Muyi Bao
Vision Mamba in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Survey of Techniques, Applications and Outlook
May 01, 2025Abstract:Deep learning has profoundly transformed remote sensing, yet prevailing architectures like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) remain constrained by critical trade-offs: CNNs suffer from limited receptive fields, while ViTs grapple with quadratic computational complexity, hindering their scalability for high-resolution remote sensing data. State Space Models (SSMs), particularly the recently proposed Mamba architecture, have emerged as a paradigm-shifting solution, combining linear computational scaling with global context modeling. This survey presents a comprehensive review of Mamba-based methodologies in remote sensing, systematically analyzing about 120 studies to construct a holistic taxonomy of innovations and applications. Our contributions are structured across five dimensions: (i) foundational principles of vision Mamba architectures, (ii) micro-architectural advancements such as adaptive scan strategies and hybrid SSM formulations, (iii) macro-architectural integrations, including CNN-Transformer-Mamba hybrids and frequency-domain adaptations, (iv) rigorous benchmarking against state-of-the-art methods in multiple application tasks, such as object detection, semantic segmentation, change detection, etc. and (v) critical analysis of unresolved challenges with actionable future directions. By bridging the gap between SSM theory and remote sensing practice, this survey establishes Mamba as a transformative framework for remote sensing analysis. To our knowledge, this paper is the first systematic review of Mamba architectures in remote sensing. Our work provides a structured foundation for advancing research in remote sensing systems through SSM-based methods. We curate an open-source repository (https://github.com/BaoBao0926/Awesome-Mamba-in-Remote-Sensing) to foster community-driven advancements.
ASP-VMUNet: Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba U-Net for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Mar 25, 2025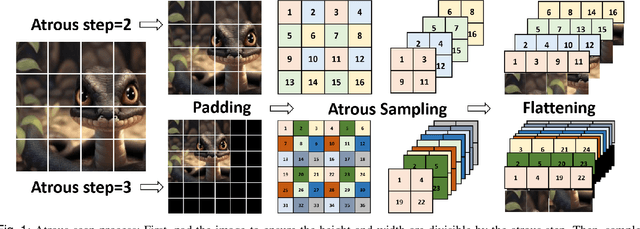
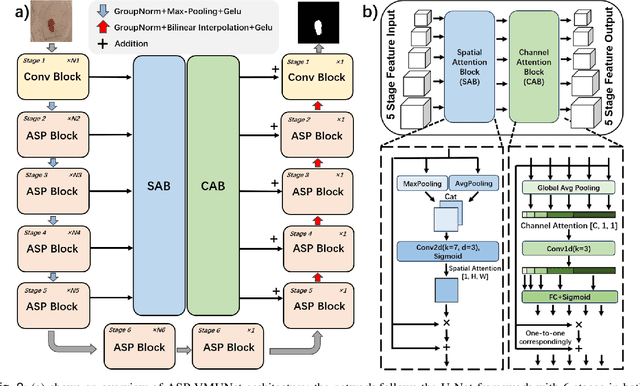
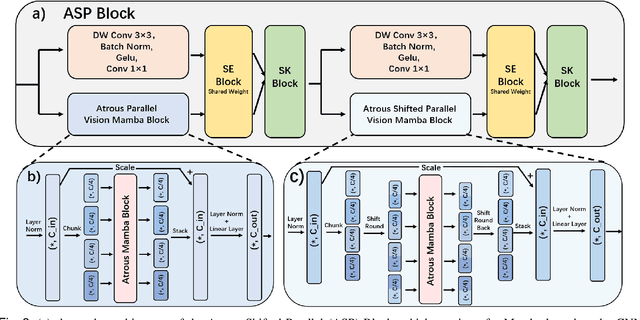
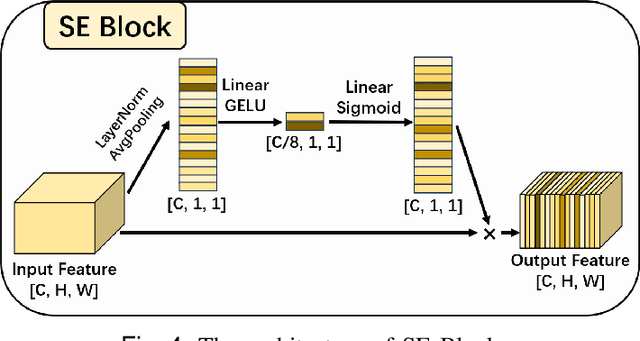
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation is a critical challenge in computer vision, and it is essential to separate pathological features from healthy skin for diagnostics accurately. Traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are limited by narrow receptive fields, and Transformers face significant computational burdens. This paper presents a novel skin lesion segmentation framework, the Atrous Shifted Parallel Vision Mamba UNet (ASP-VMUNet), which integrates the efficient and scalable Mamba architecture to overcome limitations in traditional CNNs and computationally demanding Transformers. The framework introduces an atrous scan technique that minimizes background interference and expands the receptive field, enhancing Mamba's scanning capabilities. Additionally, the inclusion of a Parallel Vision Mamba (PVM) layer and a shift round operation optimizes feature segmentation and fosters rich inter-segment information exchange. A supplementary CNN branch with a Selective-Kernel (SK) Block further refines the segmentation by blending local and global contextual information. Tested on four benchmark datasets (ISIC16/17/18 and PH2), ASP-VMUNet demonstrates superior performance in skin lesion segmentation, validated by comprehensive ablation studies. This approach not only advances medical image segmentation but also highlights the benefits of hybrid architectures in medical imaging technology. Our code is available at https://github.com/BaoBao0926/ASP-VMUNet/tree/main.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge