Durgesh Haribhau Salunkhe
LISN
Enhancing Otological Surgery: Co-Designing a Parallel Robot with Surgeon Input
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:This work presents the development of a parallel manipulator used for otological surgery from the perspective of co-design. Co-design refers to the simultaneous involvement of the end-users (surgeons), stakeholders (designers, ergonomic experts, manufacturers), and experts from the fields of optimization and mechanisms. The role of each member is discussed in detail and the interactions between the stakeholders are presented. Co-design facilitates a reduction in the parameter space considered during mechanism optimization, leading to a more efficient design process. Additionally, the co-design principles help avoid unforeseen errors and help in quicker adaptation of the proposed solution.
Necessary and sufficient condition for a generic 3R serial manipulator to be cuspidal
Feb 17, 2022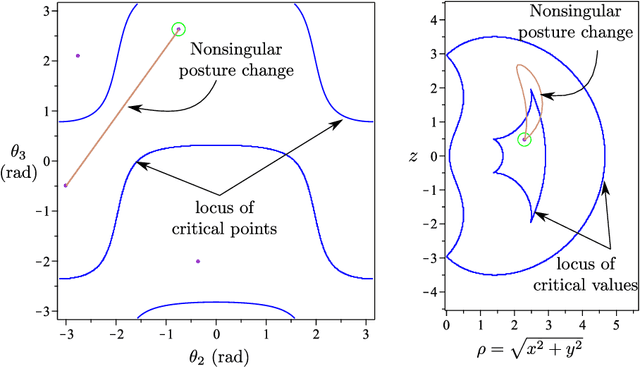
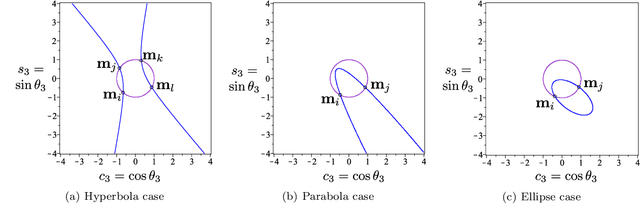

Abstract:Cuspidal robots can travel from one inverse kinematic solution to another without meeting a singularity. The name cuspidal was coined based on the existence of a cusp point in the workspace of 3R serial robots. The existence of a cusp point was proved to be a necessary and sufficient condition for orthogonal robots to be cuspidal, but it was not possible to extend this condition to non-orthogonal robots. The goal of this paper is to prove that this condition stands for any generic 3R robot. This result would give the designer more flexibility. In the presented work, the geometrical interpretation of the inverse kinematics of 3R robots is revisited and important observations on the nonsingular change of posture are noted. The paper presents a theorem regarding the existence of reduced aspects in any generic 3R serial robot. Based on these observations and on this theorem, we prove that the existence of a cusp point is a necessary and sufficient condition for any 3R generic robot to be cuspidal.
Literature Review on Endoscopic Robotic Systems in Ear and Sinus Surgery
Sep 28, 2021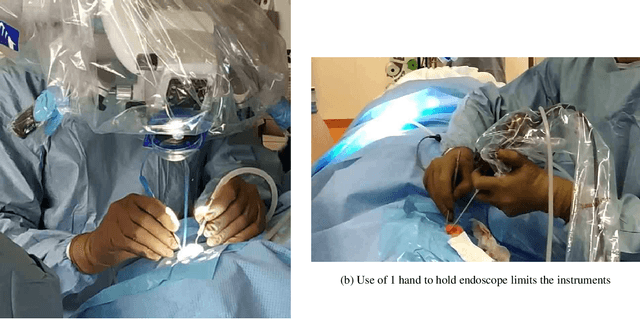



Abstract:In otolaryngologic surgery, endoscopy is increasingly used to provide a better view of hard-to-reach areas and to promote minimally invasive surgery. However, the need to manipulate the endoscope limits the surgeon's ability to operate with only one instrument at a time. Currently, several robotic systems are being developed, demonstrating the value of robotic assistance in microsurgery. The aim of this literature review is to present and classify current robotic systems that are used for otological and endonasal applications. For these solutions, an analysis of the functionalities in relation to the surgeon's needs will be carried out in order to produce a set of specifications for the creation of new robots.
Motion Planning for Multi-Mobile-Manipulator Payload Transport Systems
Mar 18, 2019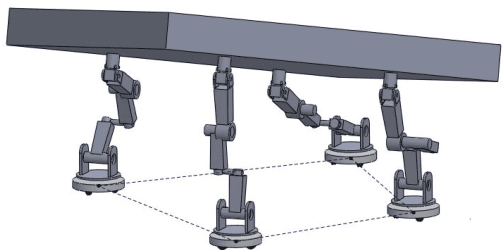
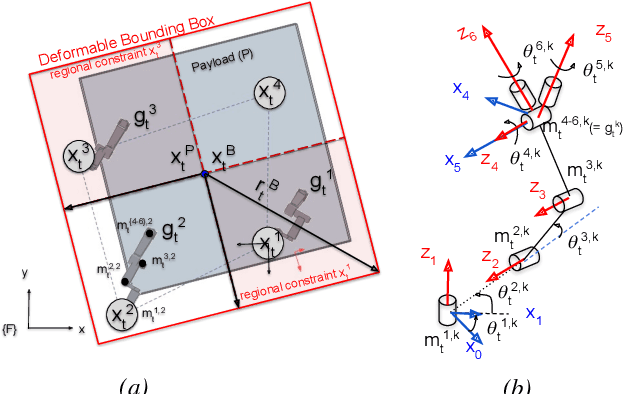
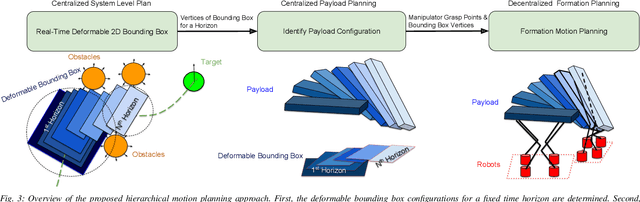
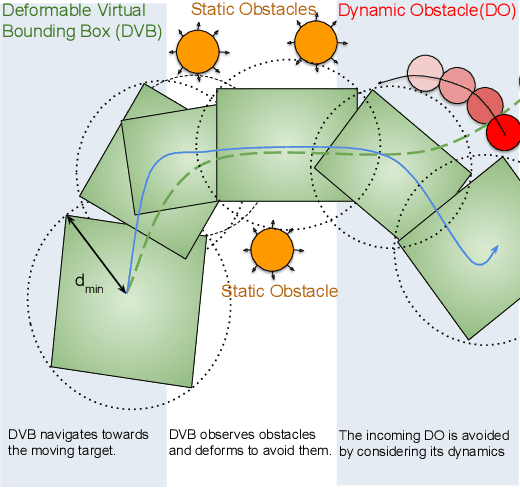
Abstract:In this paper, a kinematic motion planning algorithm for cooperative spatial payload manipulation is presented. A hierarchical approach is introduced to compute real-time collision-free motion plans for a formation of mobile manipulator robots. Initially, collision-free configurations of a deformable 2-D virtual bounding box are identified, over a planning horizon, to define a convex workspace for the entire system. Then, 3-D payload configurations whose projections lie within the defined convex workspace are computed. Finally, a convex decentralized model-predictive controller is formulated to plan collision-free trajectories for the formation of mobile manipulators. This approach facilitates real-time motion planning for the system and is scalable in the number of robots. The algorithm is validated in simulated dynamic environments. Simulation video: https://youtu.be/9EKj7RwRs_4.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge