Dongxu Liang
OneMall: One Architecture, More Scenarios -- End-to-End Generative Recommender Family at Kuaishou E-Commerce
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:In the wave of generative recommendation, we present OneMall, an end-to-end generative recommendation framework tailored for e-commerce services at Kuaishou. Our OneMall systematically unifies the e-commerce's multiple item distribution scenarios, such as Product-card, short-video and live-streaming. Specifically, it comprises three key components, aligning the entire model training pipeline to the LLM's pre-training/post-training: (1) E-commerce Semantic Tokenizer: we provide a tokenizer solution that captures both real-world semantics and business-specific item relations across different scenarios; (2) Transformer-based Architecture: we largely utilize Transformer as our model backbone, e.g., employing Query-Former for long sequence compression, Cross-Attention for multi-behavior sequence fusion, and Sparse MoE for scalable auto-regressive generation; (3) Reinforcement Learning Pipeline: we further connect retrieval and ranking models via RL, enabling the ranking model to serve as a reward signal for end-to-end policy retrieval model optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OneMall achieves consistent improvements across all e-commerce scenarios: +13.01\% GMV in product-card, +15.32\% Orders in Short-Video, and +2.78\% Orders in Live-Streaming. OneMall has been deployed, serving over 400 million daily active users at Kuaishou.
OneMall: One Model, More Scenarios -- End-to-End Generative Recommender Family at Kuaishou E-Commerce
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:In the wave of generative recommendation, we present OneMall, an end-to-end generative recommendation framework tailored for e-commerce services at Kuaishou. Our OneMall systematically unifies the e-commerce's multiple item distribution scenarios, such as Product-card, short-video and live-streaming. Specifically, it comprises three key components, aligning the entire model training pipeline to the LLM's pre-training/post-training: (1) E-commerce Semantic Tokenizer: we provide a tokenizer solution that captures both real-world semantics and business-specific item relations across different scenarios; (2) Transformer-based Architecture: we largely utilize Transformer as our model backbone, e.g., employing Query-Former for long sequence compression, Cross-Attention for multi-behavior sequence fusion, and Sparse MoE for scalable auto-regressive generation; (3) Reinforcement Learning Pipeline: we further connect retrieval and ranking models via RL, enabling the ranking model to serve as a reward signal for end-to-end policy retrieval model optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OneMall achieves consistent improvements across all e-commerce scenarios: +13.01\% GMV in product-card, +15.32\% Orders in Short-Video, and +2.78\% Orders in Live-Streaming. OneMall has been deployed, serving over 400 million daily active users at Kuaishou.
CounterCLR: Counterfactual Contrastive Learning with Non-random Missing Data in Recommendation
Feb 08, 2024


Abstract:Recommender systems are designed to learn user preferences from observed feedback and comprise many fundamental tasks, such as rating prediction and post-click conversion rate (pCVR) prediction. However, the observed feedback usually suffer from two issues: selection bias and data sparsity, where biased and insufficient feedback seriously degrade the performance of recommender systems in terms of accuracy and ranking. Existing solutions for handling the issues, such as data imputation and inverse propensity score, are highly susceptible to additional trained imputation or propensity models. In this work, we propose a novel counterfactual contrastive learning framework for recommendation, named CounterCLR, to tackle the problem of non-random missing data by exploiting the advances in contrast learning. Specifically, the proposed CounterCLR employs a deep representation network, called CauNet, to infer non-random missing data in recommendations and perform user preference modeling by further introducing a self-supervised contrastive learning task. Our CounterCLR mitigates the selection bias problem without the need for additional models or estimators, while also enhancing the generalization ability in cases of sparse data. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
Exploring and Exploiting Data Heterogeneity in Recommendation
May 21, 2023


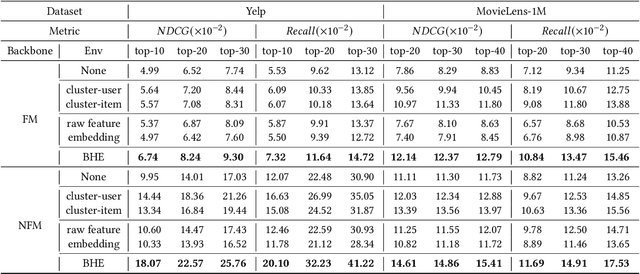
Abstract:Massive amounts of data are the foundation of data-driven recommendation models. As an inherent nature of big data, data heterogeneity widely exists in real-world recommendation systems. It reflects the differences in the properties among sub-populations. Ignoring the heterogeneity in recommendation data could limit the performance of recommendation models, hurt the sub-populational robustness, and make the models misled by biases. However, data heterogeneity has not attracted substantial attention in the recommendation community. Therefore, it inspires us to adequately explore and exploit heterogeneity for solving the above problems and assisting data analysis. In this work, we focus on exploring two representative categories of heterogeneity in recommendation data that is the heterogeneity of prediction mechanism and covariate distribution and propose an algorithm that explores the heterogeneity through a bilevel clustering method. Furthermore, the uncovered heterogeneity is exploited for two purposes in recommendation scenarios which are prediction with multiple sub-models and supporting debias. Extensive experiments on real-world data validate the existence of heterogeneity in recommendation data and the effectiveness of exploring and exploiting data heterogeneity in recommendation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge