Dmitry Demidov
Thinking Beyond Labels: Vocabulary-Free Fine-Grained Recognition using Reasoning-Augmented LMMs
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Vocabulary-free fine-grained image recognition aims to distinguish visually similar categories within a meta-class without a fixed, human-defined label set. Existing solutions for this problem are limited by either the usage of a large and rigid list of vocabularies or by the dependency on complex pipelines with fragile heuristics where errors propagate across stages. Meanwhile, the ability of recent large multi-modal models (LMMs) equipped with explicit or implicit reasoning to comprehend visual-language data, decompose problems, retrieve latent knowledge, and self-correct suggests a more principled and effective alternative. Building on these capabilities, we propose FiNDR (Fine-grained Name Discovery via Reasoning), the first reasoning-augmented LMM-based framework for vocabulary-free fine-grained recognition. The system operates in three automated steps: (i) a reasoning-enabled LMM generates descriptive candidate labels for each image; (ii) a vision-language model filters and ranks these candidates to form a coherent class set; and (iii) the verified names instantiate a lightweight multi-modal classifier used at inference time. Extensive experiments on popular fine-grained classification benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance under the vocabulary-free setting, with a significant relative margin of up to 18.8% over previous approaches. Remarkably, the proposed method surpasses zero-shot baselines that exploit pre-defined ground-truth names, challenging the assumption that human-curated vocabularies define an upper bound. Additionally, we show that carefully curated prompts enable open-source LMMs to match proprietary counterparts. These findings establish reasoning-augmented LMMs as an effective foundation for scalable, fully automated, open-world fine-grained visual recognition. The source code is available on github.com/demidovd98/FiNDR.
Beyond Simple Edits: Composed Video Retrieval with Dense Modifications
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:Composed video retrieval is a challenging task that strives to retrieve a target video based on a query video and a textual description detailing specific modifications. Standard retrieval frameworks typically struggle to handle the complexity of fine-grained compositional queries and variations in temporal understanding limiting their retrieval ability in the fine-grained setting. To address this issue, we introduce a novel dataset that captures both fine-grained and composed actions across diverse video segments, enabling more detailed compositional changes in retrieved video content. The proposed dataset, named Dense-WebVid-CoVR, consists of 1.6 million samples with dense modification text that is around seven times more than its existing counterpart. We further develop a new model that integrates visual and textual information through Cross-Attention (CA) fusion using grounded text encoder, enabling precise alignment between dense query modifications and target videos. The proposed model achieves state-of-the-art results surpassing existing methods on all metrics. Notably, it achieves 71.3\% Recall@1 in visual+text setting and outperforms the state-of-the-art by 3.4\%, highlighting its efficacy in terms of leveraging detailed video descriptions and dense modification texts. Our proposed dataset, code, and model are available at :https://github.com/OmkarThawakar/BSE-CoVR
TransResNet: Integrating the Strengths of ViTs and CNNs for High Resolution Medical Image Segmentation via Feature Grafting
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:High-resolution images are preferable in medical imaging domain as they significantly improve the diagnostic capability of the underlying method. In particular, high resolution helps substantially in improving automatic image segmentation. However, most of the existing deep learning-based techniques for medical image segmentation are optimized for input images having small spatial dimensions and perform poorly on high-resolution images. To address this shortcoming, we propose a parallel-in-branch architecture called TransResNet, which incorporates Transformer and CNN in a parallel manner to extract features from multi-resolution images independently. In TransResNet, we introduce Cross Grafting Module (CGM), which generates the grafted features, enriched in both global semantic and low-level spatial details, by combining the feature maps from Transformer and CNN branches through fusion and self-attention mechanism. Moreover, we use these grafted features in the decoding process, increasing the information flow for better prediction of the segmentation mask. Extensive experiments on ten datasets demonstrate that TransResNet achieves either state-of-the-art or competitive results on several segmentation tasks, including skin lesion, retinal vessel, and polyp segmentation. The source code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/Sharifmhamza/TransResNet.
Extract More from Less: Efficient Fine-Grained Visual Recognition in Low-Data Regimes
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:The emerging task of fine-grained image classification in low-data regimes assumes the presence of low inter-class variance and large intra-class variation along with a highly limited amount of training samples per class. However, traditional ways of separately dealing with fine-grained categorisation and extremely scarce data may be inefficient under both these harsh conditions presented together. In this paper, we present a novel framework, called AD-Net, aiming to enhance deep neural network performance on this challenge by leveraging the power of Augmentation and Distillation techniques. Specifically, our approach is designed to refine learned features through self-distillation on augmented samples, mitigating harmful overfitting. We conduct comprehensive experiments on popular fine-grained image classification benchmarks where our AD-Net demonstrates consistent improvement over traditional fine-tuning and state-of-the-art low-data techniques. Remarkably, with the smallest data available, our framework shows an outstanding relative accuracy increase of up to 45 % compared to standard ResNet-50 and up to 27 % compared to the closest SOTA runner-up. We emphasise that our approach is practically architecture-independent and adds zero extra cost at inference time. Additionally, we provide an extensive study on the impact of every framework's component, highlighting the importance of each in achieving optimal performance. Source code and trained models are publicly available at github.com/demidovd98/fgic_lowd.
Distilling Local Texture Features for Colorectal Tissue Classification in Low Data Regimes
Jan 02, 2024Abstract:Multi-class colorectal tissue classification is a challenging problem that is typically addressed in a setting, where it is assumed that ample amounts of training data is available. However, manual annotation of fine-grained colorectal tissue samples of multiple classes, especially the rare ones like stromal tumor and anal cancer is laborious and expensive. To address this, we propose a knowledge distillation-based approach, named KD-CTCNet, that effectively captures local texture information from few tissue samples, through a distillation loss, to improve the standard CNN features. The resulting enriched feature representation achieves improved classification performance specifically in low data regimes. Extensive experiments on two public datasets of colorectal tissues reveal the merits of the proposed contributions, with a consistent gain achieved over different approaches across low data settings. The code and models are publicly available on GitHub.
Salient Mask-Guided Vision Transformer for Fine-Grained Classification
May 11, 2023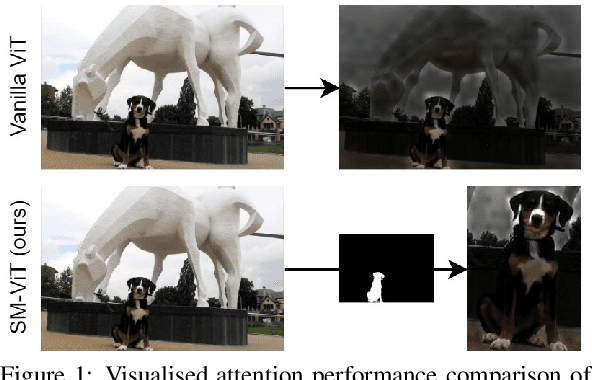
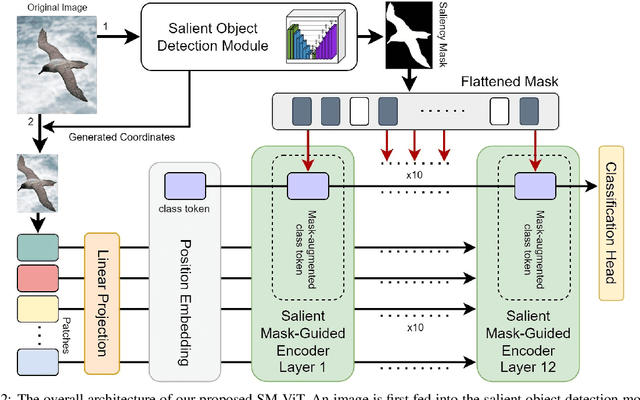
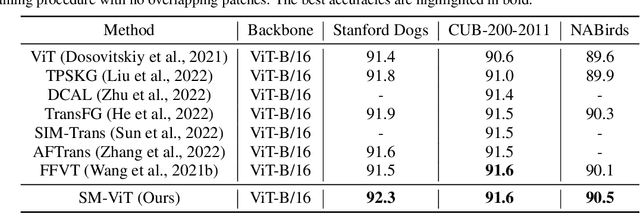
Abstract:Fine-grained visual classification (FGVC) is a challenging computer vision problem, where the task is to automatically recognise objects from subordinate categories. One of its main difficulties is capturing the most discriminative inter-class variances among visually similar classes. Recently, methods with Vision Transformer (ViT) have demonstrated noticeable achievements in FGVC, generally by employing the self-attention mechanism with additional resource-consuming techniques to distinguish potentially discriminative regions while disregarding the rest. However, such approaches may struggle to effectively focus on truly discriminative regions due to only relying on the inherent self-attention mechanism, resulting in the classification token likely aggregating global information from less-important background patches. Moreover, due to the immense lack of the datapoints, classifiers may fail to find the most helpful inter-class distinguishing features, since other unrelated but distinctive background regions may be falsely recognised as being valuable. To this end, we introduce a simple yet effective Salient Mask-Guided Vision Transformer (SM-ViT), where the discriminability of the standard ViT`s attention maps is boosted through salient masking of potentially discriminative foreground regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that with the standard training procedure our SM-ViT achieves state-of-the-art performance on popular FGVC benchmarks among existing ViT-based approaches while requiring fewer resources and lower input image resolution.
* Accepted by VISAPP 2023 (Best Student Paper Award)
Object Detection in Aerial Imagery
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:Object detection in natural images has achieved remarkable results over the years. However, a similar progress has not yet been observed in aerial object detection due to several challenges, such as high resolution images, instances scale variation, class imbalance etc. We show the performance of two-stage, one-stage and attention based object detectors on the iSAID dataset. Furthermore, we describe some modifications and analysis performed for different models - a) In two stage detector: introduced weighted attention based FPN, class balanced sampler and density prediction head. b) In one stage detector: used weighted focal loss and introduced FPN. c) In attention based detector: compare single,multi-scale attention and demonstrate effect of different backbones. Finally, we show a comparative study highlighting the pros and cons of different models in aerial imagery setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge