Robot-stated limitations but not intentions promote user assistance
Paper and Code
Jun 08, 2016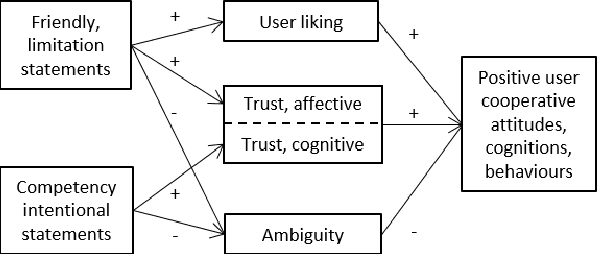
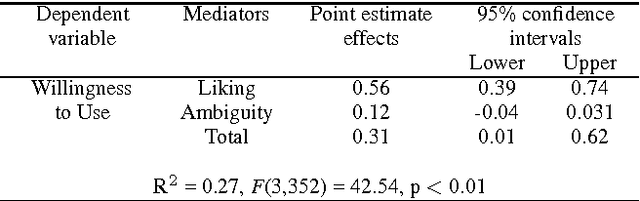

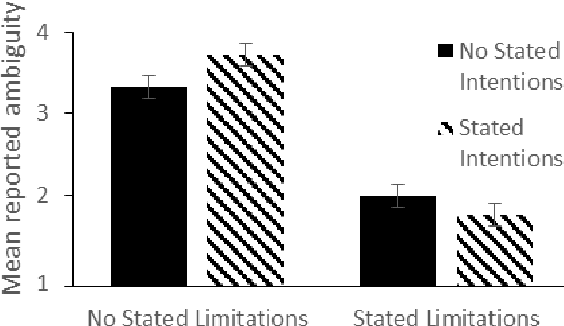
Human-Robot-Interaction (HRI) research is typically built around the premise that the robot serves to assist a human in achieving a human-led goal or shared task. However, there are many circumstances during HRI in which a robot may need the assistance of a human in shared tasks or to achieve goals. We use the ROBO-GUIDE model as a case study, and insights from social psychology, to examine how a robot's personality can impact on user cooperation. A study of 364 participants indicates that individuals may prefer to use likable social robots ahead of those designed to appear more capable; this outcome reflects known social decisions in human interpersonal relationships. This work further demonstrates the value of social psychology in developing social robots and exploring HRI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge