Diansheng Guo
Deep Multi-View Channel-Wise Spatio-Temporal Network for Traffic Flow Prediction
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Accurately forecasting traffic flows is critically important to many real applications including public safety and intelligent transportation systems. The challenges of this problem include both the dynamic mobility patterns of the people and the complex spatial-temporal correlations of the urban traffic data. Meanwhile, most existing models ignore the diverse impacts of the various traffic observations (e.g. vehicle speed and road occupancy) on the traffic flow prediction, and different traffic observations can be considered as different channels of input features. We argue that the analysis in multiple-channel traffic observations might help to better address this problem. In this paper, we study the novel problem of multi-channel traffic flow prediction, and propose a deep \underline{M}ulti-\underline{V}iew \underline{C}hannel-wise \underline{S}patio-\underline{T}emporal \underline{Net}work (MVC-STNet) model to effectively address it. Specifically, we first construct the localized and globalized spatial graph where the multi-view fusion module is used to effectively extract the local and global spatial dependencies. Then LSTM is used to learn the temporal correlations. To effectively model the different impacts of various traffic observations on traffic flow prediction, a channel-wise graph convolutional network is also designed. Extensive experiments are conducted over the PEMS04 and PEMS08 datasets. The results demonstrate that the proposed MVC-STNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
MemDA: Forecasting Urban Time Series with Memory-based Drift Adaptation
Sep 25, 2023Abstract:Urban time series data forecasting featuring significant contributions to sustainable development is widely studied as an essential task of the smart city. However, with the dramatic and rapid changes in the world environment, the assumption that data obey Independent Identically Distribution is undermined by the subsequent changes in data distribution, known as concept drift, leading to weak replicability and transferability of the model over unseen data. To address the issue, previous approaches typically retrain the model, forcing it to fit the most recent observed data. However, retraining is problematic in that it leads to model lag, consumption of resources, and model re-invalidation, causing the drift problem to be not well solved in realistic scenarios. In this study, we propose a new urban time series prediction model for the concept drift problem, which encodes the drift by considering the periodicity in the data and makes on-the-fly adjustments to the model based on the drift using a meta-dynamic network. Experiments on real-world datasets show that our design significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods and can be well generalized to existing prediction backbones by reducing their sensitivity to distribution changes.
AttnMove: History Enhanced Trajectory Recovery via Attentional Network
Jan 03, 2021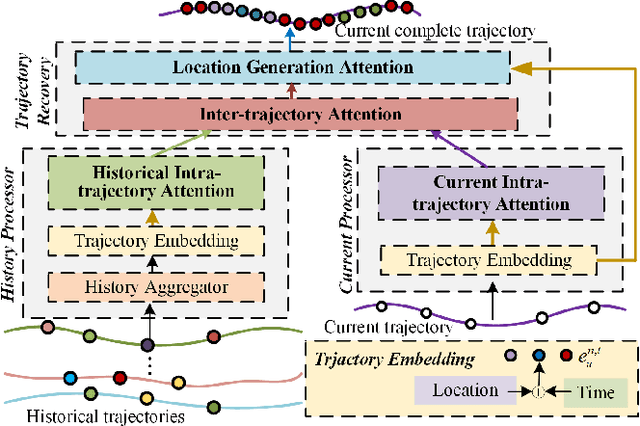
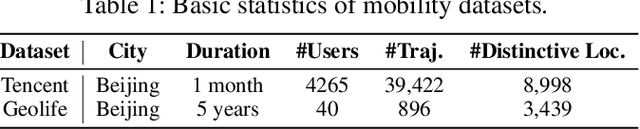
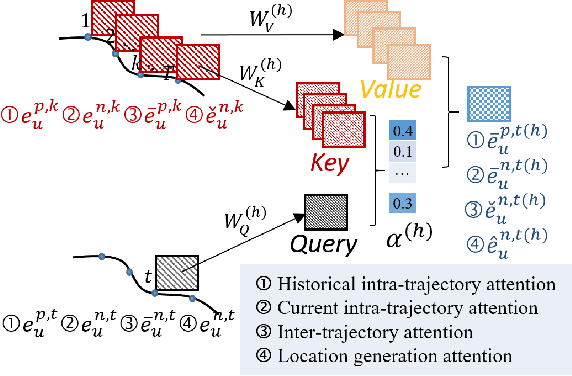
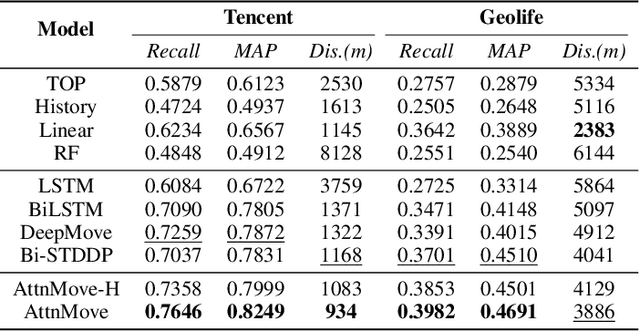
Abstract:A considerable amount of mobility data has been accumulated due to the proliferation of location-based service. Nevertheless, compared with mobility data from transportation systems like the GPS module in taxis, this kind of data is commonly sparse in terms of individual trajectories in the sense that users do not access mobile services and contribute their data all the time. Consequently, the sparsity inevitably weakens the practical value of the data even it has a high user penetration rate. To solve this problem, we propose a novel attentional neural network-based model, named AttnMove, to densify individual trajectories by recovering unobserved locations at a fine-grained spatial-temporal resolution. To tackle the challenges posed by sparsity, we design various intra- and inter- trajectory attention mechanisms to better model the mobility regularity of users and fully exploit the periodical pattern from long-term history. We evaluate our model on two real-world datasets, and extensive results demonstrate the performance gain compared with the state-of-the-art methods. This also shows that, by providing high-quality mobility data, our model can benefit a variety of mobility-oriented down-stream applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge