Christopher Chen
Standardized Evaluation of Automatic Methods for Perivascular Spaces Segmentation in MRI -- MICCAI 2024 Challenge Results
Dec 20, 2025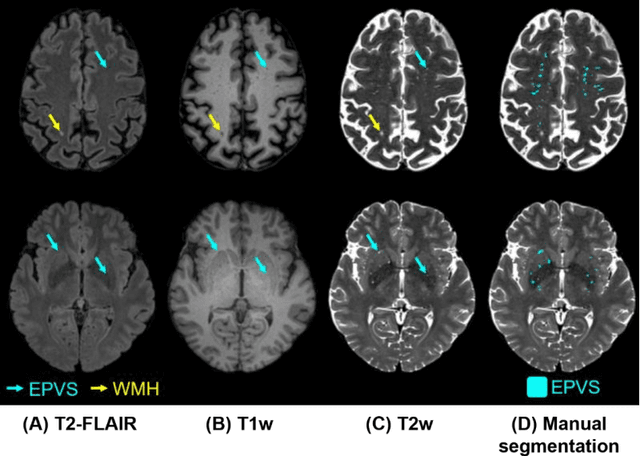
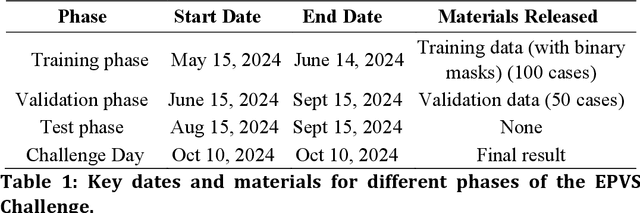
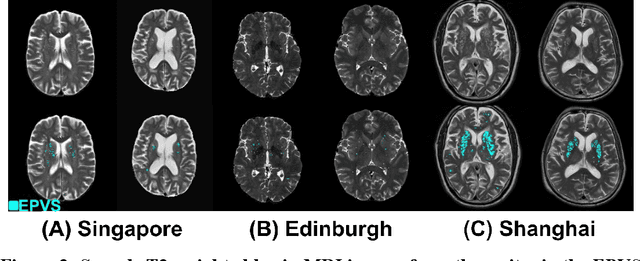
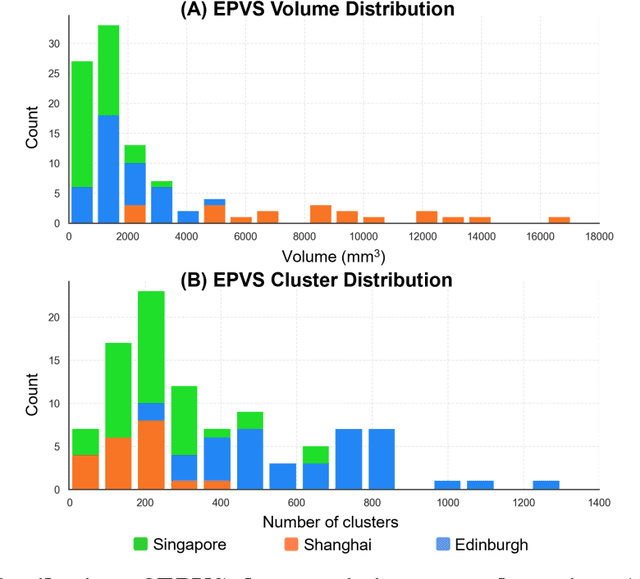
Abstract:Perivascular spaces (PVS), when abnormally enlarged and visible in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) structural sequences, are important imaging markers of cerebral small vessel disease and potential indicators of neurodegenerative conditions. Despite their clinical significance, automatic enlarged PVS (EPVS) segmentation remains challenging due to their small size, variable morphology, similarity with other pathological features, and limited annotated datasets. This paper presents the EPVS Challenge organized at MICCAI 2024, which aims to advance the development of automated algorithms for EPVS segmentation across multi-site data. We provided a diverse dataset comprising 100 training, 50 validation, and 50 testing scans collected from multiple international sites (UK, Singapore, and China) with varying MRI protocols and demographics. All annotations followed the STRIVE protocol to ensure standardized ground truth and covered the full brain parenchyma. Seven teams completed the full challenge, implementing various deep learning approaches primarily based on U-Net architectures with innovations in multi-modal processing, ensemble strategies, and transformer-based components. Performance was evaluated using dice similarity coefficient, absolute volume difference, recall, and precision metrics. The winning method employed MedNeXt architecture with a dual 2D/3D strategy for handling varying slice thicknesses. The top solutions showed relatively good performance on test data from seen datasets, but significant degradation of performance was observed on the previously unseen Shanghai cohort, highlighting cross-site generalization challenges due to domain shift. This challenge establishes an important benchmark for EPVS segmentation methods and underscores the need for the continued development of robust algorithms that can generalize in diverse clinical settings.
Energy Efficiency Tradeoffs for Sub-THz Multi-User MIMO Base Station Receivers
Feb 16, 2022Abstract:Sub-terahertz (sub-THz) antenna array architectures significantly impact power usage and communications capacity in multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) systems. In this work, we compare the energy efficiency and spectral efficiency of three MU-MIMO capable array architectures for base station receivers. We provide a sub-THz circuits power analysis, based on our review of state-of-the-art D-band and G-band components, and compare communications capabilities through wideband simulations. Our analysis reveals that digital arrays can provide the highest spectral efficiency and energy efficiency, due to the high power consumption of sub-THz active phase shifters or when SNR and system spectral efficiency requirements are high.
Standardized Assessment of Automatic Segmentation of White Matter Hyperintensities and Results of the WMH Segmentation Challenge
Apr 01, 2019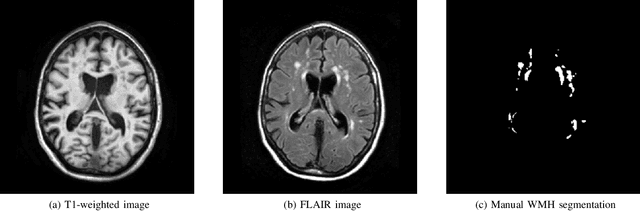
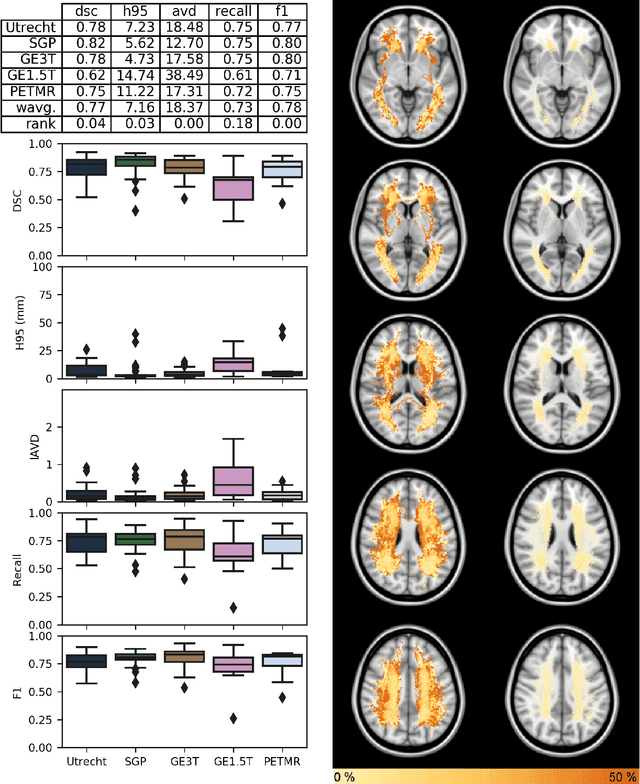
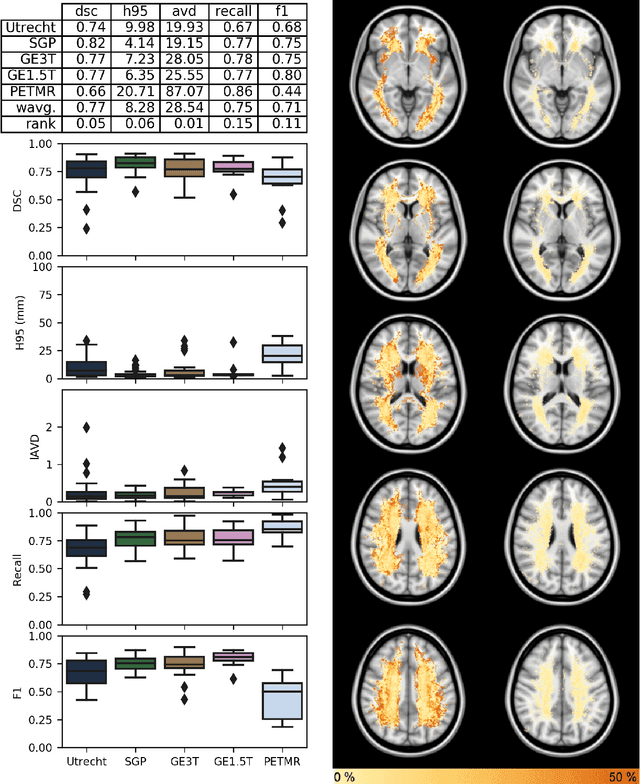
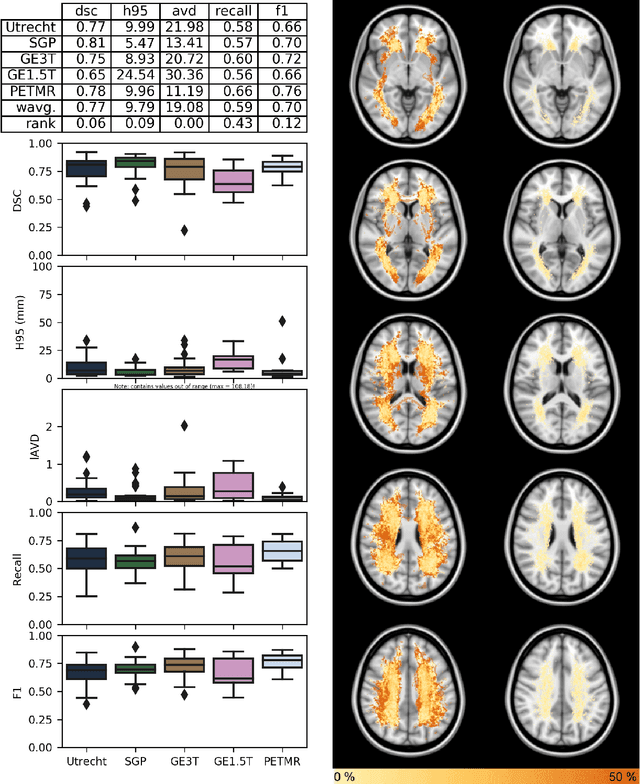
Abstract:Quantification of cerebral white matter hyperintensities (WMH) of presumed vascular origin is of key importance in many neurological research studies. Currently, measurements are often still obtained from manual segmentations on brain MR images, which is a laborious procedure. Automatic WMH segmentation methods exist, but a standardized comparison of the performance of such methods is lacking. We organized a scientific challenge, in which developers could evaluate their method on a standardized multi-center/-scanner image dataset, giving an objective comparison: the WMH Segmentation Challenge (https://wmh.isi.uu.nl/). Sixty T1+FLAIR images from three MR scanners were released with manual WMH segmentations for training. A test set of 110 images from five MR scanners was used for evaluation. Segmentation methods had to be containerized and submitted to the challenge organizers. Five evaluation metrics were used to rank the methods: (1) Dice similarity coefficient, (2) modified Hausdorff distance (95th percentile), (3) absolute log-transformed volume difference, (4) sensitivity for detecting individual lesions, and (5) F1-score for individual lesions. Additionally, methods were ranked on their inter-scanner robustness. Twenty participants submitted their method for evaluation. This paper provides a detailed analysis of the results. In brief, there is a cluster of four methods that rank significantly better than the other methods, with one clear winner. The inter-scanner robustness ranking shows that not all methods generalize to unseen scanners. The challenge remains open for future submissions and provides a public platform for method evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge