence, and feature-based assignments. We present exact solvers, Genetic Algorithms (GA), and multiple GW variants, including a proposed multi-initialization strategy (GW-MultiInit) that mitigates the risk of getting stuck in local optima alongside entropic Sinkhorn-based approximations and fused GW. Computational experiments on capacitated QAP instances show that GW-MultiInit consistently achieves near-optimal solutions and scales efficiently to large problems where exact methods become impractical, while parameterized EGW and FGW variants provide flexible trade-offs between accuracy and runtime. Our findings provide theoretical foundations, computational insights, and practical guidelines for applying OT and GW methods to QAP and other real-world matching problems, such as those in machine learning and logistics.
A Robust Support Vector Machine Approach for Raman COVID-19 Data Classification
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in healthcare technologies have led to the availability of large amounts of biological samples across several techniques and applications. In particular, in the last few years, Raman spectroscopy analysis of biological samples has been successfully applied for early-stage diagnosis. However, spectra' inherent complexity and variability make the manual analysis challenging, even for domain experts. For the same reason, the use of traditional Statistical and Machine Learning (ML) techniques could not guarantee for accurate and reliable results. ML models, combined with robust optimization techniques, offer the possibility to improve the classification accuracy and enhance the resilience of predictive models. In this paper, we investigate the performance of a novel robust formulation for Support Vector Machine (SVM) in classifying COVID-19 samples obtained from Raman Spectroscopy. Given the noisy and perturbed nature of biological samples, we protect the classification process against uncertainty through the application of robust optimization techniques. Specifically, we derive robust counterpart models of deterministic formulations using bounded-by-norm uncertainty sets around each observation. We explore the cases of both linear and kernel-induced classifiers to address binary and multiclass classification tasks. The effectiveness of our approach is validated on real-world COVID-19 datasets provided by Italian hospitals by comparing the results of our simulations with a state-of-the-art classifier.
Graph Learning in 4D: a Quaternion-valued Laplacian to Enhance Spectral GCNs
Dec 28, 2023



Abstract:We introduce QuaterGCN, a spectral Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) with quaternion-valued weights at whose core lies the Quaternionic Laplacian, a quaternion-valued Laplacian matrix by whose proposal we generalize two widely-used Laplacian matrices: the classical Laplacian (defined for undirected graphs) and the complex-valued Sign-Magnetic Laplacian (proposed to handle digraphs with weights of arbitrary sign). In addition to its generality, our Quaternionic Laplacian is the only Laplacian to completely preserve the topology of a digraph, as it can handle graphs and digraphs containing antiparallel pairs of edges (digons) of different weights without reducing them to a single (directed or undirected) edge as done with other Laplacians. Experimental results show the superior performance of QuaterGCN compared to other state-of-the-art GCNs, particularly in scenarios where the information the digons carry is crucial to successfully address the task at hand.
The Internet of Responsibilities-Connecting Human Responsibilities using Big Data and Blockchain
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:Accountability in the workplace is critically important and remains a challenging problem, especially with respect to workplace safety management. In this paper, we introduce a novel notion, the Internet of Responsibilities, for accountability management. Our method sorts through the list of responsibilities with respect to hazardous positions. The positions are interconnected using directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) indicating the hierarchy of responsibilities in the organization. In addition, the system detects and collects responsibilities, and represents risk areas in terms of the positions of the responsibility nodes. Finally, an automatic reminder and assignment system is used to enforce a strict responsibility control without human intervention. Using blockchain technology, we further extend our system with the capability to store, recover and encrypt responsibility data. We show that through the application of the Internet of Responsibility network model driven by Big Data, enterprise and government agencies can attain a highly secured and safe workplace. Therefore, our model offers a combination of interconnected responsibilities, accountability, monitoring, and safety which is crucial for the protection of employees and the success of organizations.
SigMaNet: One Laplacian to Rule Them All
May 26, 2022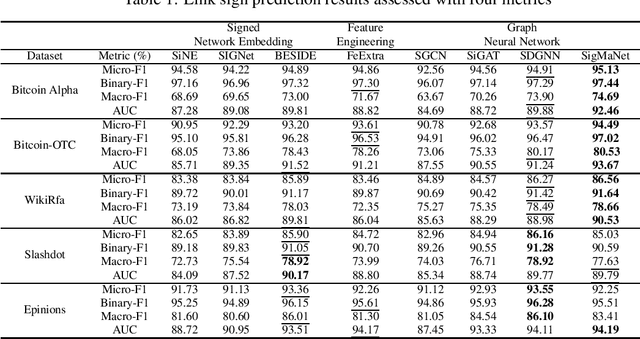

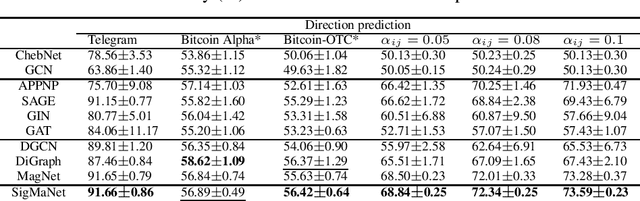

Abstract:This paper introduces SigMaNet, a generalized Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) capable of handling both undirected and directed graphs with weights not restricted in sign and magnitude. The cornerstone of SigMaNet is the introduction of a generalized Laplacian matrix: the Sign-Magnetic Laplacian ($L^\sigma$). The adoption of such a matrix allows us to bridge a gap in the current literature by extending the theory of spectral GCNs to directed graphs with both positive and negative weights. $L^{\sigma}$ exhibits several desirable properties not enjoyed by the traditional Laplacian matrices on which several state-of-the-art architectures are based. In particular, $L^\sigma$ is completely parameter-free, which is not the case of Laplacian operators such as the Magnetic Laplacian $L^{(q)}$, where the calibration of the parameter q is an essential yet problematic component of the operator. $L^\sigma$ simplifies the approach, while also allowing for a natural interpretation of the signs of the edges in terms of their directions. The versatility of the proposed approach is amply demonstrated experimentally; the proposed network SigMaNet turns out to be competitive in all the tasks we considered, regardless of the graph structure.
Using Machine Learning to Automate Mammogram Images Analysis
Dec 06, 2020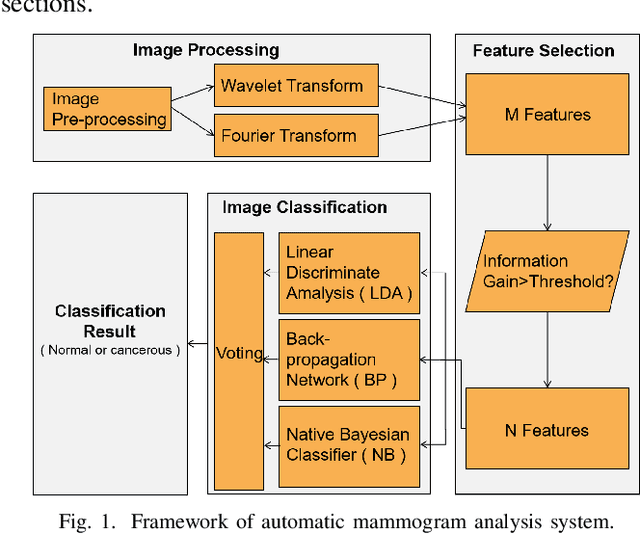
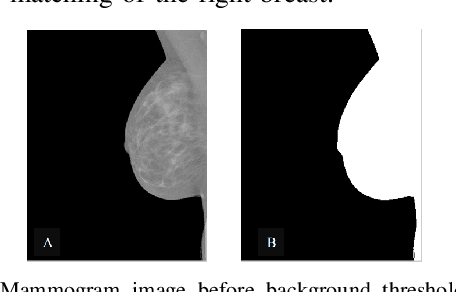
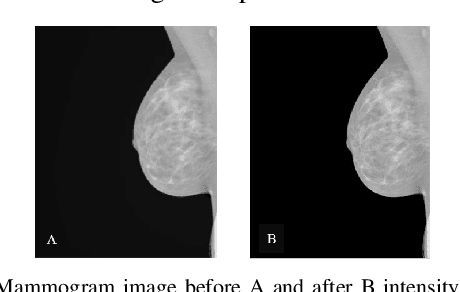
Abstract:Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death after lung cancer in women. Early detection of breast cancer in X-ray mammography is believed to have effectively reduced the mortality rate. However, a relatively high false positive rate and a low specificity in mammography technology still exist. In this work, a computer-aided automatic mammogram analysis system is proposed to process the mammogram images and automatically discriminate them as either normal or cancerous, consisting of three consecutive image processing, feature selection, and image classification stages. In designing the system, the discrete wavelet transforms (Daubechies 2, Daubechies 4, and Biorthogonal 6.8) and the Fourier cosine transform were first used to parse the mammogram images and extract statistical features. Then, an entropy-based feature selection method was implemented to reduce the number of features. Finally, different pattern recognition methods (including the Back-propagation Network, the Linear Discriminant Analysis, and the Naive Bayes Classifier) and a voting classification scheme were employed. The performance of each classification strategy was evaluated for sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy and for general performance using the Receiver Operating Curve. Our method is validated on the dataset from the Eastern Health in Newfoundland and Labrador of Canada. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed automatic mammogram analysis system could effectively improve the classification performances.
Efficient Kernel-based Subsequence Search for User Identification from Walking Activity
Jul 16, 2019

Abstract:This paper presents an efficient approach for subsequence search in data streams. The problem consists in identifying coherent repetitions of a given reference time-series, eventually multi-variate, within a longer data stream. Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) is the metric most widely used to implement pattern query, but its computational complexity is a well-known issue. In this paper we present an approach aimed at learning a kernel able to approximate DTW to be used for efficiently analyse streaming data collected from wearable sensors, reducing the burden of computation. Contrary to kernel, DTW allows for comparing time series with different length. Thus, to use a kernel, a feature embedding is used to represent a time-series as a fixed length vector. Each vector component is the DTW between the given time-series and a set of 'basis' series, usually randomly chosen. The vector size is the number of basis series used for the feature embedding. Searching for the portion of the data stream minimizing the DTW with the reference subsequence leads to a global optimization problem. The proposed approach has been validated on a benchmark dataset related to the identification of users depending on their walking activity. A comparison with a traditional DTW implementation is also provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge