Cheng-Chun Hsu
SPOT: SE(3) Pose Trajectory Diffusion for Object-Centric Manipulation
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:We introduce SPOT, an object-centric imitation learning framework. The key idea is to capture each task by an object-centric representation, specifically the SE(3) object pose trajectory relative to the target. This approach decouples embodiment actions from sensory inputs, facilitating learning from various demonstration types, including both action-based and action-less human hand demonstrations, as well as cross-embodiment generalization. Additionally, object pose trajectories inherently capture planning constraints from demonstrations without the need for manually crafted rules. To guide the robot in executing the task, the object trajectory is used to condition a diffusion policy. We show improvement compared to prior work on RLBench simulated tasks. In real-world evaluation, using only eight demonstrations shot on an iPhone, our approach completed all tasks while fully complying with task constraints. Project page: https://nvlabs.github.io/object_centric_diffusion
KinScene: Model-Based Mobile Manipulation of Articulated Scenes
Sep 24, 2024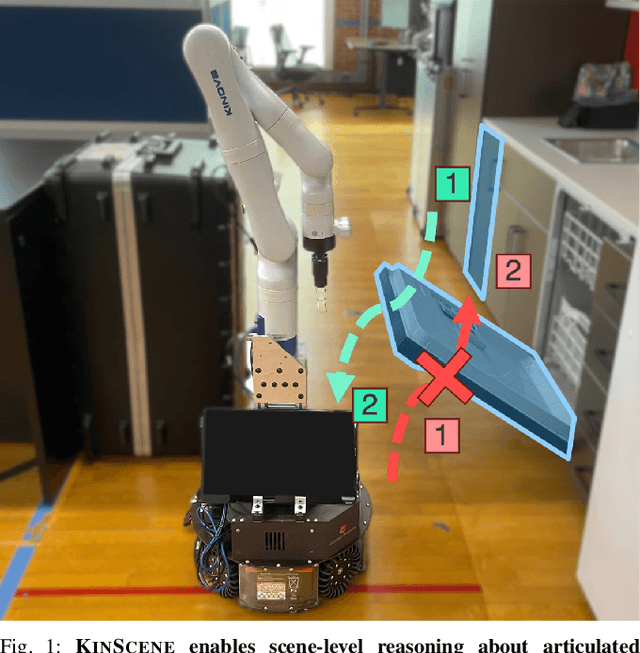
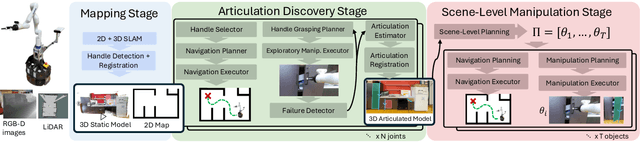
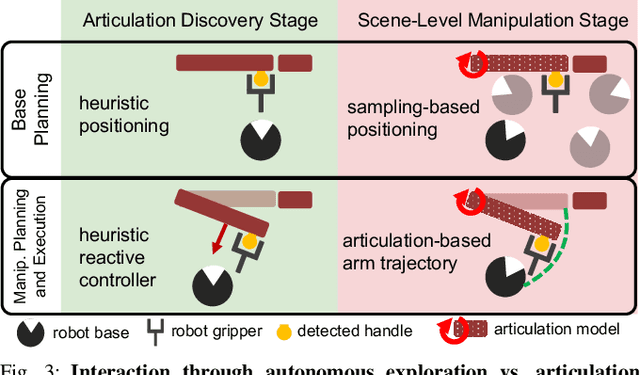

Abstract:Sequentially interacting with articulated objects is crucial for a mobile manipulator to operate effectively in everyday environments. To enable long-horizon tasks involving articulated objects, this study explores building scene-level articulation models for indoor scenes through autonomous exploration. While previous research has studied mobile manipulation with articulated objects by considering object kinematic constraints, it primarily focuses on individual-object scenarios and lacks extension to a scene-level context for task-level planning. To manipulate multiple object parts sequentially, the robot needs to reason about the resultant motion of each part and anticipate its impact on future actions.We introduce \ourtool{}, a full-stack approach for long-horizon manipulation tasks with articulated objects. The robot maps the scene, detects and physically interacts with articulated objects, collects observations, and infers the articulation properties. For sequential tasks, the robot plans a feasible series of object interactions based on the inferred articulation model. We demonstrate that our approach repeatably constructs accurate scene-level kinematic and geometric models, enabling long-horizon mobile manipulation in a real-world scene. Code and additional results are available at https://chengchunhsu.github.io/KinScene/
Ditto in the House: Building Articulation Models of Indoor Scenes through Interactive Perception
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Virtualizing the physical world into virtual models has been a critical technique for robot navigation and planning in the real world. To foster manipulation with articulated objects in everyday life, this work explores building articulation models of indoor scenes through a robot's purposeful interactions in these scenes. Prior work on articulation reasoning primarily focuses on siloed objects of limited categories. To extend to room-scale environments, the robot has to efficiently and effectively explore a large-scale 3D space, locate articulated objects, and infer their articulations. We introduce an interactive perception approach to this task. Our approach, named Ditto in the House, discovers possible articulated objects through affordance prediction, interacts with these objects to produce articulated motions, and infers the articulation properties from the visual observations before and after each interaction. It tightly couples affordance prediction and articulation inference to improve both tasks. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in both simulation and real-world scenes. Code and additional results are available at https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/HouseDitto/
Ditto: Building Digital Twins of Articulated Objects from Interaction
Feb 16, 2022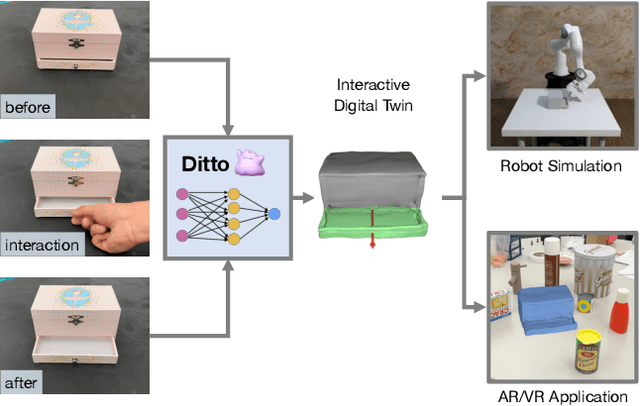
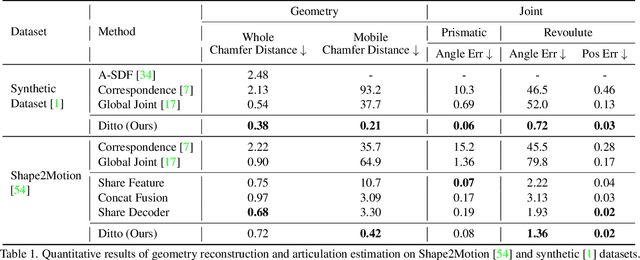
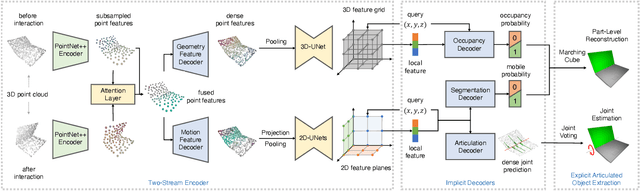
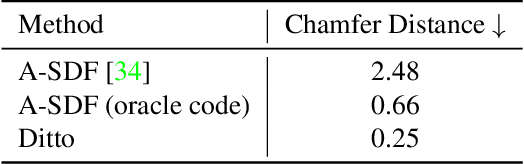
Abstract:Digitizing physical objects into the virtual world has the potential to unlock new research and applications in embodied AI and mixed reality. This work focuses on recreating interactive digital twins of real-world articulated objects, which can be directly imported into virtual environments. We introduce Ditto to learn articulation model estimation and 3D geometry reconstruction of an articulated object through interactive perception. Given a pair of visual observations of an articulated object before and after interaction, Ditto reconstructs part-level geometry and estimates the articulation model of the object. We employ implicit neural representations for joint geometry and articulation modeling. Our experiments show that Ditto effectively builds digital twins of articulated objects in a category-agnostic way. We also apply Ditto to real-world objects and deploy the recreated digital twins in physical simulation. Code and additional results are available at https://ut-austin-rpl.github.io/Ditto
Every Pixel Matters: Center-aware Feature Alignment for Domain Adaptive Object Detector
Aug 19, 2020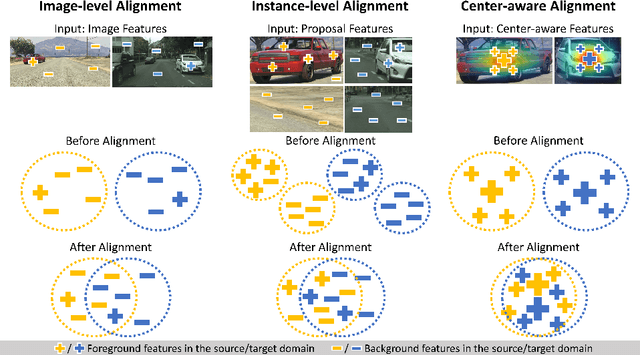
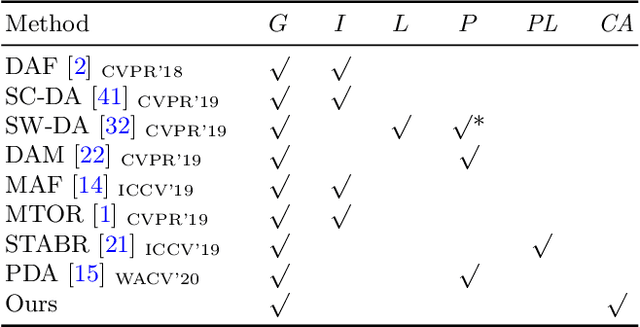
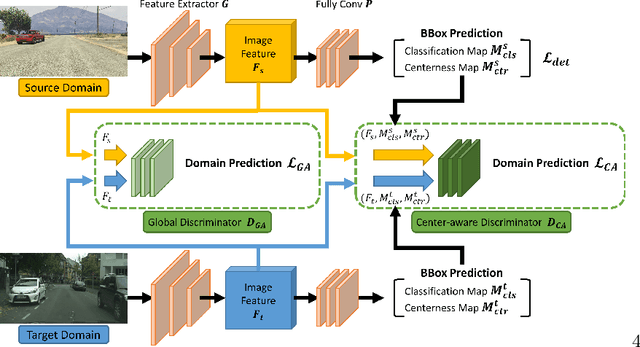
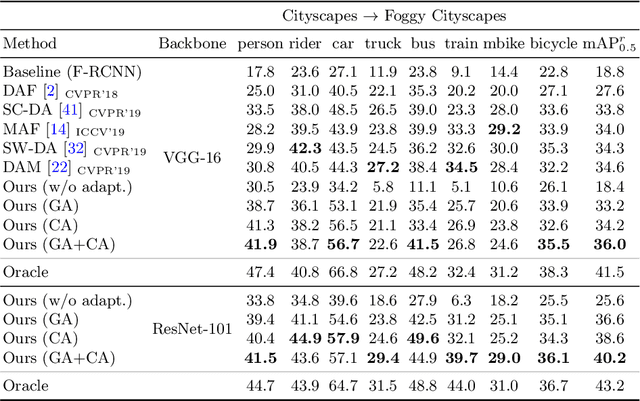
Abstract:A domain adaptive object detector aims to adapt itself to unseen domains that may contain variations of object appearance, viewpoints or backgrounds. Most existing methods adopt feature alignment either on the image level or instance level. However, image-level alignment on global features may tangle foreground/background pixels at the same time, while instance-level alignment using proposals may suffer from the background noise. Different from existing solutions, we propose a domain adaptation framework that accounts for each pixel via predicting pixel-wise objectness and centerness. Specifically, the proposed method carries out center-aware alignment by paying more attention to foreground pixels, hence achieving better adaptation across domains. We demonstrate our method on numerous adaptation settings with extensive experimental results and show favorable performance against existing state-of-the-art algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge