Chulhong Min
DEX: Data Channel Extension for Efficient CNN Inference on Tiny AI Accelerators
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Tiny machine learning (TinyML) aims to run ML models on small devices and is increasingly favored for its enhanced privacy, reduced latency, and low cost. Recently, the advent of tiny AI accelerators has revolutionized the TinyML field by significantly enhancing hardware processing power. These accelerators, equipped with multiple parallel processors and dedicated per-processor memory instances, offer substantial performance improvements over traditional microcontroller units (MCUs). However, their limited data memory often necessitates downsampling input images, resulting in accuracy degradation. To address this challenge, we propose Data channel EXtension (DEX), a novel approach for efficient CNN execution on tiny AI accelerators. DEX incorporates additional spatial information from original images into input images through patch-wise even sampling and channel-wise stacking, effectively extending data across input channels. By leveraging underutilized processors and data memory for channel extension, DEX facilitates parallel execution without increasing inference latency. Our evaluation with four models and four datasets on tiny AI accelerators demonstrates that this simple idea improves accuracy on average by 3.5%p while keeping the inference latency the same on the AI accelerator. The source code is available at https://github.com/Nokia-Bell-Labs/data-channel-extension.
Time-bound Contextual Bio-ID Generation for Minimalist Wearables
Mar 01, 2024



Abstract:As wearable devices become increasingly miniaturized and powerful, a new opportunity arises for instant and dynamic device-to-device collaboration and human-to-device interaction. However, this progress presents a unique challenge: these minimalist wearables lack inherent mechanisms for real-time authentication, posing significant risks to data privacy and overall security. To address this, we introduce Proteus that realizes an innovative concept of time-bound contextual bio-IDs, which are generated from on-device sensor data and embedded into a common latent space. These bio-IDs act as a time-bound unique user identifier that can be used to identify the wearer in a certain context. Proteus enables dynamic and contextual device collaboration as well as robust human-to-device interaction. Our evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, particularly in the context of minimalist wearables.
Enabling Cross-Camera Collaboration for Video Analytics on Distributed Smart Cameras
Jan 27, 2024



Abstract:Overlapping cameras offer exciting opportunities to view a scene from different angles, allowing for more advanced, comprehensive and robust analysis. However, existing visual analytics systems for multi-camera streams are mostly limited to (i) per-camera processing and aggregation and (ii) workload-agnostic centralized processing architectures. In this paper, we present Argus, a distributed video analytics system with cross-camera collaboration on smart cameras. We identify multi-camera, multi-target tracking as the primary task of multi-camera video analytics and develop a novel technique that avoids redundant, processing-heavy identification tasks by leveraging object-wise spatio-temporal association in the overlapping fields of view across multiple cameras. We further develop a set of techniques to perform these operations across distributed cameras without cloud support at low latency by (i) dynamically ordering the camera and object inspection sequence and (ii) flexibly distributing the workload across smart cameras, taking into account network transmission and heterogeneous computational capacities. Evaluation of three real-world overlapping camera datasets with two Nvidia Jetson devices shows that Argus reduces the number of object identifications and end-to-end latency by up to 7.13x and 2.19x (4.86x and 1.60x compared to the state-of-the-art), while achieving comparable tracking quality.
Automatic Detection of Reactions to Music via Earable Sensing
Apr 06, 2023Abstract:We present GrooveMeter, a novel system that automatically detects vocal and motion reactions to music via earable sensing and supports music engagement-aware applications. To this end, we use smart earbuds as sensing devices, which are already widely used for music listening, and devise reaction detection techniques by leveraging an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and a microphone on earbuds. To explore reactions in daily music-listening situations, we collect the first kind of dataset, MusicReactionSet, containing 926-minute-long IMU and audio data with 30 participants. With the dataset, we discover a set of unique challenges in detecting music listening reactions accurately and robustly using audio and motion sensing. We devise sophisticated processing pipelines to make reaction detection accurate and efficient. We present a comprehensive evaluation to examine the performance of reaction detection and system cost. It shows that GrooveMeter achieves the macro F1 scores of 0.89 for vocal reaction and 0.81 for motion reaction with leave-one-subject-out cross-validation. More importantly, GrooveMeter shows higher accuracy and robustness compared to alternative methods. We also show that our filtering approach reduces 50% or more of the energy overhead. Finally, we demonstrate the potential use cases through a case study.
ColloSSL: Collaborative Self-Supervised Learning for Human Activity Recognition
Feb 01, 2022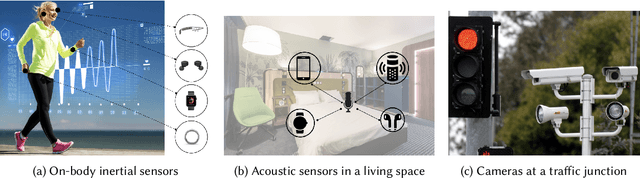
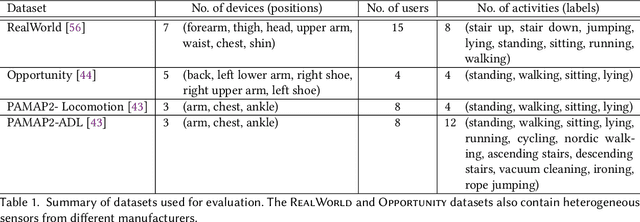

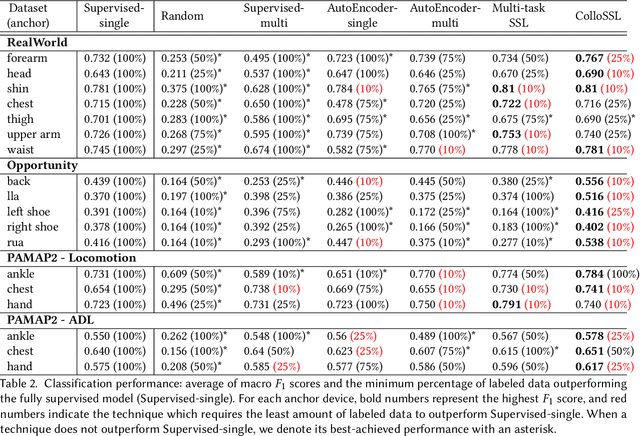
Abstract:A major bottleneck in training robust Human-Activity Recognition models (HAR) is the need for large-scale labeled sensor datasets. Because labeling large amounts of sensor data is an expensive task, unsupervised and semi-supervised learning techniques have emerged that can learn good features from the data without requiring any labels. In this paper, we extend this line of research and present a novel technique called Collaborative Self-Supervised Learning (ColloSSL) which leverages unlabeled data collected from multiple devices worn by a user to learn high-quality features of the data. A key insight that underpins the design of ColloSSL is that unlabeled sensor datasets simultaneously captured by multiple devices can be viewed as natural transformations of each other, and leveraged to generate a supervisory signal for representation learning. We present three technical innovations to extend conventional self-supervised learning algorithms to a multi-device setting: a Device Selection approach which selects positive and negative devices to enable contrastive learning, a Contrastive Sampling algorithm which samples positive and negative examples in a multi-device setting, and a loss function called Multi-view Contrastive Loss which extends standard contrastive loss to a multi-device setting. Our experimental results on three multi-device datasets show that ColloSSL outperforms both fully-supervised and semi-supervised learning techniques in majority of the experiment settings, resulting in an absolute increase of upto 7.9% in F_1 score compared to the best performing baselines. We also show that ColloSSL outperforms the fully-supervised methods in a low-data regime, by just using one-tenth of the available labeled data in the best case.
SensiX++: Bringing MLOPs and Multi-tenant Model Serving to Sensory Edge Devices
Sep 08, 2021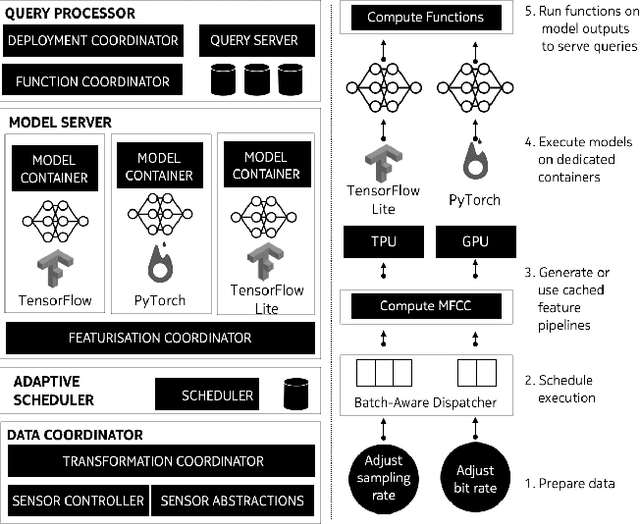
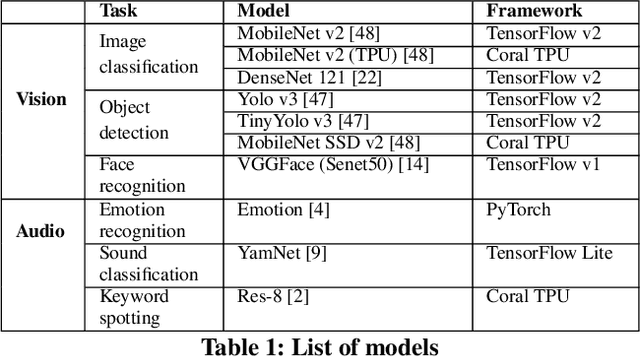

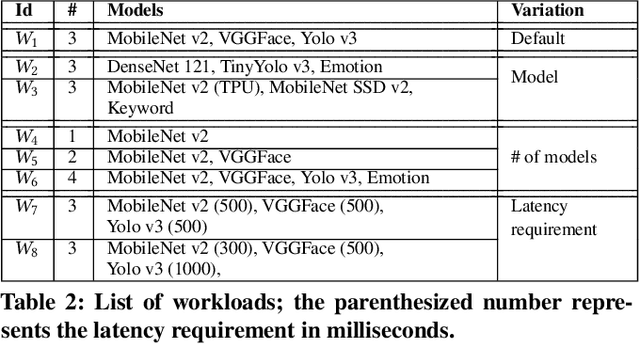
Abstract:We present SensiX++ - a multi-tenant runtime for adaptive model execution with integrated MLOps on edge devices, e.g., a camera, a microphone, or IoT sensors. SensiX++ operates on two fundamental principles - highly modular componentisation to externalise data operations with clear abstractions and document-centric manifestation for system-wide orchestration. First, a data coordinator manages the lifecycle of sensors and serves models with correct data through automated transformations. Next, a resource-aware model server executes multiple models in isolation through model abstraction, pipeline automation and feature sharing. An adaptive scheduler then orchestrates the best-effort executions of multiple models across heterogeneous accelerators, balancing latency and throughput. Finally, microservices with REST APIs serve synthesised model predictions, system statistics, and continuous deployment. Collectively, these components enable SensiX++ to serve multiple models efficiently with fine-grained control on edge devices while minimising data operation redundancy, managing data and device heterogeneity, reducing resource contention and removing manual MLOps. We benchmark SensiX++ with ten different vision and acoustics models across various multi-tenant configurations on different edge accelerators (Jetson AGX and Coral TPU) designed for sensory devices. We report on the overall throughput and quantified benefits of various automation components of SensiX++ and demonstrate its efficacy to significantly reduce operational complexity and lower the effort to deploy, upgrade, reconfigure and serve embedded models on edge devices.
SensiX: A Platform for Collaborative Machine Learning on the Edge
Dec 04, 2020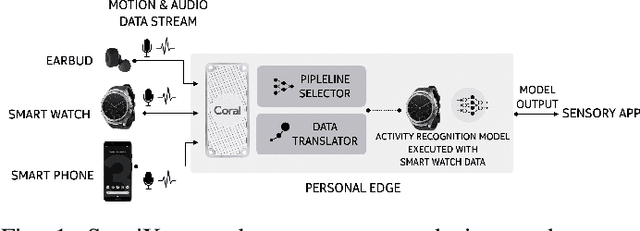
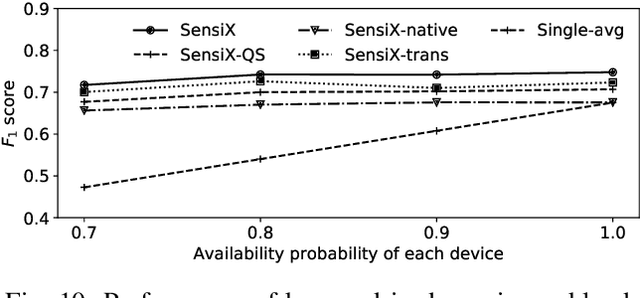
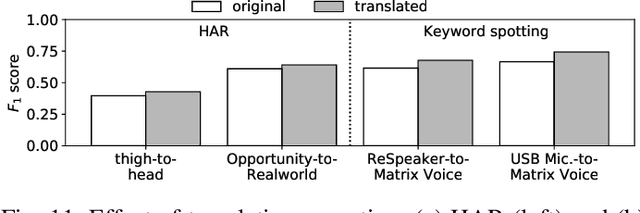
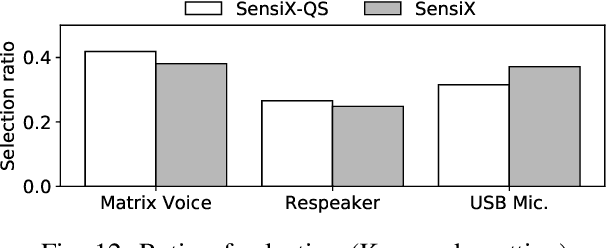
Abstract:The emergence of multiple sensory devices on or near a human body is uncovering new dynamics of extreme edge computing. In this, a powerful and resource-rich edge device such as a smartphone or a Wi-Fi gateway is transformed into a personal edge, collaborating with multiple devices to offer remarkable sensory al eapplications, while harnessing the power of locality, availability, and proximity. Naturally, this transformation pushes us to rethink how to construct accurate, robust, and efficient sensory systems at personal edge. For instance, how do we build a reliable activity tracker with multiple on-body IMU-equipped devices? While the accuracy of sensing models is improving, their runtime performance still suffers, especially under this emerging multi-device, personal edge environments. Two prime caveats that impact their performance are device and data variabilities, contributed by several runtime factors, including device availability, data quality, and device placement. To this end, we present SensiX, a personal edge platform that stays between sensor data and sensing models, and ensures best-effort inference under any condition while coping with device and data variabilities without demanding model engineering. SensiX externalises model execution away from applications, and comprises of two essential functions, a translation operator for principled mapping of device-to-device data and a quality-aware selection operator to systematically choose the right execution path as a function of model accuracy. We report the design and implementation of SensiX and demonstrate its efficacy in developing motion and audio-based multi-device sensing systems. Our evaluation shows that SensiX offers a 7-13% increase in overall accuracy and up to 30% increase across different environment dynamics at the expense of 3mW power overhead.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge