Gunther Gust
Persistent Homology-induced Graph Ensembles for Time Series Regressions
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:The effectiveness of Spatio-temporal Graph Neural Networks (STGNNs) in time-series applications is often limited by their dependence on fixed, hand-crafted input graph structures. Motivated by insights from the Topological Data Analysis (TDA) paradigm, of which real-world data exhibits multi-scale patterns, we construct several graphs using Persistent Homology Filtration -- a mathematical framework describing the multiscale structural properties of data points. Then, we use the constructed graphs as an input to create an ensemble of Graph Neural Networks. The ensemble aggregates the signals from the individual learners via an attention-based routing mechanism, thus systematically encoding the inherent multiscale structures of data. Four different real-world experiments on seismic activity prediction and traffic forecasting (PEMS-BAY, METR-LA) demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms single-graph baselines while providing interpretable insights.
An Enriched Automated PV Registry: Combining Image Recognition and 3D Building Data
Dec 07, 2020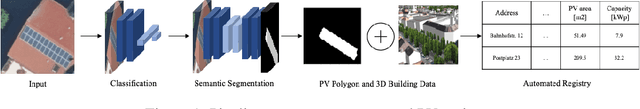
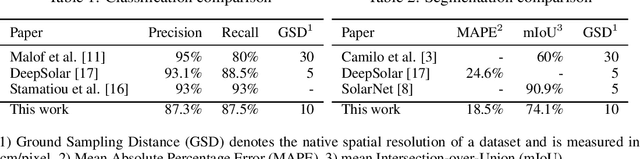
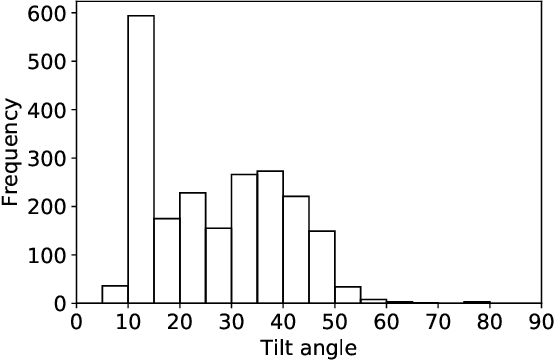
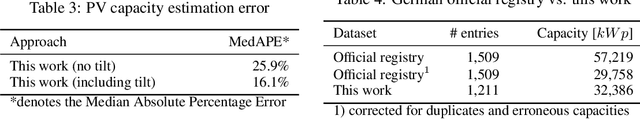
Abstract:While photovoltaic (PV) systems are installed at an unprecedented rate, reliable information on an installation level remains scarce. As a result, automatically created PV registries are a timely contribution to optimize grid planning and operations. This paper demonstrates how aerial imagery and three-dimensional building data can be combined to create an address-level PV registry, specifying area, tilt, and orientation angles. We demonstrate the benefits of this approach for PV capacity estimation. In addition, this work presents, for the first time, a comparison between automated and officially-created PV registries. Our results indicate that our enriched automated registry proves to be useful to validate, update, and complement official registries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge