Dirk Neumann
Solving the Paint Shop Problem with Flexible Management of Multi-Lane Buffers Using Reinforcement Learning and Action Masking
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:In the paint shop problem, an unordered incoming sequence of cars assigned to different colors has to be reshuffled with the objective of minimizing the number of color changes. To reshuffle the incoming sequence, manufacturers can employ a first-in-first-out multi-lane buffer system allowing store and retrieve operations. So far, prior studies primarily focused on simple decision heuristics like greedy or simplified problem variants that do not allow full flexibility when performing store and retrieve operations. In this study, we propose a reinforcement learning approach to minimize color changes for the flexible problem variant, where store and retrieve operations can be performed in an arbitrary order. After proving that greedy retrieval is optimal, we incorporate this finding into the model using action masking. Our evaluation, based on 170 problem instances with 2-8 buffer lanes and 5-15 colors, shows that our approach reduces color changes compared to existing methods by considerable margins depending on the problem size. Furthermore, we demonstrate the robustness of our approach towards different buffer sizes and imbalanced color distributions.
Integrating Human Knowledge Through Action Masking in Reinforcement Learning for Operations Research
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) provides a powerful method to address problems in operations research. However, its real-world application often fails due to a lack of user acceptance and trust. A possible remedy is to provide managers with the possibility of altering the RL policy by incorporating human expert knowledge. In this study, we analyze the benefits and caveats of including human knowledge via action masking. While action masking has so far been used to exclude invalid actions, its ability to integrate human expertise remains underexplored. Human knowledge is often encapsulated in heuristics, which suggest reasonable, near-optimal actions in certain situations. Enforcing such actions should hence increase trust among the human workforce to rely on the model's decisions. Yet, a strict enforcement of heuristic actions may also restrict the policy from exploring superior actions, thereby leading to overall lower performance. We analyze the effects of action masking based on three problems with different characteristics, namely, paint shop scheduling, peak load management, and inventory management. Our findings demonstrate that incorporating human knowledge through action masking can achieve substantial improvements over policies trained without action masking. In addition, we find that action masking is crucial for learning effective policies in constrained action spaces, where certain actions can only be performed a limited number of times. Finally, we highlight the potential for suboptimal outcomes when action masks are overly restrictive.
Which linguistic cues make people fall for fake news? A comparison of cognitive and affective processing
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:Fake news on social media has large, negative implications for society. However, little is known about what linguistic cues make people fall for fake news and, hence, how to design effective countermeasures for social media. In this study, we seek to understand which linguistic cues make people fall for fake news. Linguistic cues (e.g., adverbs, personal pronouns, positive emotion words, negative emotion words) are important characteristics of any text and also affect how people process real vs. fake news. Specifically, we compare the role of linguistic cues across both cognitive processing (related to careful thinking) and affective processing (related to unconscious automatic evaluations). To this end, we performed a within-subject experiment where we collected neurophysiological measurements of 42 subjects while these read a sample of 40 real and fake news articles. During our experiment, we measured cognitive processing through eye fixations, and affective processing in situ through heart rate variability. We find that users engage more in cognitive processing for longer fake news articles, while affective processing is more pronounced for fake news written in analytic words. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work studying the role of linguistic cues in fake news processing. Altogether, our findings have important implications for designing online platforms that encourage users to engage in careful thinking and thus prevent them from falling for fake news.
An Enriched Automated PV Registry: Combining Image Recognition and 3D Building Data
Dec 07, 2020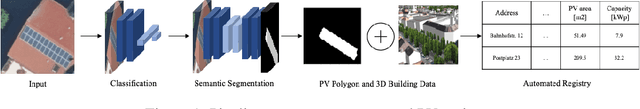
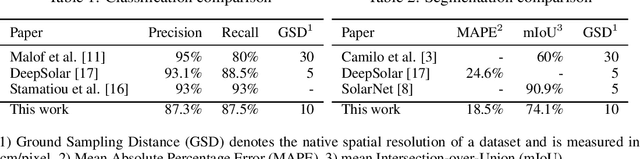
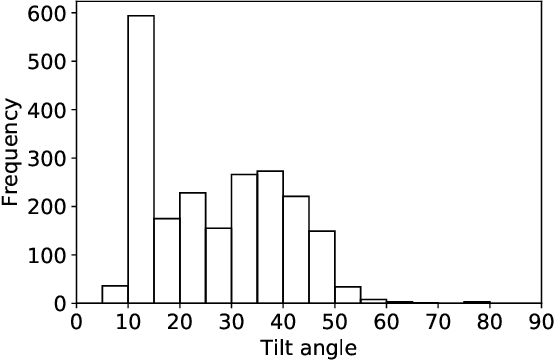
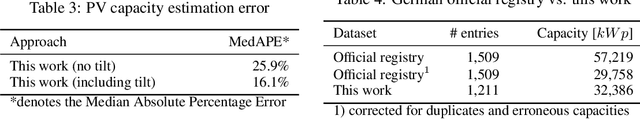
Abstract:While photovoltaic (PV) systems are installed at an unprecedented rate, reliable information on an installation level remains scarce. As a result, automatically created PV registries are a timely contribution to optimize grid planning and operations. This paper demonstrates how aerial imagery and three-dimensional building data can be combined to create an address-level PV registry, specifying area, tilt, and orientation angles. We demonstrate the benefits of this approach for PV capacity estimation. In addition, this work presents, for the first time, a comparison between automated and officially-created PV registries. Our results indicate that our enriched automated registry proves to be useful to validate, update, and complement official registries.
The Longer the Better? The Interplay Between Review Length and Line of Argumentation in Online Consumer Reviews
Sep 26, 2019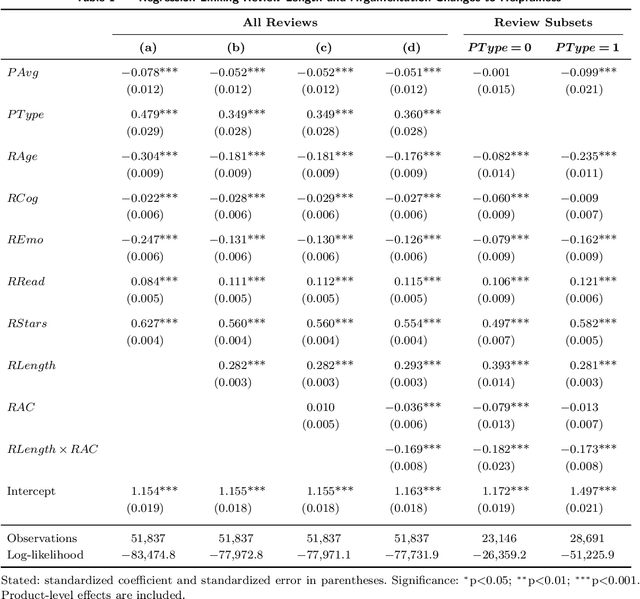
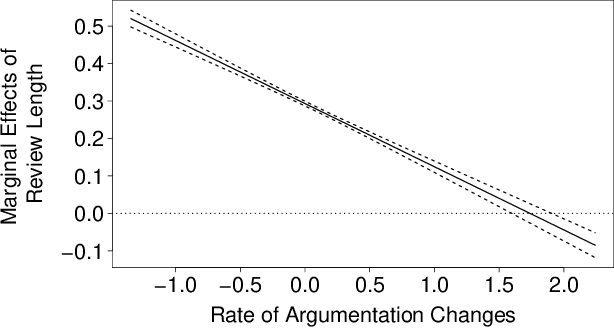
Abstract:Review helpfulness serves as focal point in understanding customers' purchase decision-making process on online retailer platforms. An overwhelming majority of previous works find longer reviews to be more helpful than short reviews. In this paper, we propose that longer reviews should not be assumed to be uniformly more helpful; instead, we argue that the effect depends on the line of argumentation in the review text. To test this idea, we use a large dataset of customer reviews from Amazon in combination with a state-of-the-art approach from natural language processing that allows us to study argumentation lines at sentence level. Our empirical analysis suggests that the frequency of argumentation changes moderates the effect of review length on helpfulness. Altogether, we disprove the prevailing narrative that longer reviews are uniformly perceived as more helpful. Our findings allow retailer platforms to improve their customer feedback systems and to feature more useful product reviews.
Sentence-Level Sentiment Analysis of Financial News Using Distributed Text Representations and Multi-Instance Learning
Dec 31, 2018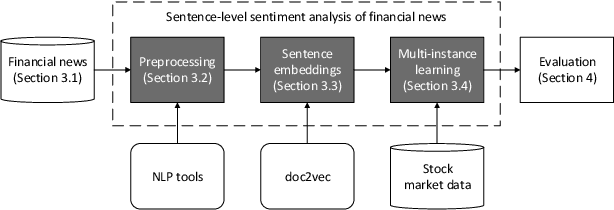
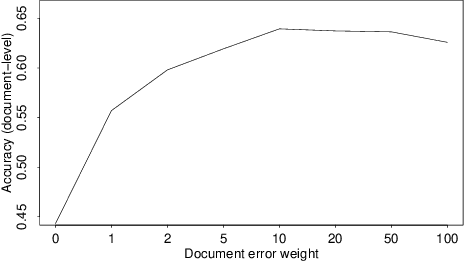
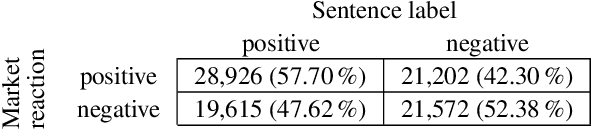

Abstract:Researchers and financial professionals require robust computerized tools that allow users to rapidly operationalize and assess the semantic textual content in financial news. However, existing methods commonly work at the document-level while deeper insights into the actual structure and the sentiment of individual sentences remain blurred. As a result, investors are required to apply the utmost attention and detailed, domain-specific knowledge in order to assess the information on a fine-grained basis. To facilitate this manual process, this paper proposes the use of distributed text representations and multi-instance learning to transfer information from the document-level to the sentence-level. Compared to alternative approaches, this method features superior predictive performance while preserving context and interpretability. Our analysis of a manually-labeled dataset yields a predictive accuracy of up to 69.90%, exceeding the performance of alternative approaches by at least 3.80 percentage points. Accordingly, this study not only benefits investors with regard to their financial decision-making, but also helps companies to communicate their messages as intended.
Understanding the Role of Two-Sided Argumentation in Online Consumer Reviews: A Language-Based Perspective
Oct 25, 2018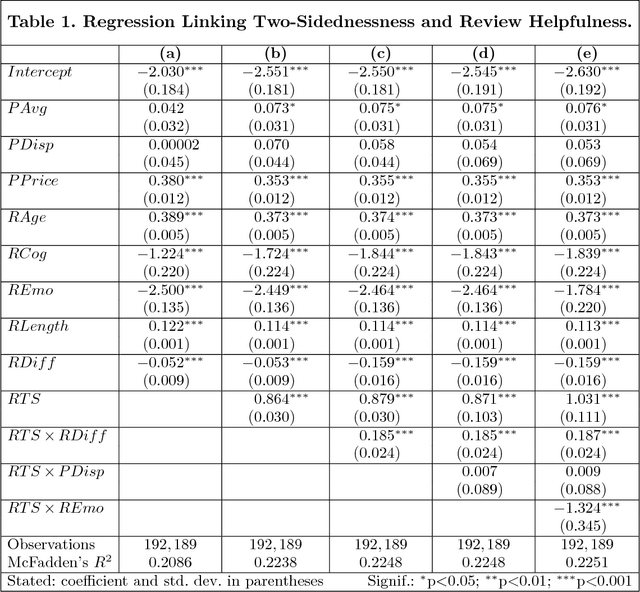
Abstract:This paper examines the effect of two-sided argumentation on the perceived helpfulness of online consumer reviews. In contrast to previous works, our analysis thereby sheds light on the reception of reviews from a language-based perspective. For this purpose, we propose an intriguing text analysis approach based on distributed text representations and multi-instance learning to operationalize the two-sidedness of argumentation in review texts. A subsequent empirical analysis using a large corpus of Amazon reviews suggests that two-sided argumentation in reviews significantly increases their helpfulness. We find this effect to be stronger for positive reviews than for negative reviews, whereas a higher degree of emotional language weakens the effect. Our findings have immediate implications for retailer platforms, which can utilize our results to optimize their customer feedback system and to present more useful product reviews.
Transfer Learning versus Multi-agent Learning regarding Distributed Decision-Making in Highway Traffic
Oct 19, 2018
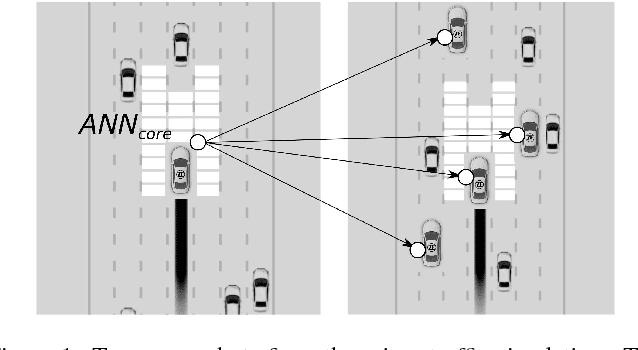
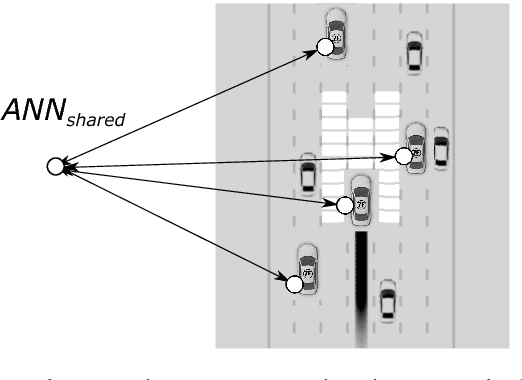
Abstract:Transportation and traffic are currently undergoing a rapid increase in terms of both scale and complexity. At the same time, an increasing share of traffic participants are being transformed into agents driven or supported by artificial intelligence resulting in mixed-intelligence traffic. This work explores the implications of distributed decision-making in mixed-intelligence traffic. The investigations are carried out on the basis of an online-simulated highway scenario, namely the MIT \emph{DeepTraffic} simulation. In the first step traffic agents are trained by means of a deep reinforcement learning approach, being deployed inside an elitist evolutionary algorithm for hyperparameter search. The resulting architectures and training parameters are then utilized in order to either train a single autonomous traffic agent and transfer the learned weights onto a multi-agent scenario or else to conduct multi-agent learning directly. Both learning strategies are evaluated on different ratios of mixed-intelligence traffic. The strategies are assessed according to the average speed of all agents driven by artificial intelligence. Traffic patterns that provoke a reduction in traffic flow are analyzed with respect to the different strategies.
* Proc. of the 10th International Workshop on Agents in Traffic and Transportation (ATT 2018), co-located with ECAI/IJCAI, AAMAS and ICML 2018 conferences (FAIM 2018)
Statistical Inferences for Polarity Identification in Natural Language
Apr 05, 2018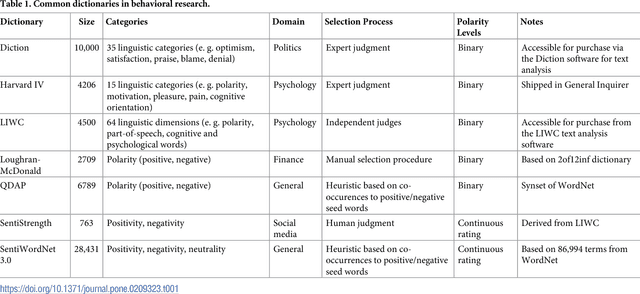
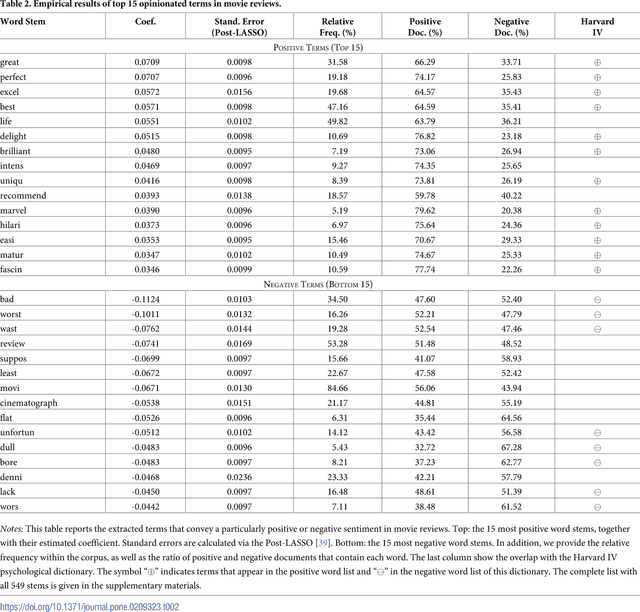
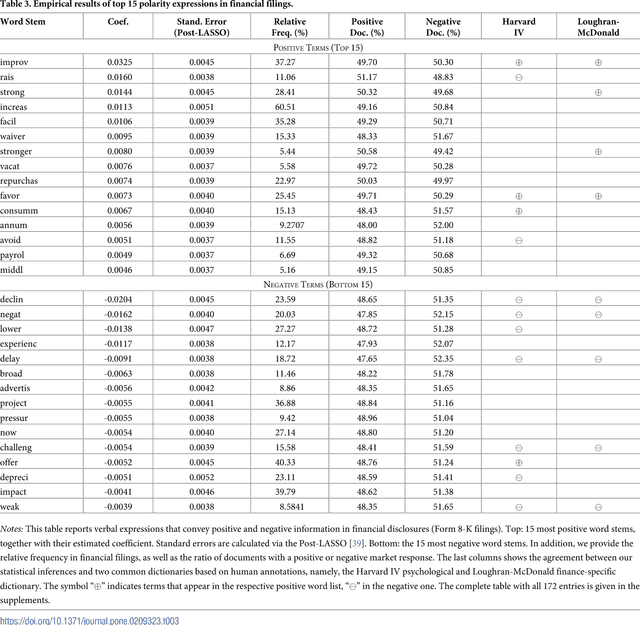
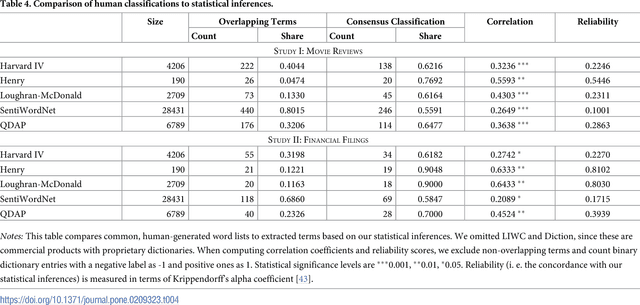
Abstract:Information forms the basis for all human behavior, including the ubiquitous decision-making that people constantly perform in their every day lives. It is thus the mission of researchers to understand how humans process information to reach decisions. In order to facilitate this task, this work proposes a novel method of studying the reception of granular expressions in natural language. The approach utilizes LASSO regularization as a statistical tool to extract decisive words from textual content and draw statistical inferences based on the correspondence between the occurrences of words and an exogenous response variable. Accordingly, the method immediately suggests significant implications for social sciences and Information Systems research: everyone can now identify text segments and word choices that are statistically relevant to authors or readers and, based on this knowledge, test hypotheses from behavioral research. We demonstrate the contribution of our method by examining how authors communicate subjective information through narrative materials. This allows us to answer the question of which words to choose when communicating negative information. On the other hand, we show that investors trade not only upon facts in financial disclosures but are distracted by filler words and non-informative language. Practitioners - for example those in the fields of investor communications or marketing - can exploit our insights to enhance their writings based on the true perception of word choice.
Understanding Negations in Information Processing: Learning from Replicating Human Behavior
Apr 18, 2017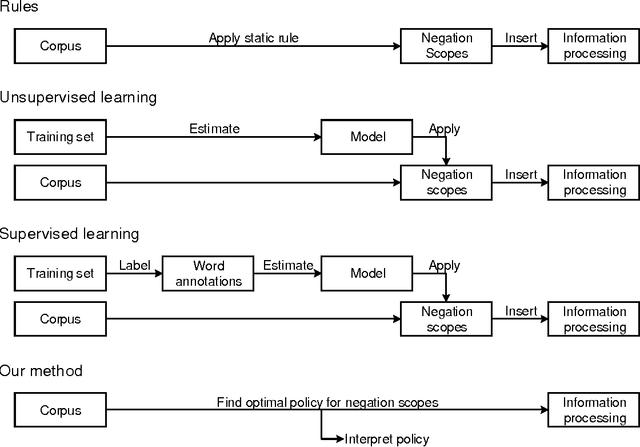
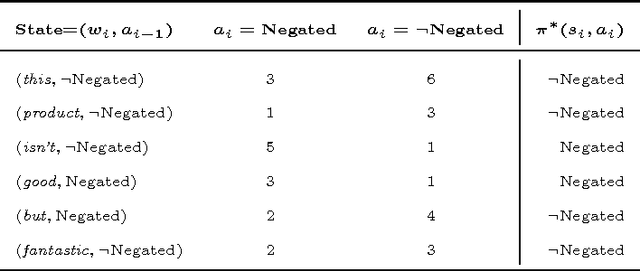
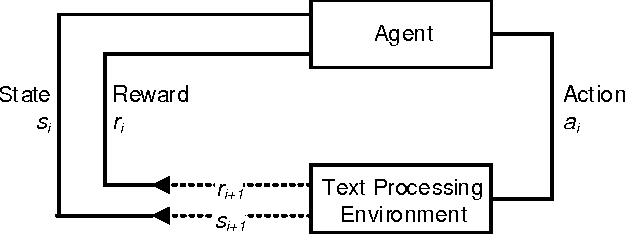
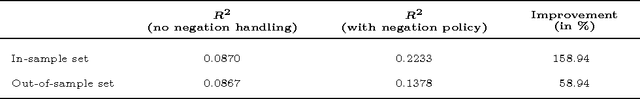
Abstract:Information systems experience an ever-growing volume of unstructured data, particularly in the form of textual materials. This represents a rich source of information from which one can create value for people, organizations and businesses. For instance, recommender systems can benefit from automatically understanding preferences based on user reviews or social media. However, it is difficult for computer programs to correctly infer meaning from narrative content. One major challenge is negations that invert the interpretation of words and sentences. As a remedy, this paper proposes a novel learning strategy to detect negations: we apply reinforcement learning to find a policy that replicates the human perception of negations based on an exogenous response, such as a user rating for reviews. Our method yields several benefits, as it eliminates the former need for expensive and subjective manual labeling in an intermediate stage. Moreover, the inferred policy can be used to derive statistical inferences and implications regarding how humans process and act on negations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge