Dávid Péter Kovács
Zero Shot Molecular Generation via Similarity Kernels
Feb 13, 2024



Abstract:Generative modelling aims to accelerate the discovery of novel chemicals by directly proposing structures with desirable properties. Recently, score-based, or diffusion, generative models have significantly outperformed previous approaches. Key to their success is the close relationship between the score and physical force, allowing the use of powerful equivariant neural networks. However, the behaviour of the learnt score is not yet well understood. Here, we analyse the score by training an energy-based diffusion model for molecular generation. We find that during the generation the score resembles a restorative potential initially and a quantum-mechanical force at the end. In between the two endpoints, it exhibits special properties that enable the building of large molecules. Using insights from the trained model, we present Similarity-based Molecular Generation (SiMGen), a new method for zero shot molecular generation. SiMGen combines a time-dependent similarity kernel with descriptors from a pretrained machine learning force field to generate molecules without any further training. Our approach allows full control over the molecular shape through point cloud priors and supports conditional generation. We also release an interactive web tool that allows users to generate structures with SiMGen online (https://zndraw.icp.uni-stuttgart.de).
Hyperactive Learning (HAL) for Data-Driven Interatomic Potentials
Oct 09, 2022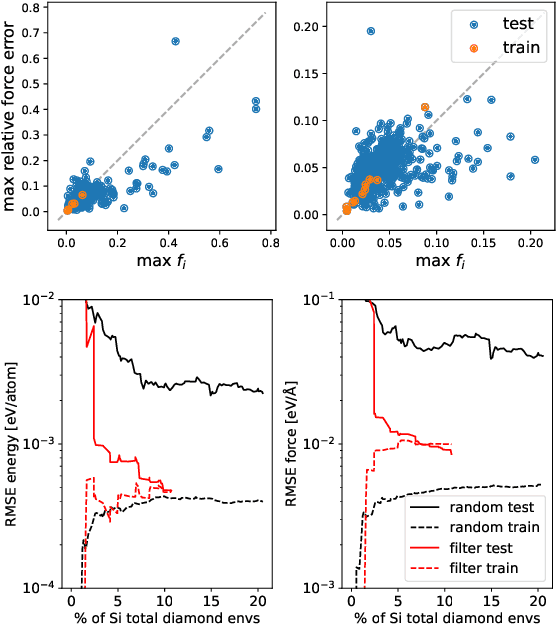
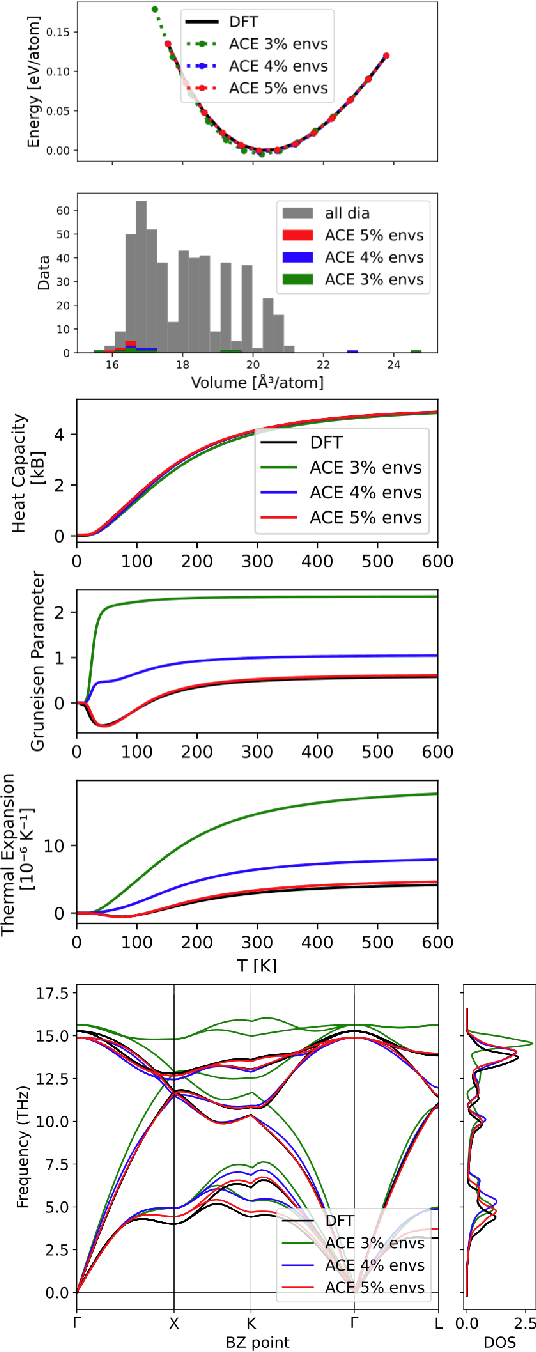
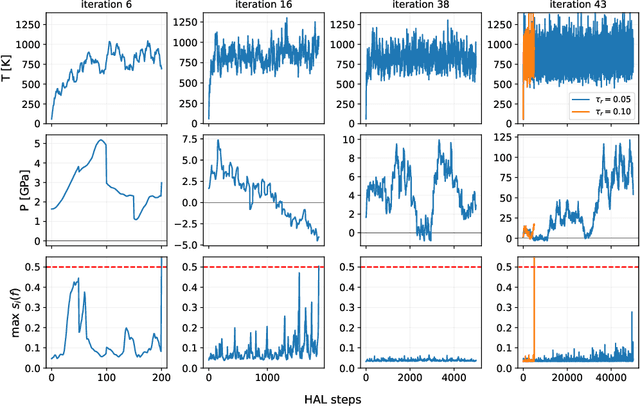
Abstract:Data-driven interatomic potentials have emerged as a powerful class of surrogate models for ab initio potential energy surfaces that are able to reliably predict macroscopic properties with experimental accuracy. In generating accurate and transferable potentials the most time-consuming and arguably most important task is generating the training set, which still requires significant expert user input. To accelerate this process, this work presents hyperactive learning (HAL), a framework for formulating an accelerated sampling algorithm specifically for the task of training database generation. The overarching idea is to start from a physically motivated sampler (e.g., molecular dynamics) and a biasing term that drives the system towards high uncertainty and thus to unseen training configurations. Building on this framework, general protocols for building training databases for alloys and polymers leveraging the HAL framework will be presented. For alloys, fast (< 100 microsecond/atom/cpu-core) ACE potentials for AlSi10 are created that able to predict the melting temperature with good accuracy by fitting to a minimal HAL-generated database containing 88 configurations (32 atoms each) in 17 seconds using 8 cpu threads. For polymers, a HAL database is built using ACE able to determine the density of a long polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymer formed of 200 monomer units with experimental accuracy by only fitting to small isolated PEG polymers with sizes ranging from 2 to 32.
MACE: Higher Order Equivariant Message Passing Neural Networks for Fast and Accurate Force Fields
Jun 15, 2022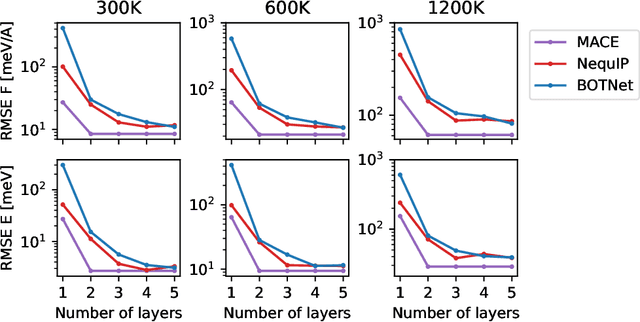
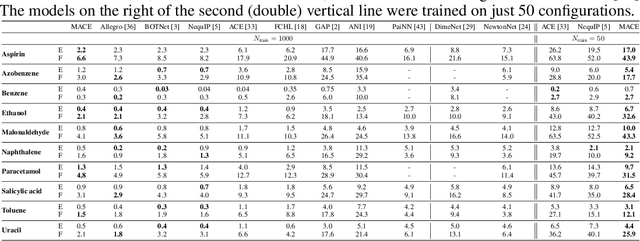

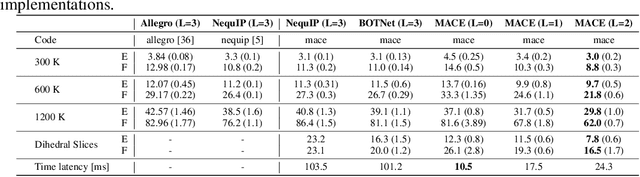
Abstract:Creating fast and accurate force fields is a long-standing challenge in computational chemistry and materials science. Recently, several equivariant message passing neural networks (MPNNs) have been shown to outperform models built using other approaches in terms of accuracy. However, most MPNNs suffer from high computational cost and poor scalability. We propose that these limitations arise because MPNNs only pass two-body messages leading to a direct relationship between the number of layers and the expressivity of the network. In this work, we introduce MACE, a new equivariant MPNN model that uses higher body order messages. In particular, we show that using four-body messages reduces the required number of message passing iterations to just \emph{two}, resulting in a fast and highly parallelizable model, reaching or exceeding state-of-the-art accuracy on the rMD17, 3BPA, and AcAc benchmark tasks. We also demonstrate that using higher order messages leads to an improved steepness of the learning curves.
The Design Space of E-Equivariant Atom-Centered Interatomic Potentials
May 13, 2022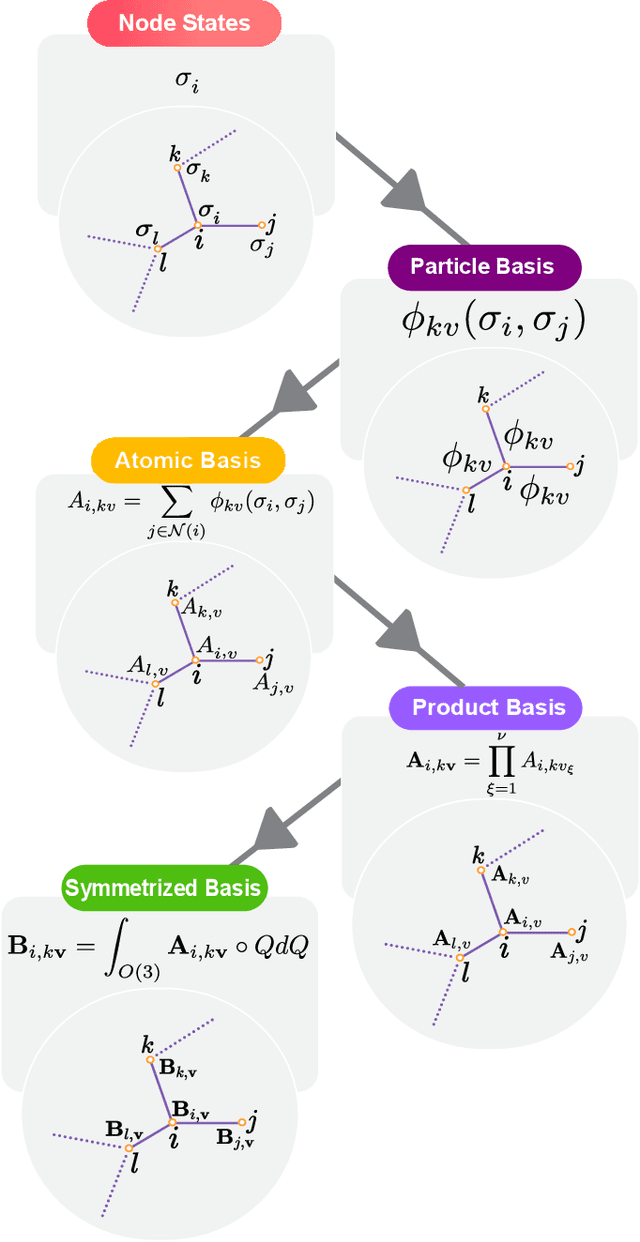
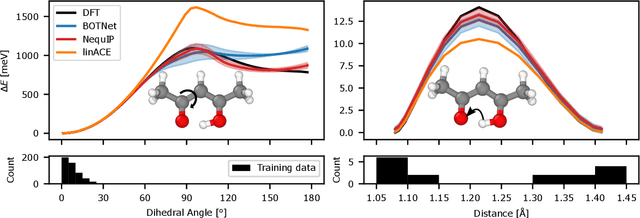
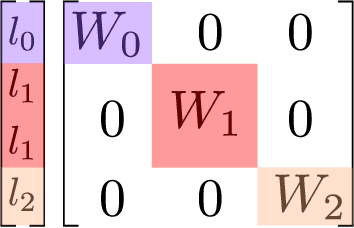
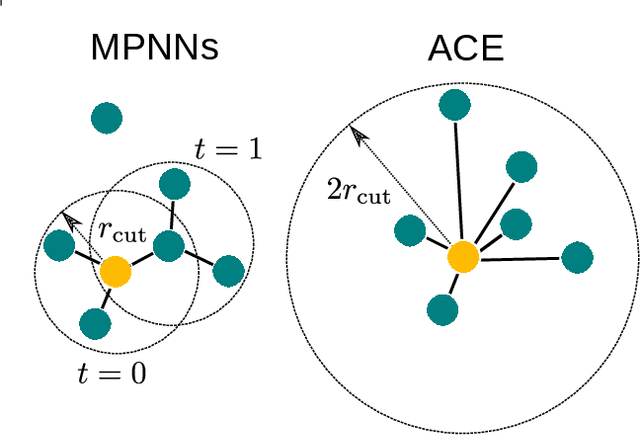
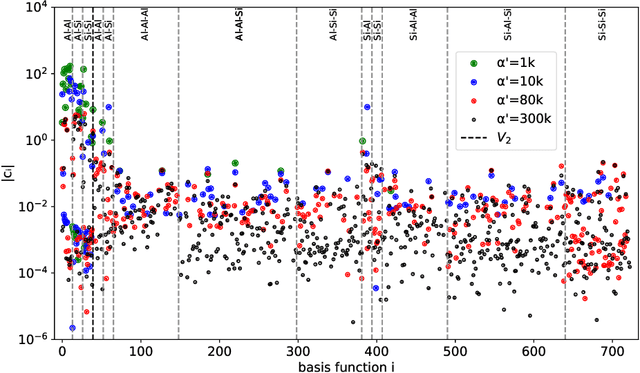
Abstract:The rapid progress of machine learning interatomic potentials over the past couple of years produced a number of new architectures. Particularly notable among these are the Atomic Cluster Expansion (ACE), which unified many of the earlier ideas around atom density-based descriptors, and Neural Equivariant Interatomic Potentials (NequIP), a message passing neural network with equivariant features that showed state of the art accuracy. In this work, we construct a mathematical framework that unifies these models: ACE is generalised so that it can be recast as one layer of a multi-layer architecture. From another point of view, the linearised version of NequIP is understood as a particular sparsification of a much larger polynomial model. Our framework also provides a practical tool for systematically probing different choices in the unified design space. We demonstrate this by an ablation study of NequIP via a set of experiments looking at in- and out-of-domain accuracy and smooth extrapolation very far from the training data, and shed some light on which design choices are critical for achieving high accuracy. Finally, we present BOTNet (Body-Ordered-Tensor-Network), a much-simplified version of NequIP, which has an interpretable architecture and maintains accuracy on benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge