Daniel Whitehouse
Continuous Online Adaptation Driven by User Interaction for Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Interactive segmentation models use real-time user interactions, such as mouse clicks, as extra inputs to dynamically refine the model predictions. After model deployment, user corrections of model predictions could be used to adapt the model to the post-deployment data distribution, countering distribution-shift and enhancing reliability. Motivated by this, we introduce an online adaptation framework that enables an interactive segmentation model to continuously learn from user interaction and improve its performance on new data distributions, as it processes a sequence of test images. We introduce the Gaussian Point Loss function to train the model how to leverage user clicks, along with a two-stage online optimization method that adapts the model using the corrected predictions generated via user interactions. We demonstrate that this simple and therefore practical approach is very effective. Experiments on 5 fundus and 4 brain MRI databases demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches under various data distribution shifts, including segmentation of image modalities and pathologies not seen during training.
Feasibility of Federated Learning from Client Databases with Different Brain Diseases and MRI Modalities
Jun 17, 2024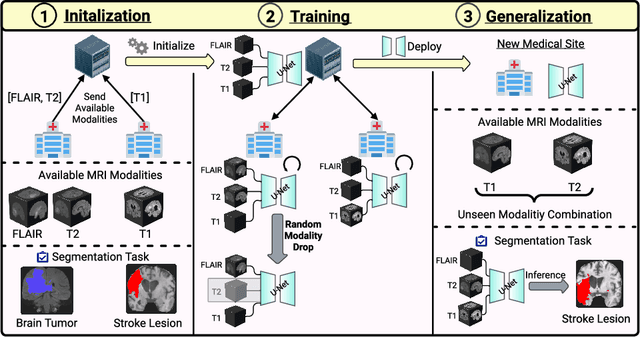
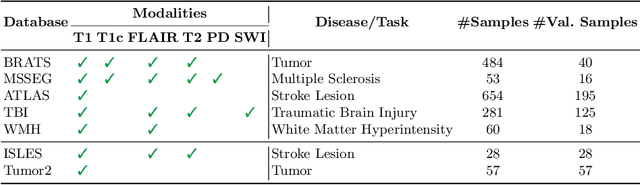
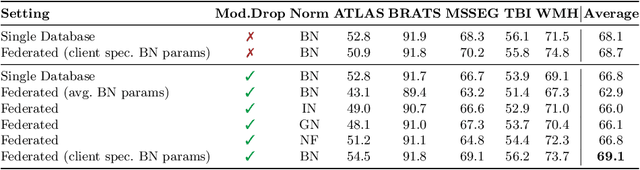
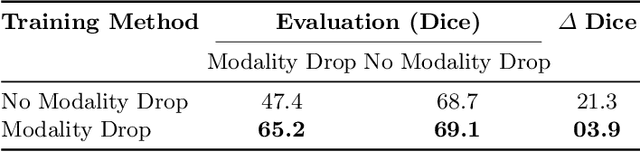
Abstract:Segmentation models for brain lesions in MRI are commonly developed for a specific disease and trained on data with a predefined set of MRI modalities. Each such model cannot segment the disease using data with a different set of MRI modalities, nor can it segment any other type of disease. Moreover, this training paradigm does not allow a model to benefit from learning from heterogeneous databases that may contain scans and segmentation labels for different types of brain pathologies and diverse sets of MRI modalities. Is it feasible to use Federated Learning (FL) for training a single model on client databases that contain scans and labels of different brain pathologies and diverse sets of MRI modalities? We demonstrate promising results by combining appropriate, simple, and practical modifications to the model and training strategy: Designing a model with input channels that cover the whole set of modalities available across clients, training with random modality drop, and exploring the effects of feature normalization methods. Evaluation on 7 brain MRI databases with 5 different diseases shows that such FL framework can train a single model that is shown to be very promising in segmenting all disease types seen during training. Importantly, it is able to segment these diseases in new databases that contain sets of modalities different from those in training clients. These results demonstrate, for the first time, feasibility and effectiveness of using FL to train a single segmentation model on decentralised data with diverse brain diseases and MRI modalities, a necessary step towards leveraging heterogeneous real-world databases. Code will be made available at: https://github.com/FelixWag/FL-MultiDisease-MRI
Feasibility and benefits of joint learning from MRI databases with different brain diseases and modalities for segmentation
May 28, 2024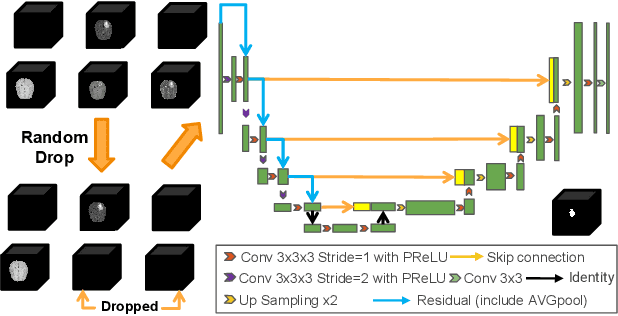
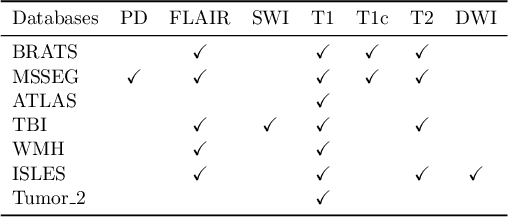
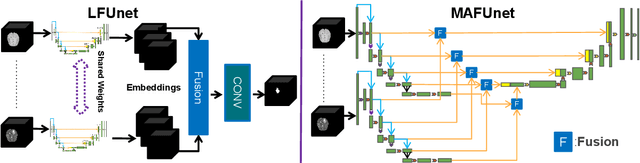

Abstract:Models for segmentation of brain lesions in multi-modal MRI are commonly trained for a specific pathology using a single database with a predefined set of MRI modalities, determined by a protocol for the specific disease. This work explores the following open questions: Is it feasible to train a model using multiple databases that contain varying sets of MRI modalities and annotations for different brain pathologies? Will this joint learning benefit performance on the sets of modalities and pathologies available during training? Will it enable analysis of new databases with different sets of modalities and pathologies? We develop and compare different methods and show that promising results can be achieved with appropriate, simple and practical alterations to the model and training framework. We experiment with 7 databases containing 5 types of brain pathologies and different sets of MRI modalities. Results demonstrate, for the first time, that joint training on multi-modal MRI databases with different brain pathologies and sets of modalities is feasible and offers practical benefits. It enables a single model to segment pathologies encountered during training in diverse sets of modalities, while facilitating segmentation of new types of pathologies such as via follow-up fine-tuning. The insights this study provides into the potential and limitations of this paradigm should prove useful for guiding future advances in the direction. Code and pretrained models: https://github.com/WenTXuL/MultiUnet
* Accepted to MIDL 2024
Transductive image segmentation: Self-training and effect of uncertainty estimation
Aug 02, 2021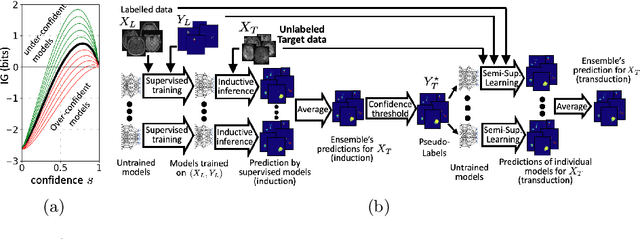
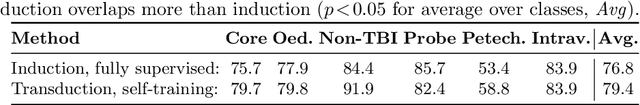
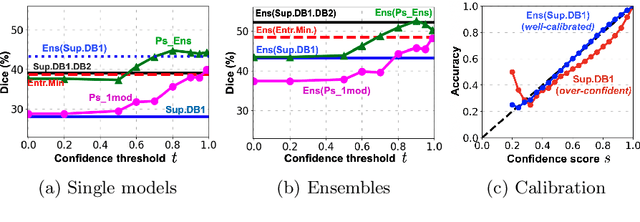
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) uses unlabeled data during training to learn better models. Previous studies on SSL for medical image segmentation focused mostly on improving model generalization to unseen data. In some applications, however, our primary interest is not generalization but to obtain optimal predictions on a specific unlabeled database that is fully available during model development. Examples include population studies for extracting imaging phenotypes. This work investigates an often overlooked aspect of SSL, transduction. It focuses on the quality of predictions made on the unlabeled data of interest when they are included for optimization during training, rather than improving generalization. We focus on the self-training framework and explore its potential for transduction. We analyze it through the lens of Information Gain and reveal that learning benefits from the use of calibrated or under-confident models. Our extensive experiments on a large MRI database for multi-class segmentation of traumatic brain lesions shows promising results when comparing transductive with inductive predictions. We believe this study will inspire further research on transductive learning, a well-suited paradigm for medical image analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge