Cindy M. Grimm
An autonomous robot for pruning modern, planar fruit trees
Jun 14, 2022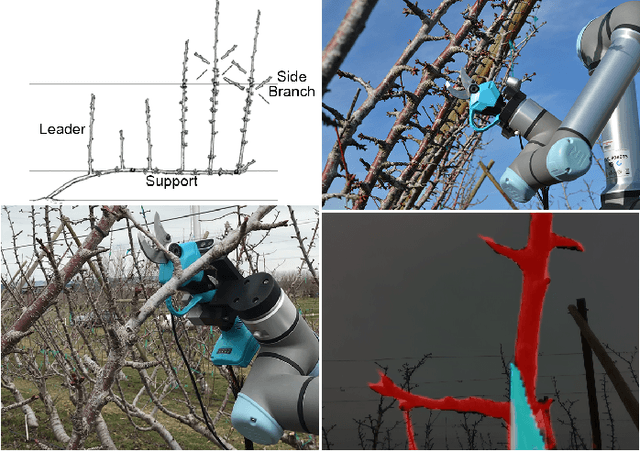
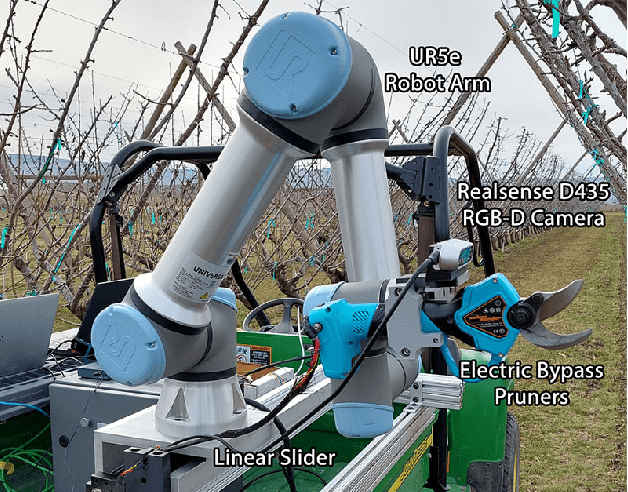


Abstract:Dormant pruning of fruit trees is an important task for maintaining tree health and ensuring high-quality fruit. Due to decreasing labor availability, pruning is a prime candidate for robotic automation. However, pruning also represents a uniquely difficult problem for robots, requiring robust systems for perception, pruning point determination, and manipulation that must operate under variable lighting conditions and in complex, highly unstructured environments. In this paper, we introduce a system for pruning sweet cherry trees (in a planar tree architecture called an upright fruiting offshoot configuration) that integrates various subsystems from our previous work on perception and manipulation. The resulting system is capable of operating completely autonomously and requires minimal control of the environment. We validate the performance of our system through field trials in a sweet cherry orchard, ultimately achieving a cutting success rate of 58%. Though not fully robust and requiring improvements in throughput, our system is the first to operate on fruit trees and represents a useful base platform to be improved in the future.
Framing Effects on Privacy Concerns about a Home Telepresence Robot
Nov 12, 2019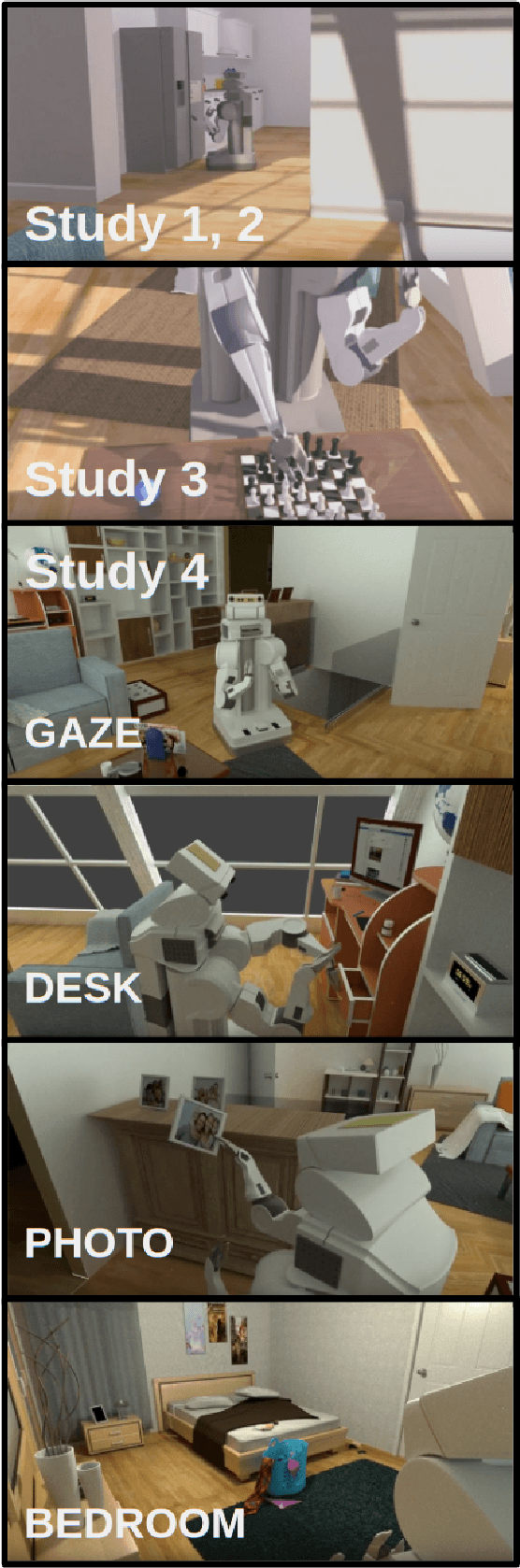
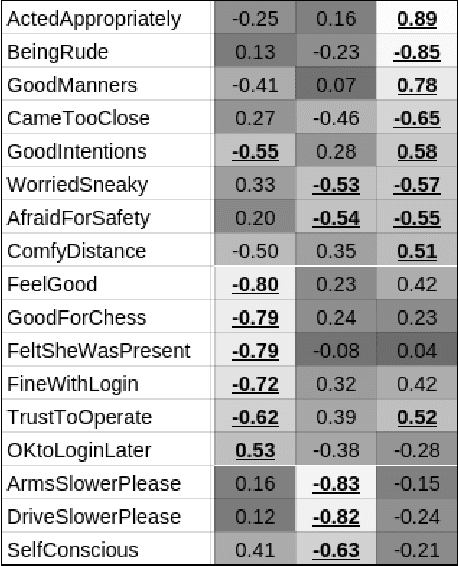
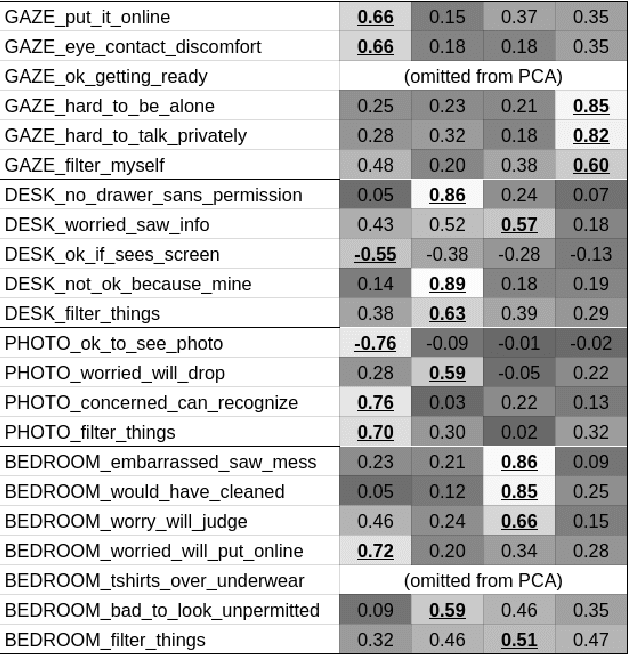
Abstract:Privacy-sensitive robotics is an emerging area of HRI research. Judgments about privacy would seem to be context-dependent, but none of the promising work on contextual "frames" has focused on privacy concerns. This work studies the impact of contextual "frames" on local users' privacy judgments in a home telepresence setting. Our methodology consists of using an online questionnaire to collect responses to animated videos of a telepresence robot after framing people with an introductory paragraph. The results of four studies indicate a large effect of manipulating the robot operator's identity between a stranger and a close confidante. It also appears that this framing effect persists throughout several videos. These findings serve to caution HRI researchers that a change in frame could cause their results to fail to replicate or generalize. We also recommend that robots be designed to encourage or discourage certain frames.
A Taxonomy of Privacy Constructs for Privacy-Sensitive Robotics
Jan 03, 2017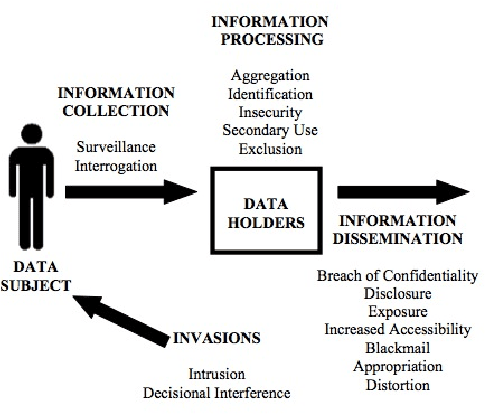
Abstract:The introduction of robots into our society will also introduce new concerns about personal privacy. In order to study these concerns, we must do human-subject experiments that involve measuring privacy-relevant constructs. This paper presents a taxonomy of privacy constructs based on a review of the privacy literature. Future work in operationalizing privacy constructs for HRI studies is also discussed.
Human-Planned Robotic Grasp Ranges: Capture and Validation
Jul 12, 2016
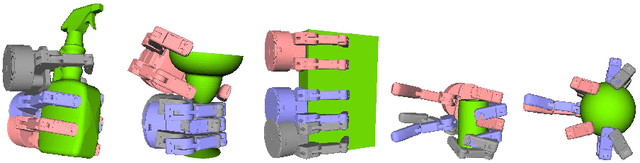

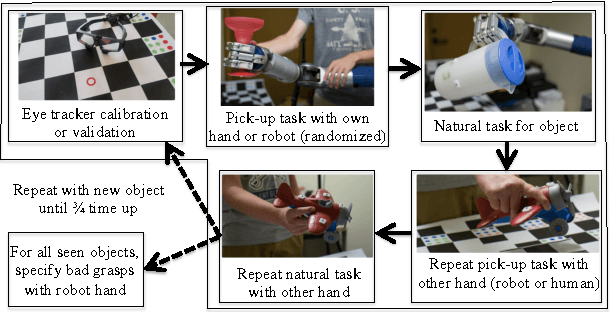
Abstract:Leveraging human grasping skills to teach a robot to perform a manipulation task is appealing, but there are several limitations to this approach: time-inefficient data capture procedures, limited generalization of the data to other grasps and objects, and inability to use that data to learn more about how humans perform and evaluate grasps. This paper presents a data capture protocol that partially addresses these deficiencies by asking participants to specify ranges over which a grasp is valid. The protocol is verified both qualitatively through online survey questions (where 95.38% of within-range grasps are identified correctly with the nearest extreme grasp) and quantitatively by showing that there is small variation in grasps ranges from different participants as measured by joint angles, contact points, and position. We demonstrate that these grasp ranges are valid through testing on a physical robot (93.75% of grasps interpolated from grasp ranges are successful).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge