Corrado Monti
Bias and Identifiability in the Bounded Confidence Model
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Opinion dynamics models such as the bounded confidence models (BCMs) describe how a population can reach consensus, fragmentation, or polarization, depending on a few parameters. Connecting such models to real-world data could help understanding such phenomena, testing model assumptions. To this end, estimation of model parameters is a key aspect, and maximum likelihood estimation provides a principled way to tackle it. Here, our goal is to outline the properties of statistical estimators of the two key BCM parameters: the confidence bound and the convergence rate. We find that their maximum likelihood estimators present different characteristics: the one for the confidence bound presents a small-sample bias but is consistent, while the estimator of the convergence rate shows a persistent bias. Moreover, the joint parameter estimation is affected by identifiability issues for specific regions of the parameter space, as several local maxima are present in the likelihood function. Our results show how the analysis of the likelihood function is a fruitful approach for better understanding the pitfalls and possibilities of estimating the parameters of opinion dynamics models, and more in general, agent-based models, and for offering formal guarantees for their calibration.
Learning Individual Behavior in Agent-Based Models with Graph Diffusion Networks
May 27, 2025
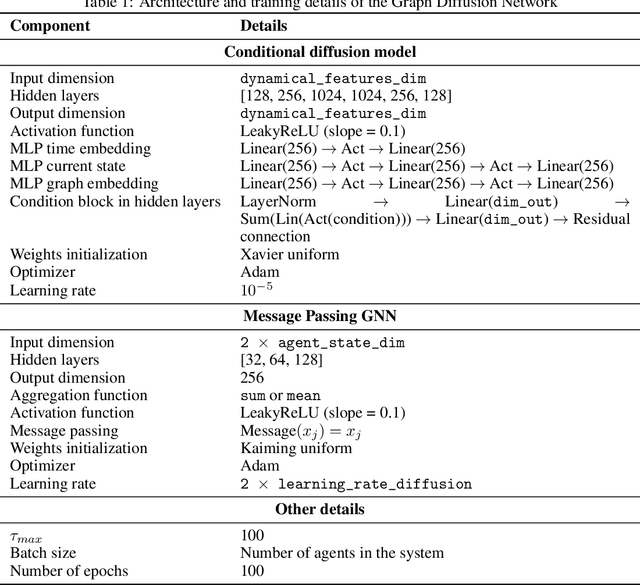

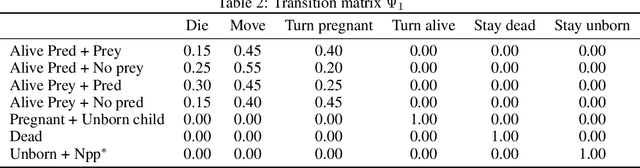
Abstract:Agent-Based Models (ABMs) are powerful tools for studying emergent properties in complex systems. In ABMs, agent behaviors are governed by local interactions and stochastic rules. However, these rules are, in general, non-differentiable, limiting the use of gradient-based methods for optimization, and thus integration with real-world data. We propose a novel framework to learn a differentiable surrogate of any ABM by observing its generated data. Our method combines diffusion models to capture behavioral stochasticity and graph neural networks to model agent interactions. Distinct from prior surrogate approaches, our method introduces a fundamental shift: rather than approximating system-level outputs, it models individual agent behavior directly, preserving the decentralized, bottom-up dynamics that define ABMs. We validate our approach on two ABMs (Schelling's segregation model and a Predator-Prey ecosystem) showing that it replicates individual-level patterns and accurately forecasts emergent dynamics beyond training. Our results demonstrate the potential of combining diffusion models and graph learning for data-driven ABM simulation.
Cascade-based Echo Chamber Detection
Aug 09, 2022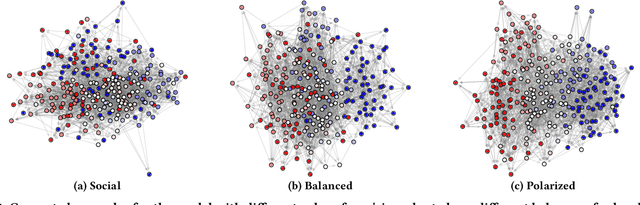
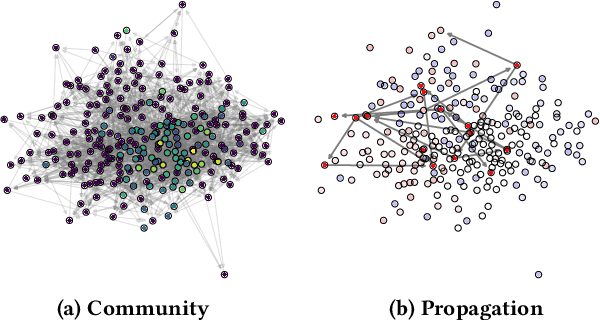

Abstract:Despite echo chambers in social media have been under considerable scrutiny, general models for their detection and analysis are missing. In this work, we aim to fill this gap by proposing a probabilistic generative model that explains social media footprints -- i.e., social network structure and propagations of information -- through a set of latent communities, characterized by a degree of echo-chamber behavior and by an opinion polarity. Specifically, echo chambers are modeled as communities that are permeable to pieces of information with similar ideological polarity, and impermeable to information of opposed leaning: this allows discriminating echo chambers from communities that lack a clear ideological alignment. To learn the model parameters we propose a scalable, stochastic adaptation of the Generalized Expectation Maximization algorithm, that optimizes the joint likelihood of observing social connections and information propagation. Experiments on synthetic data show that our algorithm is able to correctly reconstruct ground-truth latent communities with their degree of echo-chamber behavior and opinion polarity. Experiments on real-world data about polarized social and political debates, such as the Brexit referendum or the COVID-19 vaccine campaign, confirm the effectiveness of our proposal in detecting echo chambers. Finally, we show how our model can improve accuracy in auxiliary predictive tasks, such as stance detection and prediction of future propagations.
On learning agent-based models from data
May 10, 2022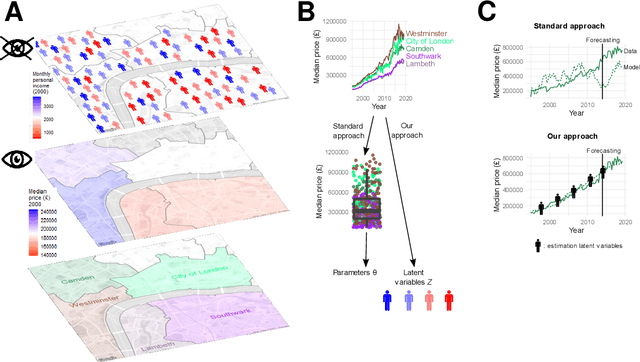
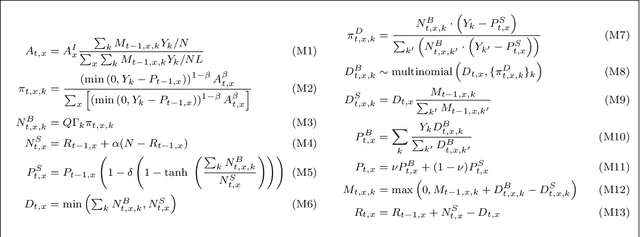
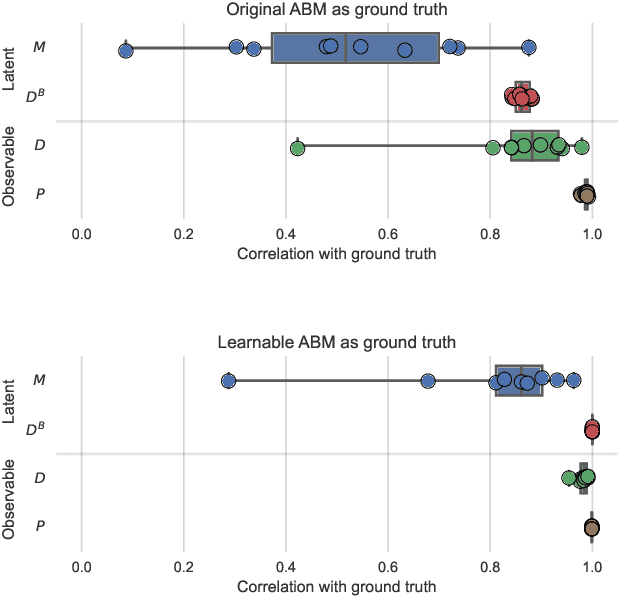
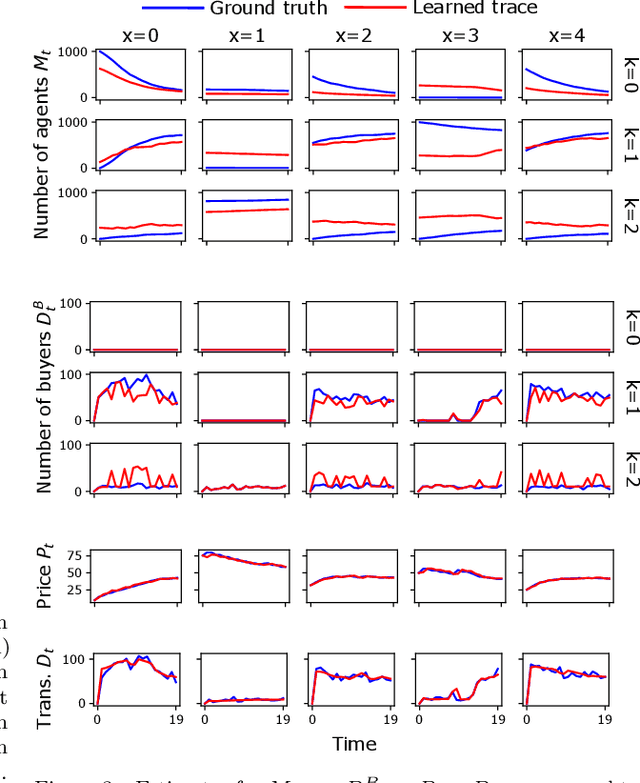
Abstract:Agent-Based Models (ABMs) are used in several fields to study the evolution of complex systems from micro-level assumptions. However, ABMs typically can not estimate agent-specific (or "micro") variables: this is a major limitation which prevents ABMs from harnessing micro-level data availability and which greatly limits their predictive power. In this paper, we propose a protocol to learn the latent micro-variables of an ABM from data. The first step of our protocol is to reduce an ABM to a probabilistic model, characterized by a computationally tractable likelihood. This reduction follows two general design principles: balance of stochasticity and data availability, and replacement of unobservable discrete choices with differentiable approximations. Then, our protocol proceeds by maximizing the likelihood of the latent variables via a gradient-based expectation maximization algorithm. We demonstrate our protocol by applying it to an ABM of the housing market, in which agents with different incomes bid higher prices to live in high-income neighborhoods. We demonstrate that the obtained model allows accurate estimates of the latent variables, while preserving the general behavior of the ABM. We also show that our estimates can be used for out-of-sample forecasting. Our protocol can be seen as an alternative to black-box data assimilation methods, that forces the modeler to lay bare the assumptions of the model, to think about the inferential process, and to spot potential identification problems.
Learning Ideological Embeddings from Information Cascades
Sep 28, 2021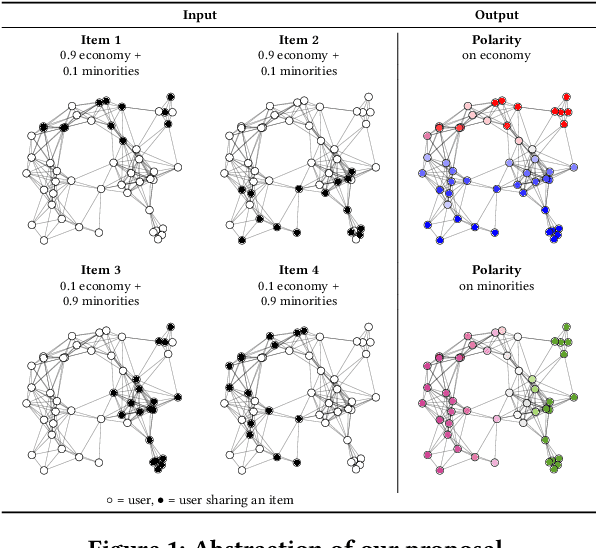

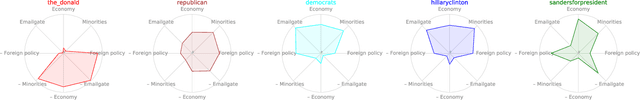
Abstract:Modeling information cascades in a social network through the lenses of the ideological leaning of its users can help understanding phenomena such as misinformation propagation and confirmation bias, and devising techniques for mitigating their toxic effects. In this paper we propose a stochastic model to learn the ideological leaning of each user in a multidimensional ideological space, by analyzing the way politically salient content propagates. In particular, our model assumes that information propagates from one user to another if both users are interested in the topic and ideologically aligned with each other. To infer the parameters of our model, we devise a gradient-based optimization procedure maximizing the likelihood of an observed set of information cascades. Our experiments on real-world political discussions on Twitter and Reddit confirm that our model is able to learn the political stance of the social media users in a multidimensional ideological space.
* Published in CIKM 2021
Learning Opinion Dynamics From Social Traces
Jun 02, 2020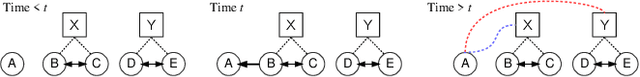
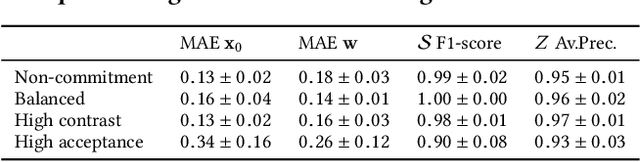
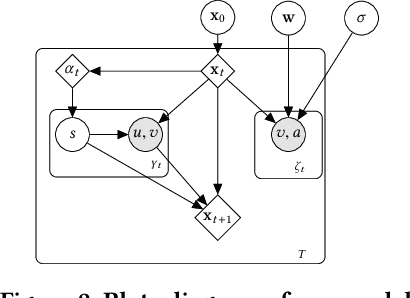
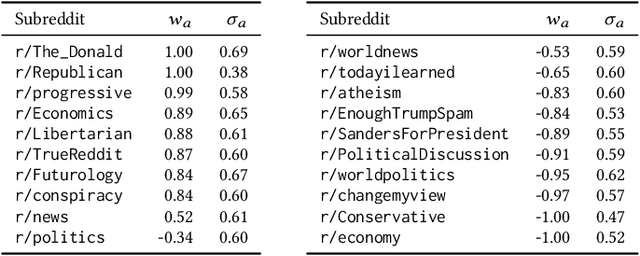
Abstract:Opinion dynamics - the research field dealing with how people's opinions form and evolve in a social context - traditionally uses agent-based models to validate the implications of sociological theories. These models encode the causal mechanism that drives the opinion formation process, and have the advantage of being easy to interpret. However, as they do not exploit the availability of data, their predictive power is limited. Moreover, parameter calibration and model selection are manual and difficult tasks. In this work we propose an inference mechanism for fitting a generative, agent-like model of opinion dynamics to real-world social traces. Given a set of observables (e.g., actions and interactions between agents), our model can recover the most-likely latent opinion trajectories that are compatible with the assumptions about the process dynamics. This type of model retains the benefits of agent-based ones (i.e., causal interpretation), while adding the ability to perform model selection and hypothesis testing on real data. We showcase our proposal by translating a classical agent-based model of opinion dynamics into its generative counterpart. We then design an inference algorithm based on online expectation maximization to learn the latent parameters of the model. Such algorithm can recover the latent opinion trajectories from traces generated by the classical agent-based model. In addition, it can identify the most likely set of macro parameters used to generate a data trace, thus allowing testing of sociological hypotheses. Finally, we apply our model to real-world data from Reddit to explore the long-standing question about the impact of backfire effect. Our results suggest a low prominence of the effect in Reddit's political conversation.
* Published at KDD2020
Estimating latent feature-feature interactions in large feature-rich graphs
Oct 07, 2017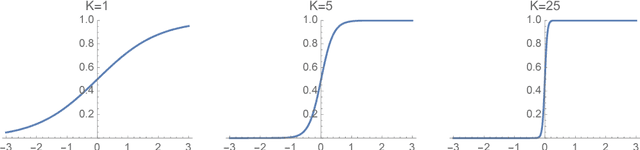
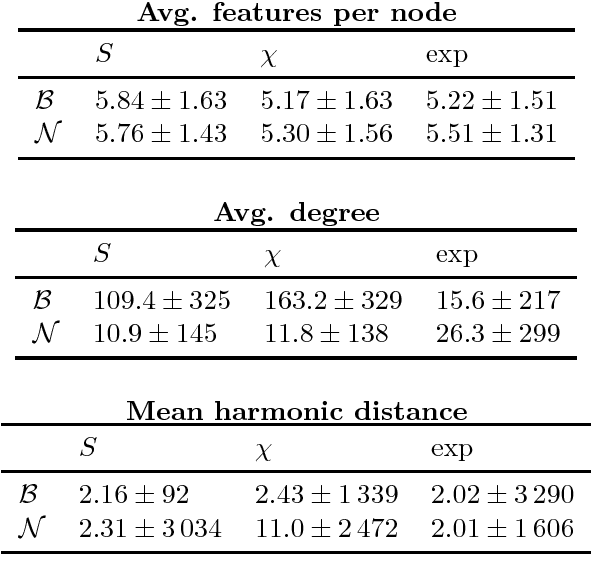
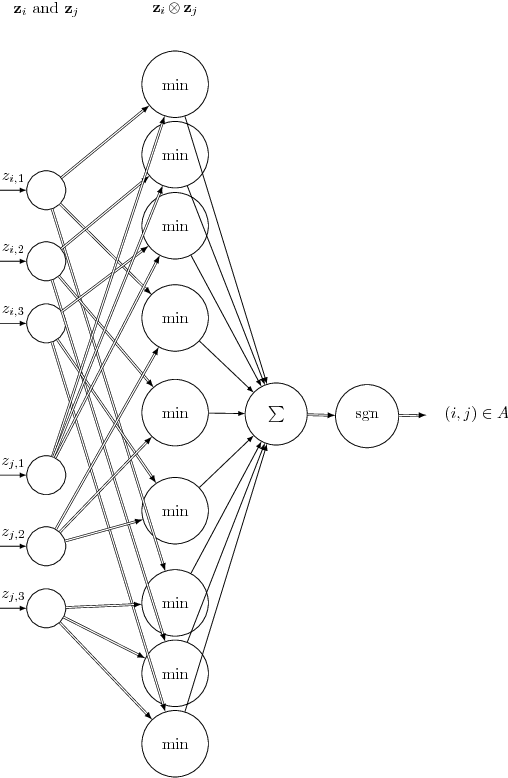
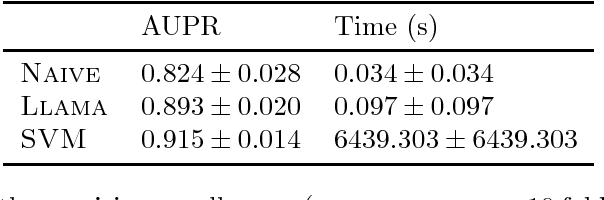
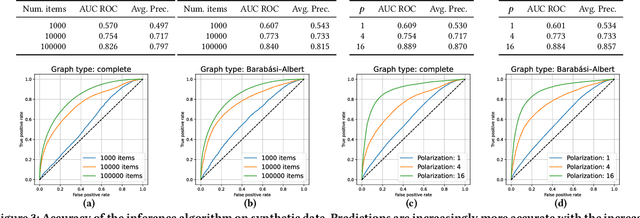
Abstract:Real-world complex networks describe connections between objects; in reality, those objects are often endowed with some kind of features. How does the presence or absence of such features interplay with the network link structure? Although the situation here described is truly ubiquitous, there is a limited body of research dealing with large graphs of this kind. Many previous works considered homophily as the only possible transmission mechanism translating node features into links. Other authors, instead, developed more sophisticated models, that are able to handle complex feature interactions, but are unfit to scale to very large networks. We expand on the MGJ model, where interactions between pairs of features can foster or discourage link formation. In this work, we will investigate how to estimate the latent feature-feature interactions in this model. We shall propose two solutions: the first one assumes feature independence and it is essentially based on Naive Bayes; the second one, which relaxes the independence assumption assumption, is based on perceptrons. In fact, we show it is possible to cast the model equation in order to see it as the prediction rule of a perceptron. We analyze how classical results for the perceptrons can be interpreted in this context; then, we define a fast and simple perceptron-like algorithm for this task, which can process $10^8$ links in minutes. We then compare these two techniques, first with synthetic datasets that follows our model, gaining evidence that the Naive independence assumptions are detrimental in practice. Secondly, we consider a real, large-scale citation network where each node (i.e., paper) can be described by different types of characteristics; there, our algorithm can assess how well each set of features can explain the links, and thus finding meaningful latent feature-feature interactions.
Political Disaffection: a case study on the Italian Twitter community
Feb 08, 2013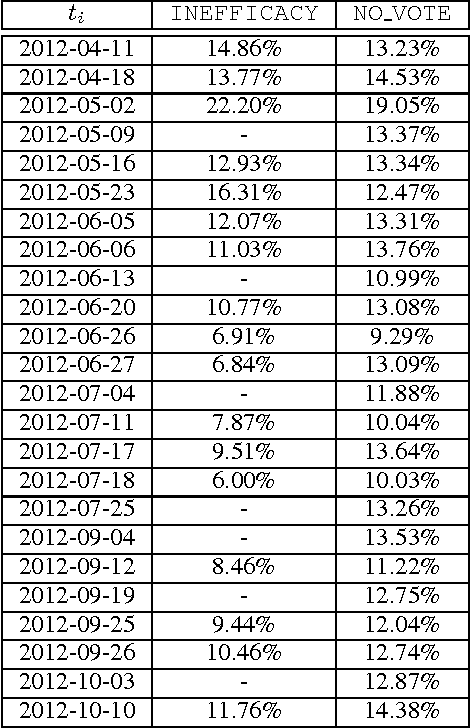
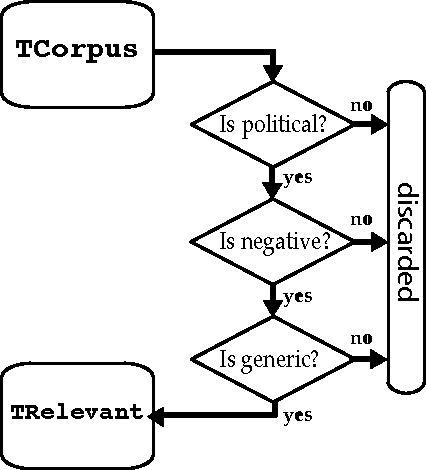
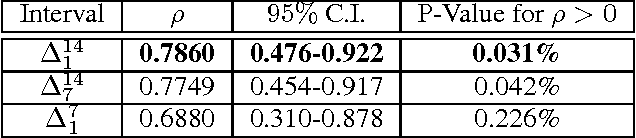

Abstract:In our work we analyse the political disaffection or "the subjective feeling of powerlessness, cynicism, and lack of confidence in the political process, politicians, and democratic institutions, but with no questioning of the political regime" by exploiting Twitter data through machine learning techniques. In order to validate the quality of the time-series generated by the Twitter data, we highlight the relations of these data with political disaffection as measured by means of public opinion surveys. Moreover, we show that important political news of Italian newspapers are often correlated with the highest peaks of the produced time-series.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge