Dongkai Wang
TimeCNN: Refining Cross-Variable Interaction on Time Point for Time Series Forecasting
Oct 07, 2024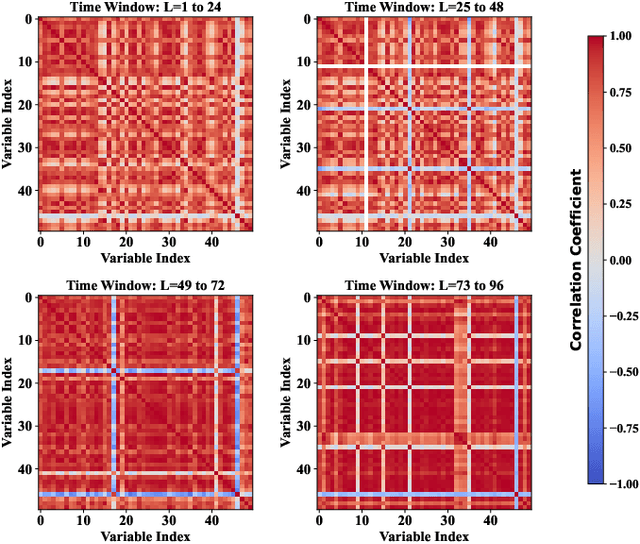
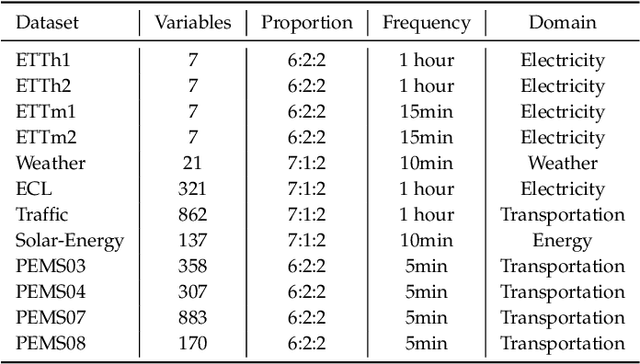
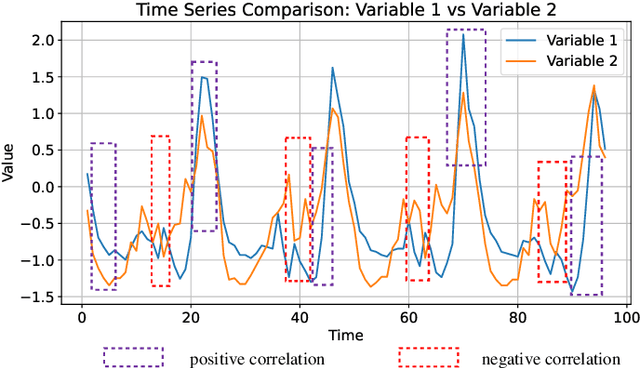
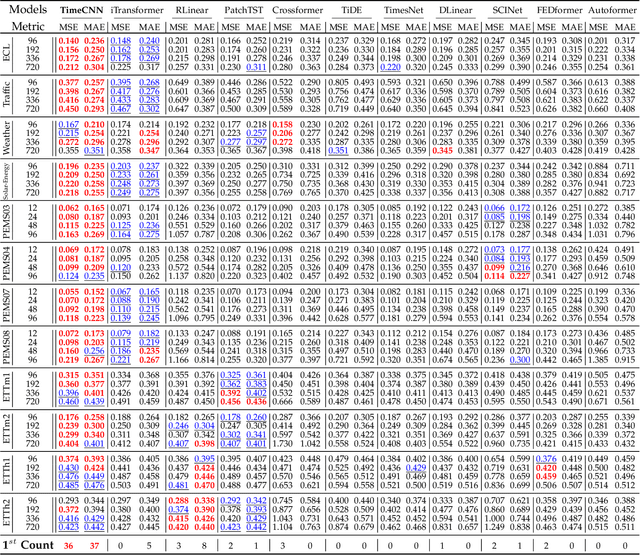
Abstract:Time series forecasting is extensively applied across diverse domains. Transformer-based models demonstrate significant potential in modeling cross-time and cross-variable interaction. However, we notice that the cross-variable correlation of multivariate time series demonstrates multifaceted (positive and negative correlations) and dynamic progression over time, which is not well captured by existing Transformer-based models. To address this issue, we propose a TimeCNN model to refine cross-variable interactions to enhance time series forecasting. Its key innovation is timepoint-independent, where each time point has an independent convolution kernel, allowing each time point to have its independent model to capture relationships among variables. This approach effectively handles both positive and negative correlations and adapts to the evolving nature of variable relationships over time. Extensive experiments conducted on 12 real-world datasets demonstrate that TimeCNN consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models. Notably, our model achieves significant reductions in computational requirements (approximately 60.46%) and parameter count (about 57.50%), while delivering inference speeds 3 to 4 times faster than the benchmark iTransformer model
LocLLM: Exploiting Generalizable Human Keypoint Localization via Large Language Model
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:The capacity of existing human keypoint localization models is limited by keypoint priors provided by the training data. To alleviate this restriction and pursue more general model, this work studies keypoint localization from a different perspective by reasoning locations based on keypiont clues in text descriptions. We propose LocLLM, the first Large-Language Model (LLM) based keypoint localization model that takes images and text instructions as inputs and outputs the desired keypoint coordinates. LocLLM leverages the strong reasoning capability of LLM and clues of keypoint type, location, and relationship in textual descriptions for keypoint localization. To effectively tune LocLLM, we construct localization-based instruction conversations to connect keypoint description with corresponding coordinates in input image, and fine-tune the whole model in a parameter-efficient training pipeline. LocLLM shows remarkable performance on standard 2D/3D keypoint localization benchmarks. Moreover, incorporating language clues into the localization makes LocLLM show superior flexibility and generalizable capability in cross dataset keypoint localization, and even detecting novel type of keypoints unseen during training.
Unsupervised Person Re-identification via Multi-label Classification
Apr 20, 2020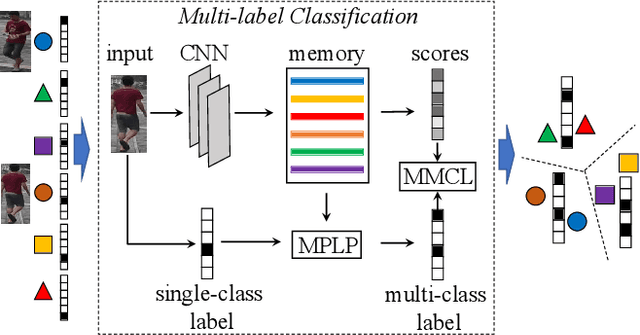
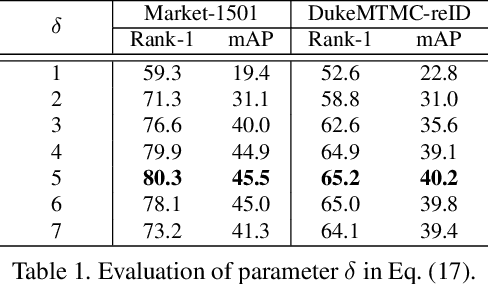

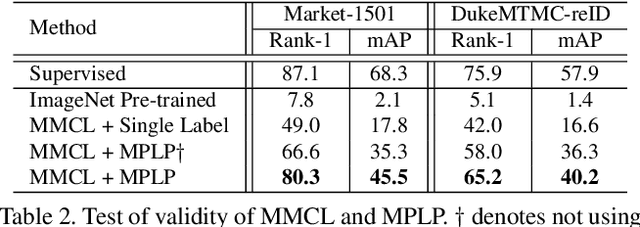
Abstract:The challenge of unsupervised person re-identification (ReID) lies in learning discriminative features without true labels. This paper formulates unsupervised person ReID as a multi-label classification task to progressively seek true labels. Our method starts by assigning each person image with a single-class label, then evolves to multi-label classification by leveraging the updated ReID model for label prediction. The label prediction comprises similarity computation and cycle consistency to ensure the quality of predicted labels. To boost the ReID model training efficiency in multi-label classification, we further propose the memory-based multi-label classification loss (MMCL). MMCL works with memory-based non-parametric classifier and integrates multi-label classification and single-label classification in a unified framework. Our label prediction and MMCL work iteratively and substantially boost the ReID performance. Experiments on several large-scale person ReID datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method in unsupervised person ReID. Our method also allows to use labeled person images in other domains. Under this transfer learning setting, our method also achieves state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge