Christopher Redino
Retrieval Augmented Anomaly Detection (RAAD): Nimble Model Adjustment Without Retraining
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel mechanism for real-time (human-in-the-loop) feedback focused on false positive reduction to enhance anomaly detection models. It was designed for the lightweight deployment of a behavioral network anomaly detection model. This methodology is easily integrable to similar domains that require a premium on throughput while maintaining high precision. In this paper, we introduce Retrieval Augmented Anomaly Detection, a novel method taking inspiration from Retrieval Augmented Generation. Human annotated examples are sent to a vector store, which can modify model outputs on the very next processed batch for model inference. To demonstrate the generalization of this technique, we benchmarked several different model architectures and multiple data modalities, including images, text, and graph-based data.
Leveraging Reinforcement Learning in Red Teaming for Advanced Ransomware Attack Simulations
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Ransomware presents a significant and increasing threat to individuals and organizations by encrypting their systems and not releasing them until a large fee has been extracted. To bolster preparedness against potential attacks, organizations commonly conduct red teaming exercises, which involve simulated attacks to assess existing security measures. This paper proposes a novel approach utilizing reinforcement learning (RL) to simulate ransomware attacks. By training an RL agent in a simulated environment mirroring real-world networks, effective attack strategies can be learned quickly, significantly streamlining traditional, manual penetration testing processes. The attack pathways revealed by the RL agent can provide valuable insights to the defense team, helping them identify network weak points and develop more resilient defensive measures. Experimental results on a 152-host example network confirm the effectiveness of the proposed approach, demonstrating the RL agent's capability to discover and orchestrate attacks on high-value targets while evading honeyfiles (decoy files strategically placed to detect unauthorized access).
Discovering Command and Control (C2) Channels on Tor and Public Networks Using Reinforcement Learning
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Command and control (C2) channels are an essential component of many types of cyber attacks, as they enable attackers to remotely control their malware-infected machines and execute harmful actions, such as propagating malicious code across networks, exfiltrating confidential data, or initiating distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks. Identifying these C2 channels is therefore crucial in helping to mitigate and prevent cyber attacks. However, identifying C2 channels typically involves a manual process, requiring deep knowledge and expertise in cyber operations. In this paper, we propose a reinforcement learning (RL) based approach to automatically emulate C2 attack campaigns using both the normal (public) and the Tor networks. In addition, payload size and network firewalls are configured to simulate real-world attack scenarios. Results on a typical network configuration show that the RL agent can automatically discover resilient C2 attack paths utilizing both Tor-based and conventional communication channels, while also bypassing network firewalls.
Discovering Command and Control Channels Using Reinforcement Learning
Jan 13, 2024



Abstract:Command and control (C2) paths for issuing commands to malware are sometimes the only indicators of its existence within networks. Identifying potential C2 channels is often a manually driven process that involves a deep understanding of cyber tradecraft. Efforts to improve discovery of these channels through using a reinforcement learning (RL) based approach that learns to automatically carry out C2 attack campaigns on large networks, where multiple defense layers are in place serves to drive efficiency for network operators. In this paper, we model C2 traffic flow as a three-stage process and formulate it as a Markov decision process (MDP) with the objective to maximize the number of valuable hosts whose data is exfiltrated. The approach also specifically models payload and defense mechanisms such as firewalls which is a novel contribution. The attack paths learned by the RL agent can in turn help the blue team identify high-priority vulnerabilities and develop improved defense strategies. The method is evaluated on a large network with more than a thousand hosts and the results demonstrate that the agent can effectively learn attack paths while avoiding firewalls.
FedBayes: A Zero-Trust Federated Learning Aggregation to Defend Against Adversarial Attacks
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Federated learning has created a decentralized method to train a machine learning model without needing direct access to client data. The main goal of a federated learning architecture is to protect the privacy of each client while still contributing to the training of the global model. However, the main advantage of privacy in federated learning is also the easiest aspect to exploit. Without being able to see the clients' data, it is difficult to determine the quality of the data. By utilizing data poisoning methods, such as backdoor or label-flipping attacks, or by sending manipulated information about their data back to the server, malicious clients are able to corrupt the global model and degrade performance across all clients within a federation. Our novel aggregation method, FedBayes, mitigates the effect of a malicious client by calculating the probabilities of a client's model weights given to the prior model's weights using Bayesian statistics. Our results show that this approach negates the effects of malicious clients and protects the overall federation.
Exposing Surveillance Detection Routes via Reinforcement Learning, Attack Graphs, and Cyber Terrain
Nov 06, 2022Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) operating on attack graphs leveraging cyber terrain principles are used to develop reward and state associated with determination of surveillance detection routes (SDR). This work extends previous efforts on developing RL methods for path analysis within enterprise networks. This work focuses on building SDR where the routes focus on exploring the network services while trying to evade risk. RL is utilized to support the development of these routes by building a reward mechanism that would help in realization of these paths. The RL algorithm is modified to have a novel warm-up phase which decides in the initial exploration which areas of the network are safe to explore based on the rewards and penalty scale factor.
Zero Day Threat Detection Using Metric Learning Autoencoders
Nov 01, 2022Abstract:The proliferation of zero-day threats (ZDTs) to companies' networks has been immensely costly and requires novel methods to scan traffic for malicious behavior at massive scale. The diverse nature of normal behavior along with the huge landscape of attack types makes deep learning methods an attractive option for their ability to capture highly-nonlinear behavior patterns. In this paper, the authors demonstrate an improvement upon a previously introduced methodology, which used a dual-autoencoder approach to identify ZDTs in network flow telemetry. In addition to the previously-introduced asset-level graph features, which help abstractly represent the role of a host in its network, this new model uses metric learning to train the second autoencoder on labeled attack data. This not only produces stronger performance, but it has the added advantage of improving the interpretability of the model by allowing for multiclass classification in the latent space. This can potentially save human threat hunters time when they investigate predicted ZDTs by showing them which known attack classes were nearby in the latent space. The models presented here are also trained and evaluated with two more datasets, and continue to show promising results even when generalizing to new network topologies.
Anomaly Detection via Federated Learning
Oct 12, 2022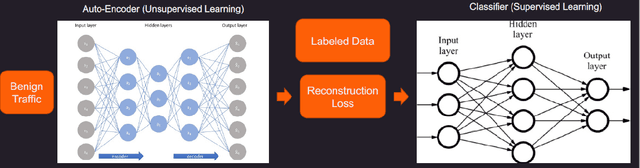
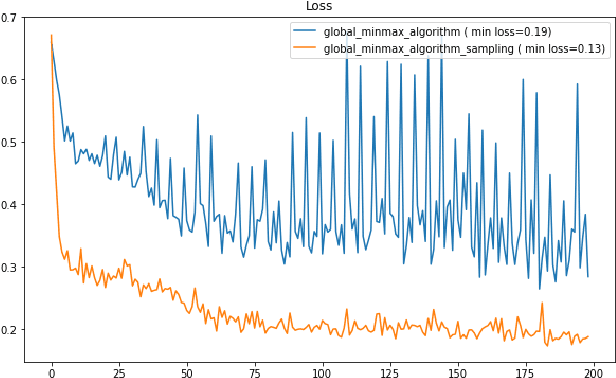
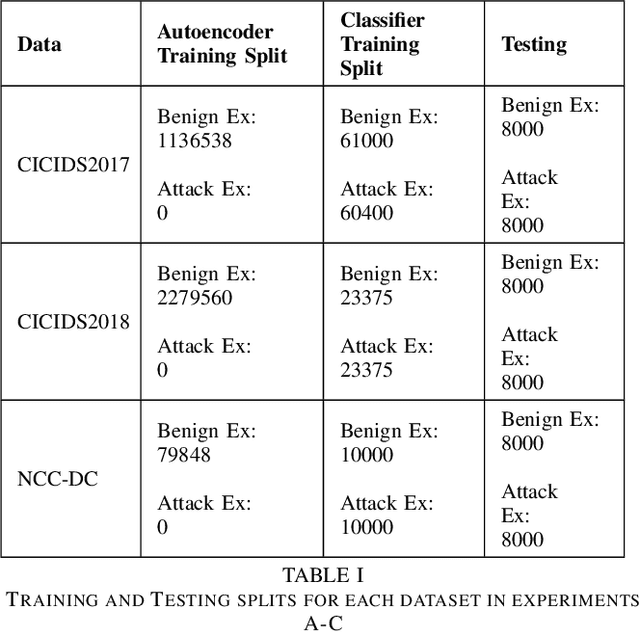
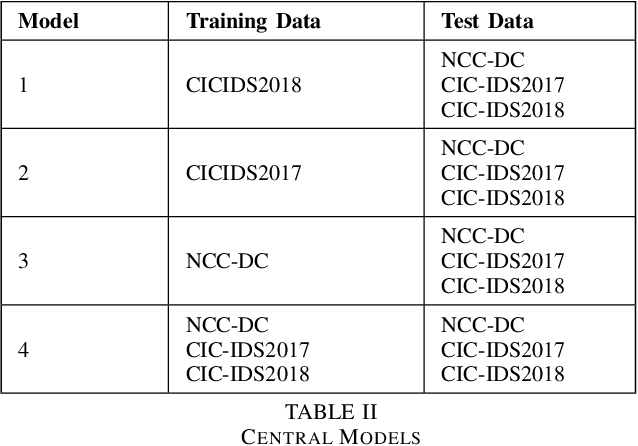
Abstract:Machine learning has helped advance the field of anomaly detection by incorporating classifiers and autoencoders to decipher between normal and anomalous behavior. Additionally, federated learning has provided a way for a global model to be trained with multiple clients' data without requiring the client to directly share their data. This paper proposes a novel anomaly detector via federated learning to detect malicious network activity on a client's server. In our experiments, we use an autoencoder with a classifier in a federated learning framework to determine if the network activity is benign or malicious. By using our novel min-max scalar and sampling technique, called FedSam, we determined federated learning allows the global model to learn from each client's data and, in turn, provide a means for each client to improve their intrusion detection system's defense against cyber-attacks.
Lateral Movement Detection Using User Behavioral Analysis
Aug 29, 2022



Abstract:Lateral Movement refers to methods by which threat actors gain initial access to a network and then progressively move through said network collecting key data about assets until they reach the ultimate target of their attack. Lateral Movement intrusions have become more intricate with the increasing complexity and interconnected nature of enterprise networks, and require equally sophisticated detection mechanisms to proactively detect such threats in near real-time at enterprise scale. In this paper, the authors propose a novel, lightweight method for Lateral Movement detection using user behavioral analysis and machine learning. Specifically, this paper introduces a novel methodology for cyber domain-specific feature engineering that identifies Lateral Movement behavior on a per-user basis. Furthermore, the engineered features have also been used to develop two supervised machine learning models for Lateral Movement identification that have demonstrably outperformed models previously seen in literature while maintaining robust performance on datasets with high class imbalance. The models and methodology introduced in this paper have also been designed in collaboration with security operators to be relevant and interpretable in order to maximize impact and minimize time to value as a cyber threat detection toolkit. The underlying goal of the paper is to provide a computationally efficient, domain-specific approach to near real-time Lateral Movement detection that is interpretable and robust to enterprise-scale data volumes and class imbalance.
Zero Day Threat Detection Using Graph and Flow Based Security Telemetry
May 04, 2022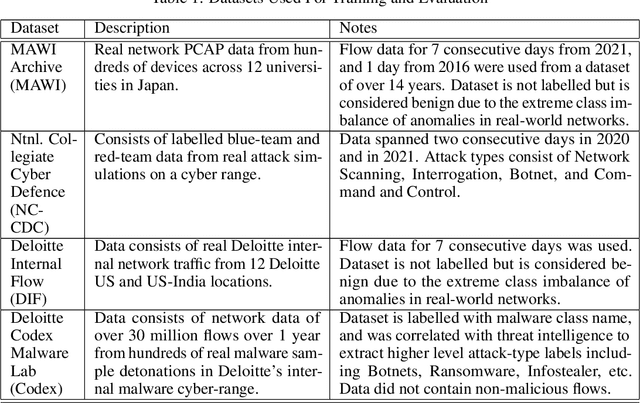
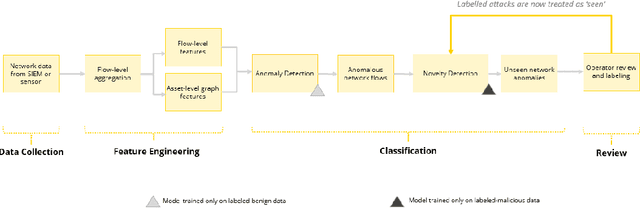
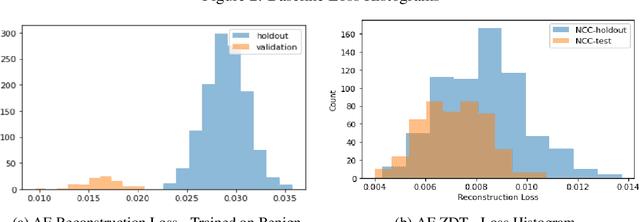

Abstract:Zero Day Threats (ZDT) are novel methods used by malicious actors to attack and exploit information technology (IT) networks or infrastructure. In the past few years, the number of these threats has been increasing at an alarming rate and have been costing organizations millions of dollars to remediate. The increasing expansion of network attack surfaces and the exponentially growing number of assets on these networks necessitate the need for a robust AI-based Zero Day Threat detection model that can quickly analyze petabyte-scale data for potentially malicious and novel activity. In this paper, the authors introduce a deep learning based approach to Zero Day Threat detection that can generalize, scale, and effectively identify threats in near real-time. The methodology utilizes network flow telemetry augmented with asset-level graph features, which are passed through a dual-autoencoder structure for anomaly and novelty detection respectively. The models have been trained and tested on four large scale datasets that are representative of real-world organizational networks and they produce strong results with high precision and recall values. The models provide a novel methodology to detect complex threats with low false-positive rates that allow security operators to avoid alert fatigue while drastically reducing their mean time to response with near-real-time detection. Furthermore, the authors also provide a novel, labelled, cyber attack dataset generated from adversarial activity that can be used for validation or training of other models. With this paper, the authors' overarching goal is to provide a novel architecture and training methodology for cyber anomaly detectors that can generalize to multiple IT networks with minimal to no retraining while still maintaining strong performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge