Chaoxiang Ma
Behind Every Domain There is a Shift: Adapting Distortion-aware Vision Transformers for Panoramic Semantic Segmentation
Jul 27, 2022

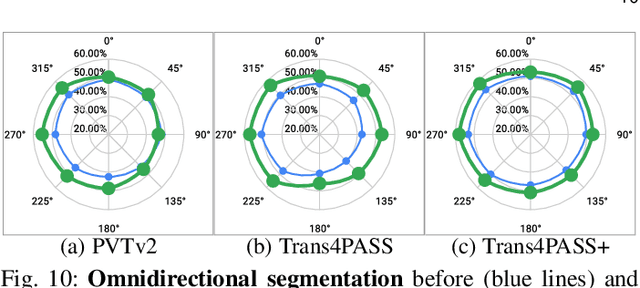

Abstract:In this paper, we address panoramic semantic segmentation, which provides a full-view and dense-pixel understanding of surroundings in a holistic way. Panoramic segmentation is under-explored due to two critical challenges: (1) image distortions and object deformations on panoramas; (2) lack of annotations for training panoramic segmenters. To tackle these problems, we propose a Transformer for Panoramic Semantic Segmentation (Trans4PASS) architecture. First, to enhance distortion awareness, Trans4PASS, equipped with Deformable Patch Embedding (DPE) and Deformable MLP (DMLP) modules, is capable of handling object deformations and image distortions whenever (before or after adaptation) and wherever (shallow or deep levels) by design. We further introduce the upgraded Trans4PASS+ model, featuring DMLPv2 with parallel token mixing to improve the flexibility and generalizability in modeling discriminative cues. Second, we propose a Mutual Prototypical Adaptation (MPA) strategy for unsupervised domain adaptation. Third, aside from Pinhole-to-Panoramic (Pin2Pan) adaptation, we create a new dataset (SynPASS) with 9,080 panoramic images to explore a Synthetic-to-Real (Syn2Real) adaptation scheme in 360{\deg} imagery. Extensive experiments are conducted, which cover indoor and outdoor scenarios, and each of them is investigated with Pin2Pan and Syn2Real regimens. Trans4PASS+ achieves state-of-the-art performances on four domain adaptive panoramic semantic segmentation benchmarks. Code is available at https://github.com/jamycheung/Trans4PASS.
Bending Reality: Distortion-aware Transformers for Adapting to Panoramic Semantic Segmentation
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Panoramic images with their 360-degree directional view encompass exhaustive information about the surrounding space, providing a rich foundation for scene understanding. To unfold this potential in the form of robust panoramic segmentation models, large quantities of expensive, pixel-wise annotations are crucial for success. Such annotations are available, but predominantly for narrow-angle, pinhole-camera images which, off the shelf, serve as sub-optimal resources for training panoramic models. Distortions and the distinct image-feature distribution in 360-degree panoramas impede the transfer from the annotation-rich pinhole domain and therefore come with a big dent in performance. To get around this domain difference and bring together semantic annotations from pinhole- and 360-degree surround-visuals, we propose to learn object deformations and panoramic image distortions in the Deformable Patch Embedding (DPE) and Deformable MLP (DMLP) components which blend into our Transformer for PAnoramic Semantic Segmentation (Trans4PASS) model. Finally, we tie together shared semantics in pinhole- and panoramic feature embeddings by generating multi-scale prototype features and aligning them in our Mutual Prototypical Adaptation (MPA) for unsupervised domain adaptation. On the indoor Stanford2D3D dataset, our Trans4PASS with MPA maintains comparable performance to fully-supervised state-of-the-arts, cutting the need for over 1,400 labeled panoramas. On the outdoor DensePASS dataset, we break state-of-the-art by 14.39% mIoU and set the new bar at 56.38%. Code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/jamycheung/Trans4PASS.
Transfer beyond the Field of View: Dense Panoramic Semantic Segmentation via Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Oct 21, 2021



Abstract:Autonomous vehicles clearly benefit from the expanded Field of View (FoV) of 360-degree sensors, but modern semantic segmentation approaches rely heavily on annotated training data which is rarely available for panoramic images. We look at this problem from the perspective of domain adaptation and bring panoramic semantic segmentation to a setting, where labelled training data originates from a different distribution of conventional pinhole camera images. To achieve this, we formalize the task of unsupervised domain adaptation for panoramic semantic segmentation and collect DensePASS - a novel densely annotated dataset for panoramic segmentation under cross-domain conditions, specifically built to study the Pinhole-to-Panoramic domain shift and accompanied with pinhole camera training examples obtained from Cityscapes. DensePASS covers both, labelled- and unlabelled 360-degree images, with the labelled data comprising 19 classes which explicitly fit the categories available in the source (i.e. pinhole) domain. Since data-driven models are especially susceptible to changes in data distribution, we introduce P2PDA - a generic framework for Pinhole-to-Panoramic semantic segmentation which addresses the challenge of domain divergence with different variants of attention-augmented domain adaptation modules, enabling the transfer in output-, feature-, and feature confidence spaces. P2PDA intertwines uncertainty-aware adaptation using confidence values regulated on-the-fly through attention heads with discrepant predictions. Our framework facilitates context exchange when learning domain correspondences and dramatically improves the adaptation performance of accuracy- and efficiency-focused models. Comprehensive experiments verify that our framework clearly surpasses unsupervised domain adaptation- and specialized panoramic segmentation approaches.
DensePASS: Dense Panoramic Semantic Segmentation via Unsupervised Domain Adaptation with Attention-Augmented Context Exchange
Aug 13, 2021



Abstract:Intelligent vehicles clearly benefit from the expanded Field of View (FoV) of the 360-degree sensors, but the vast majority of available semantic segmentation training images are captured with pinhole cameras. In this work, we look at this problem through the lens of domain adaptation and bring panoramic semantic segmentation to a setting, where labelled training data originates from a different distribution of conventional pinhole camera images. First, we formalize the task of unsupervised domain adaptation for panoramic semantic segmentation, where a network trained on labelled examples from the source domain of pinhole camera data is deployed in a different target domain of panoramic images, for which no labels are available. To validate this idea, we collect and publicly release DensePASS - a novel densely annotated dataset for panoramic segmentation under cross-domain conditions, specifically built to study the Pinhole-to-Panoramic transfer and accompanied with pinhole camera training examples obtained from Cityscapes. DensePASS covers both, labelled- and unlabelled 360-degree images, with the labelled data comprising 19 classes which explicitly fit the categories available in the source domain (i.e. pinhole) data. To meet the challenge of domain shift, we leverage the current progress of attention-based mechanisms and build a generic framework for cross-domain panoramic semantic segmentation based on different variants of attention-augmented domain adaptation modules. Our framework facilitates information exchange at local- and global levels when learning the domain correspondences and improves the domain adaptation performance of two standard segmentation networks by 6.05% and 11.26% in Mean IoU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge