Changyu Zeng
ASP-VMUNet: Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba U-Net for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Mar 25, 2025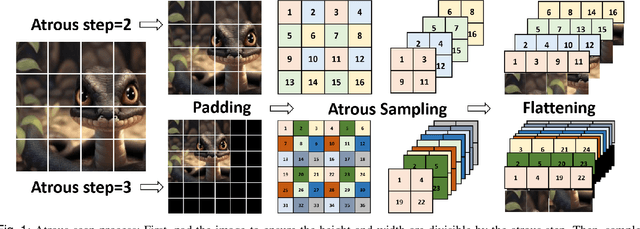
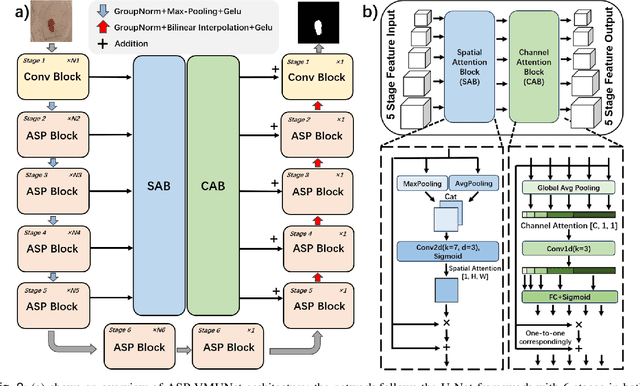
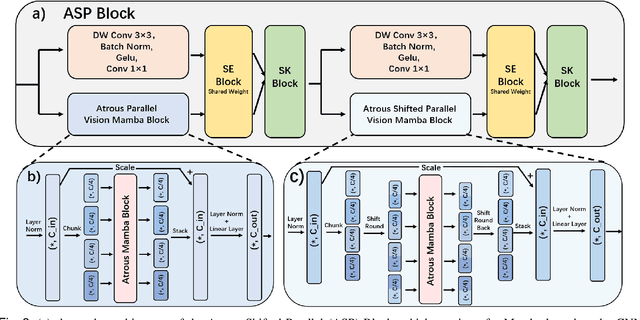
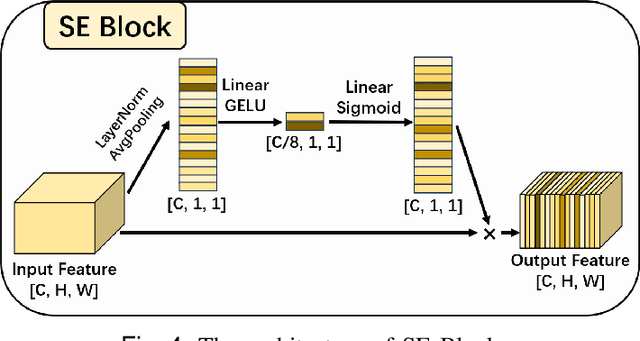
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation is a critical challenge in computer vision, and it is essential to separate pathological features from healthy skin for diagnostics accurately. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are limited by narrow receptive fields, and Transformers face significant computational burdens. This paper presents a novel skin lesion segmentation framework, the Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba UNet (ASP-VMUNet), which integrates the efficient and scalable Mamba architecture to overcome limitations in traditional CNNs and computationally demanding Transformers. The framework introduces an atrous scan technique that minimizes background interference and expands the receptive field, enhancing Mamba's scanning capabilities. Additionally, the inclusion of a Parallel Vision Mamba (PVM) layer and a shift round operation optimizes feature segmentation and fosters rich inter-segment information exchange. A supplementary CNN branch with a Selective-Kernel (SK) Block further refines the segmentation by blending local and global contextual information. Tested on four benchmark datasets (ISIC16/17/18 and PH2), ASP-VMUNet demonstrates superior performance in skin lesion segmentation, validated by comprehensive ablation studies. This approach not only advances medical image segmentation but also highlights the benefits of hybrid architectures in medical imaging technology. Our code is available at https://github.com/BaoBao0926/ASP-VMUNet/tree/main.
Self-Supervised Learning for Point Clouds Data: A Survey
May 24, 2023Abstract:3D point clouds are a crucial type of data collected by LiDAR sensors and widely used in transportation applications due to its concise descriptions and accurate localization. Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved remarkable success in processing large amount of disordered and sparse 3D point clouds, especially in various computer vision tasks, such as pedestrian detection and vehicle recognition. Among all the learning paradigms, Self-Supervised Learning (SSL), an unsupervised training paradigm that mines effective information from the data itself, is considered as an essential solution to solve the time-consuming and labor-intensive data labelling problems via smart pre-training task design. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of recent advances on SSL for point clouds. We first present an innovative taxonomy, categorizing the existing SSL methods into four broad categories based on the pretexts' characteristics. Under each category, we then further categorize the methods into more fine-grained groups and summarize the strength and limitations of the representative methods. We also compare the performance of the notable SSL methods in literature on multiple downstream tasks on benchmark datasets both quantitatively and qualitatively. Finally, we propose a number of future research directions based on the identified limitations of existing SSL research on point clouds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge