Christine Chevallereau
IRCCyN
Motion Prediction with Gaussian Processes for Safe Human-Robot Interaction in Virtual Environments
May 15, 2024



Abstract:Humans use collaborative robots as tools for accomplishing various tasks. The interaction between humans and robots happens in tight shared workspaces. However, these machines must be safe to operate alongside humans to minimize the risk of accidental collisions. Ensuring safety imposes many constraints, such as reduced torque and velocity limits during operation, thus increasing the time to accomplish many tasks. However, for applications such as using collaborative robots as haptic interfaces with intermittent contacts for virtual reality applications, speed limitations result in poor user experiences. This research aims to improve the efficiency of a collaborative robot while improving the safety of the human user. We used Gaussian process models to predict human hand motion and developed strategies for human intention detection based on hand motion and gaze to improve the time for the robot and human security in a virtual environment. We then studied the effect of prediction. Results from comparisons show that the prediction models improved the robot time by 3\% and safety by 17\%. When used alongside gaze, prediction with Gaussian process models resulted in an improvement of the robot time by 2\% and the safety by 13\%.
Self-synchronization and Self-stabilization of 3D Bipedal Walking Gaits
Jul 07, 2017
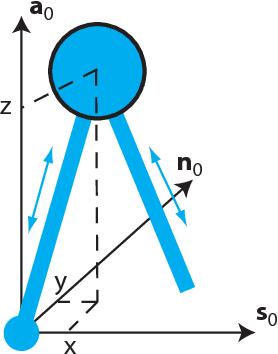
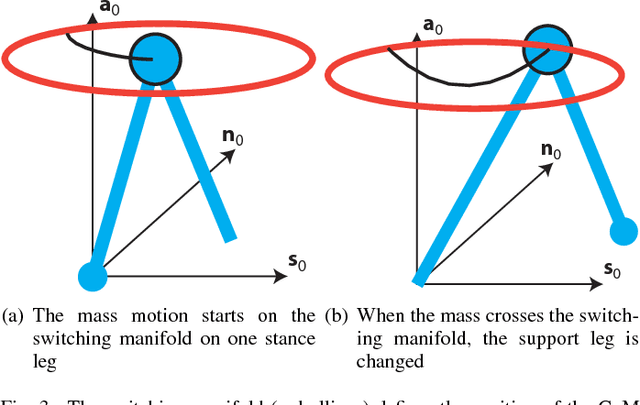
Abstract:This paper seeks insight into stabilization mechanisms for periodic walking gaits in 3D bipedal robots. Based on this insight, a control strategy based on virtual constraints, which imposes coordination between joints rather than a temporal evolution, will be proposed for achieving asymptotic convergence toward a periodic motion. For planar bipeds with one degree of underactuation, it is known that a vertical displacement of the center of mass---with downward velocity at the step transition---induces stability of a walking gait. This paper concerns the qualitative extension of this type of property to 3D walking with two degrees of underactuation. It is shown that a condition on the position of the center of mass in the horizontal plane at the transition between steps induces synchronization between the motions in the sagittal and frontal planes. A combination of the conditions for self-synchronization and vertical oscillations leads to stable gaits. The algorithm for self-stabilization of 3D walking gaits is first developed for a simplified model of a walking robot (an inverted pendulum with variable length legs), and then it is extended to a complex model of the humanoid robot Romeo using the notion of Hybrid Zero Dynamics. Simulations of the model of the robot illustrate the efficacy of the method and its robustness.
Virtual Constraints and Hybrid Zero Dynamics for Realizing Underactuated Bipedal Locomotion
Jun 04, 2017



Abstract:Underactuation is ubiquitous in human locomotion and should be ubiquitous in bipedal robotic locomotion as well. This chapter presents a coherent theory for the design of feedback controllers that achieve stable walking gaits in underactuated bipedal robots. Two fundamental tools are introduced, virtual constraints and hybrid zero dynamics. Virtual constraints are relations on the state variables of a mechanical model that are imposed through a time-invariant feedback controller. One of their roles is to synchronize the robot's joints to an internal gait phasing variable. A second role is to induce a low dimensional system, the zero dynamics, that captures the underactuated aspects of a robot's model, without any approximations. To enhance intuition, the relation between physical constraints and virtual constraints is first established. From here, the hybrid zero dynamics of an underactuated bipedal model is developed, and its fundamental role in the design of asymptotically stable walking motions is established. The chapter includes numerous references to robots on which the highlighted techniques have been implemented.
Restricted Discrete Invariance and Self-Synchronization For Stable Walking of Bipedal Robots
Jun 10, 2016
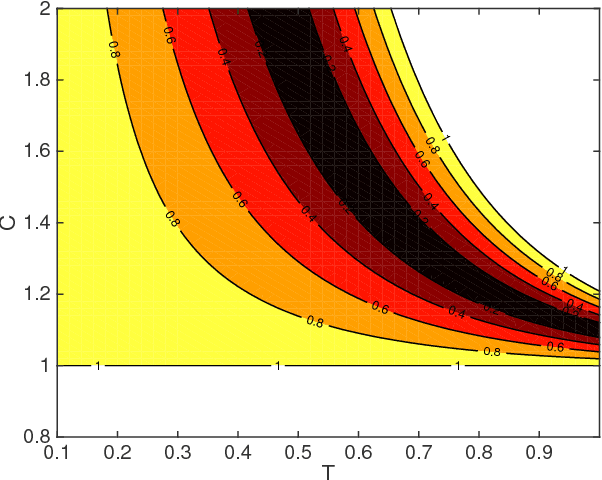
Abstract:Models of bipedal locomotion are hybrid, with a continuous component often generated by a Lagrangian plus actuators, and a discrete component where leg transfer takes place. The discrete component typically consists of a locally embedded co-dimension one submanifold in the continuous state space of the robot, called the switching surface, and a reset map that provides a new initial condition when a solution of the continuous component intersects the switching surface. The aim of this paper is to identify a low-dimensional submanifold of the switching surface, which, when it can be rendered invariant by the closed-loop dynamics, leads to asymptotically stable periodic gaits. The paper begins this process by studying the well-known 3D Linear Inverted Pendulum (LIP) model, where analytical results are much easier to obtain. A key contribution here is the notion of \textit{self-synchronization}, which refers to the periods of the pendular motions in the sagittal and frontal planes tending to a common period. The notion of invariance resulting from the study of the 3D LIP model is then extended to a 9-DOF 3D biped. A numerical study is performed to illustrate that asymptotically stable walking may be obtained.
Asymptotically Stable Walking of a Five-Link Underactuated 3D Bipedal Robot
Feb 17, 2010



Abstract:This paper presents three feedback controllers that achieve an asymptotically stable, periodic, and fast walking gait for a 3D (spatial) bipedal robot consisting of a torso, two legs, and passive (unactuated) point feet. The contact between the robot and the walking surface is assumed to inhibit yaw rotation. The studied robot has 8 DOF in the single support phase and 6 actuators. The interest of studying robots with point feet is that the robot's natural dynamics must be explicitly taken into account to achieve balance while walking. We use an extension of the method of virtual constraints and hybrid zero dynamics, in order to simultaneously compute a periodic orbit and an autonomous feedback controller that realizes the orbit. This method allows the computations to be carried out on a 2-DOF subsystem of the 8-DOF robot model. The stability of the walking gait under closed-loop control is evaluated with the linearization of the restricted Poincar\'e map of the hybrid zero dynamics. Three strategies are explored. The first strategy consists of imposing a stability condition during the search of a periodic gait by optimization. The second strategy uses an event-based controller. In the third approach, the effect of output selection is discussed and a pertinent choice of outputs is proposed, leading to stabilization without the use of a supplemental event-based controller.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge