David Cameron
Real-Time Event Detection with Random Forests and Temporal Convolutional Networks for More Sustainable Petroleum Industry
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:The petroleum industry is crucial for modern society, but the production process is complex and risky. During the production, accidents or failures, resulting from undesired production events, can cause severe environmental and economic damage. Previous studies have investigated machine learning (ML) methods for undesired event detection. However, the prediction of event probability in real-time was insufficiently addressed, which is essential since it is important to undertake early intervention when an event is expected to happen. This paper proposes two ML approaches, random forests and temporal convolutional networks, to detect undesired events in real-time. Results show that our approaches can effectively classify event types and predict the probability of their appearance, addressing the challenges uncovered in previous studies and providing a more effective solution for failure event management during the production.
The Social Triad model of Human-Robot Interaction
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Despite the increasing interest in trust in human-robot interaction (HRI), there is still relatively little exploration of trust as a social construct in HRI. We propose that integration of useful models of human-human trust from psychology, highlight a potentially overlooked aspect of trust in HRI: a robot's apparent trustworthiness may indirectly relate to the user's relationship with, and opinion of, the individual or organisation deploying the robot. Our Social Triad for HRI model (User, Robot, Deployer), identifies areas for consideration in co-creating trustworthy robotics.
An Analysis of Classification Approaches for Hit Song Prediction using Engineered Metadata Features with Lyrics and Audio Features
Jan 31, 2023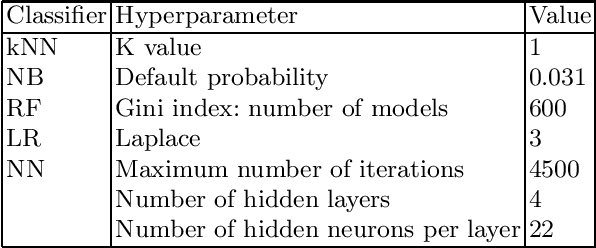

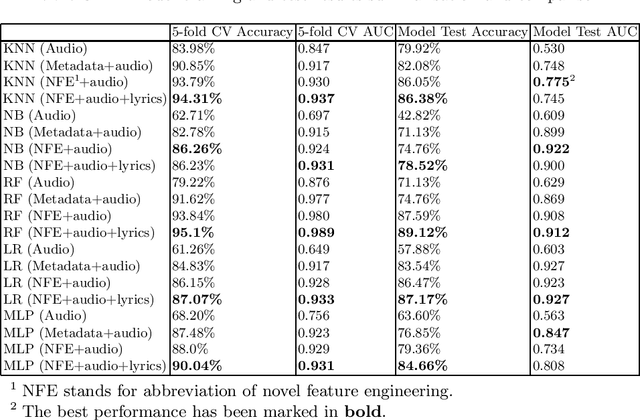
Abstract:Hit song prediction, one of the emerging fields in music information retrieval (MIR), remains a considerable challenge. Being able to understand what makes a given song a hit is clearly beneficial to the whole music industry. Previous approaches to hit song prediction have focused on using audio features of a record. This study aims to improve the prediction result of the top 10 hits among Billboard Hot 100 songs using more alternative metadata, including song audio features provided by Spotify, song lyrics, and novel metadata-based features (title topic, popularity continuity and genre class). Five machine learning approaches are applied, including: k-nearest neighbours, Naive Bayes, Random Forest, Logistic Regression and Multilayer Perceptron. Our results show that Random Forest (RF) and Logistic Regression (LR) with all features (including novel features, song audio features and lyrics features) outperforms other models, achieving 89.1% and 87.2% accuracy, and 0.91 and 0.93 AUC, respectively. Our findings also demonstrate the utility of our novel music metadata features, which contributed most to the models' discriminative performance.
When Robots Interact with Groups, Where Does the Trust Reside?
Aug 28, 2022Abstract:As robots are introduced to more and more complex scenarios, the issues of trust become more complex as various groups, peoples, and entities begin to interact with a deployed robot. This short paper explores a few scenarios in which the trust of the robot may come into conflict between one (or more) entities or groups that the robot is required to deal with. We also present a scenario concerning the idea of repairing trust through a possible apology.
User, Robot, Deployer: A New Model for Measuring Trust in HRI
Sep 02, 2021
Abstract:There is an increasing interest in considering, implementing, and measuring trust in human-robot interaction (HRI). Typically, this centres on influencing user trust within the framing of HRI as a dyadic interaction between robot and user. We propose this misses a key complexity: a robot's trustworthiness may also be contingent on the user's relationship with, and opinion of, the individual or organisation deploying the robot. Our new HRI triad model (User, Robot, Deployer), offers novel predictions for considering and measuring trust more completely.
Trust in robot-mediated health information
Dec 22, 2020
Abstract:This paper outlines a social robot platform for providing health information. In comparison with previous findings for accessing information online, the use of a social robot may affect which factors users consider important when evaluating the trustworthiness of health information provided.
Automatic recognition of child speech for robotic applications in noisy environments
Nov 08, 2016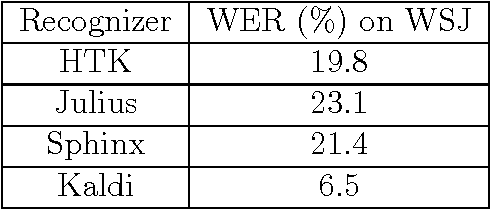



Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) allows a natural and intuitive interface for robotic educational applications for children. However there are a number of challenges to overcome to allow such an interface to operate robustly in realistic settings, including the intrinsic difficulties of recognising child speech and high levels of background noise often present in classrooms. As part of the EU EASEL project we have provided several contributions to address these challenges, implementing our own ASR module for use in robotics applications. We used the latest deep neural network algorithms which provide a leap in performance over the traditional GMM approach, and apply data augmentation methods to improve robustness to noise and speaker variation. We provide a close integration between the ASR module and the rest of the dialogue system, allowing the ASR to receive in real-time the language models relevant to the current section of the dialogue, greatly improving the accuracy. We integrated our ASR module into an interactive, multimodal system using a small humanoid robot to help children learn about exercise and energy. The system was installed at a public museum event as part of a research study where 320 children (aged 3 to 14) interacted with the robot, with our ASR achieving 90% accuracy for fluent and near-fluent speech.
Impact of robot responsiveness and adult involvement on children's social behaviours in human-robot interaction
Jun 20, 2016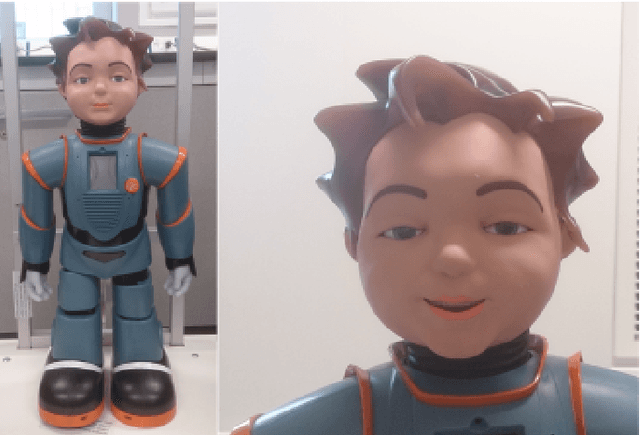
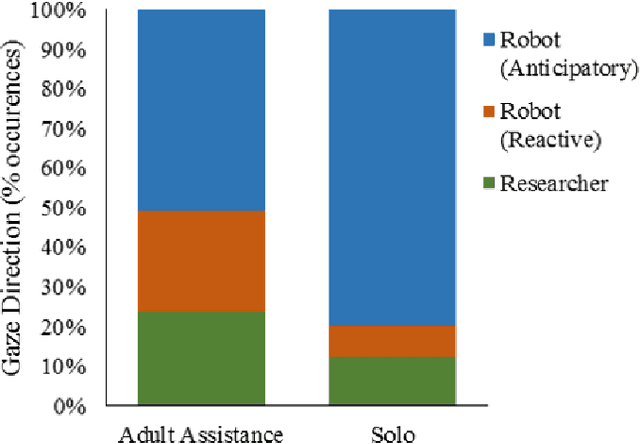
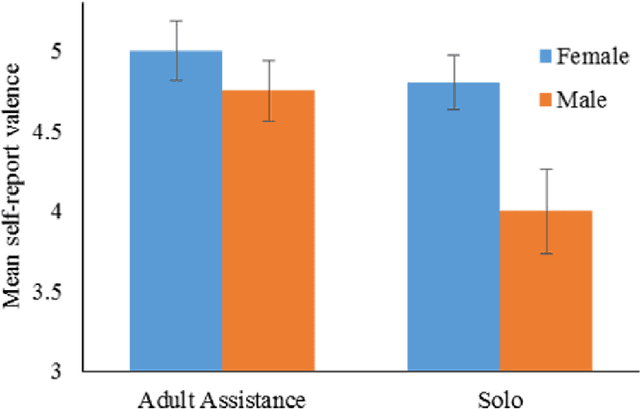
Abstract:A key challenge in developing engaging social robots is creating convincing, autonomous and responsive agents, which users perceive, and treat, as social beings. As a part of the collaborative project: Expressive Agents for Symbiotic Education and Learning (EASEL), this study examines the impact of autonomous response to children's speech, by the humanoid robot Zeno, on their interactions with it as a social entity. Results indicate that robot autonomy and adult assistance during HRI can substantially influence children's behaviour during interaction and their affect after. Children working with a fully-autonomous, responsive robot demonstrated greater physical activity following robot instruction than those working with a less responsive robot, which required adult assistance to interact with. During dialogue with the robot, children working with the fully-autonomous robot also looked towards the robot in anticipation of its vocalisations on more occasions. In contrast, a less responsive robot, requiring adult assistance to interact with, led to greater self-report positive affect and more occasions of children looking to the robot in response to its vocalisations. We discuss the broader implications of these findings in terms of anthropomorphism of social robots and in relation to the overall project strategy to further the understanding of how interactions with social robots could lead to task-appropriate symbiotic relationships.
Robot-stated limitations but not intentions promote user assistance
Jun 08, 2016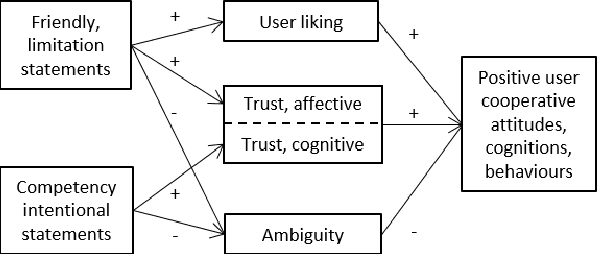
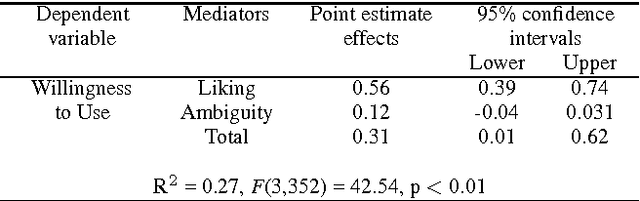

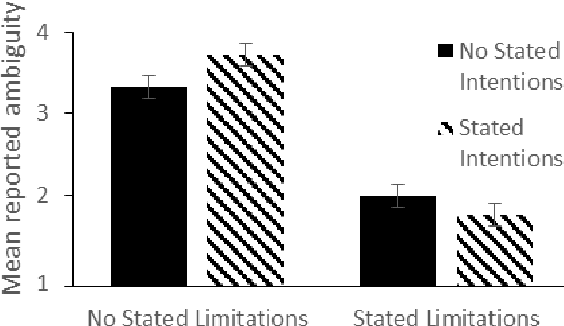
Abstract:Human-Robot-Interaction (HRI) research is typically built around the premise that the robot serves to assist a human in achieving a human-led goal or shared task. However, there are many circumstances during HRI in which a robot may need the assistance of a human in shared tasks or to achieve goals. We use the ROBO-GUIDE model as a case study, and insights from social psychology, to examine how a robot's personality can impact on user cooperation. A study of 364 participants indicates that individuals may prefer to use likable social robots ahead of those designed to appear more capable; this outcome reflects known social decisions in human interpersonal relationships. This work further demonstrates the value of social psychology in developing social robots and exploring HRI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge