Changxu Wu
Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion with Time-sensitive Relations in Hypercomplex Space
Mar 02, 2024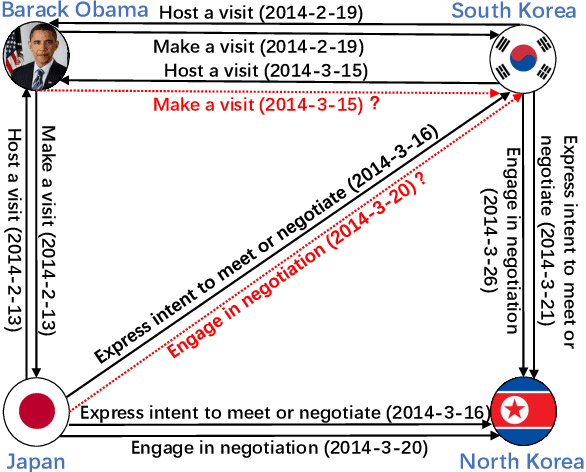
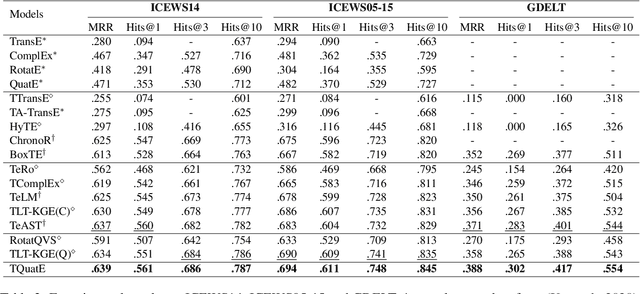
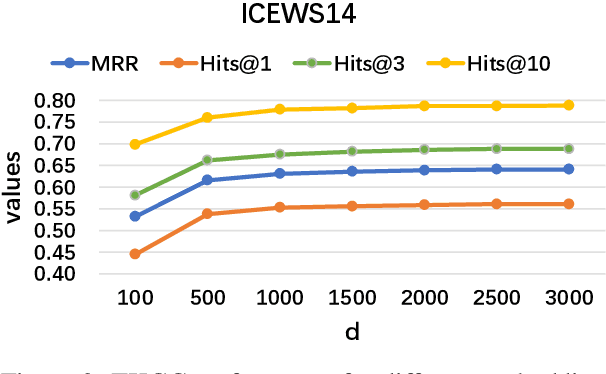
Abstract:Temporal knowledge graph completion (TKGC) aims to fill in missing facts within a given temporal knowledge graph at a specific time. Existing methods, operating in real or complex spaces, have demonstrated promising performance in this task. This paper advances beyond conventional approaches by introducing more expressive quaternion representations for TKGC within hypercomplex space. Unlike existing quaternion-based methods, our study focuses on capturing time-sensitive relations rather than time-aware entities. Specifically, we model time-sensitive relations through time-aware rotation and periodic time translation, effectively capturing complex temporal variability. Furthermore, we theoretically demonstrate our method's capability to model symmetric, asymmetric, inverse, compositional, and evolutionary relation patterns. Comprehensive experiments on public datasets validate that our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in the field of TKGC.
A Survey on Temporal Knowledge Graph: Representation Learning and Applications
Mar 02, 2024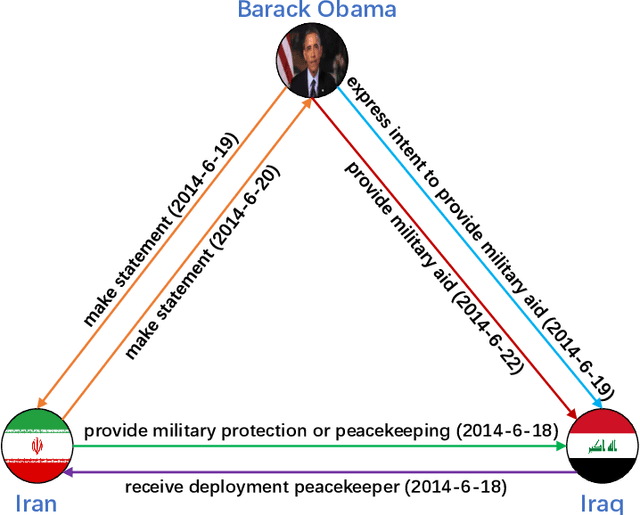
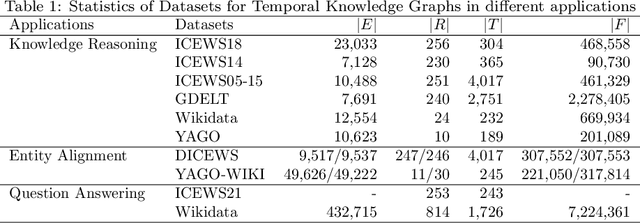
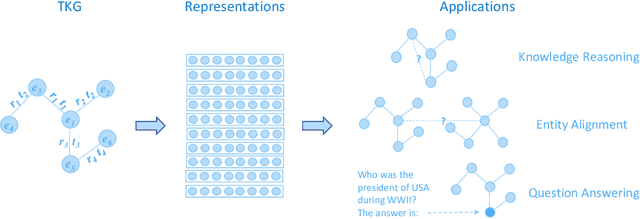

Abstract:Knowledge graphs have garnered significant research attention and are widely used to enhance downstream applications. However, most current studies mainly focus on static knowledge graphs, whose facts do not change with time, and disregard their dynamic evolution over time. As a result, temporal knowledge graphs have attracted more attention because a large amount of structured knowledge exists only within a specific period. Knowledge graph representation learning aims to learn low-dimensional vector embeddings for entities and relations in a knowledge graph. The representation learning of temporal knowledge graphs incorporates time information into the standard knowledge graph framework and can model the dynamics of entities and relations over time. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive survey of temporal knowledge graph representation learning and its applications. We begin with an introduction to the definitions, datasets, and evaluation metrics for temporal knowledge graph representation learning. Next, we propose a taxonomy based on the core technologies of temporal knowledge graph representation learning methods, and provide an in-depth analysis of different methods in each category. Finally, we present various downstream applications related to the temporal knowledge graphs. In the end, we conclude the paper and have an outlook on the future research directions in this area.
An Effective and Efficient Time-aware Entity Alignment Framework via Two-aspect Three-view Label Propagation
Jul 12, 2023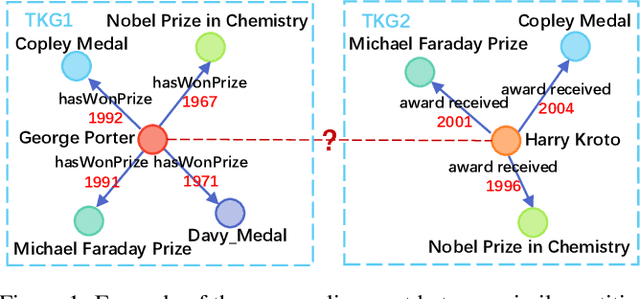
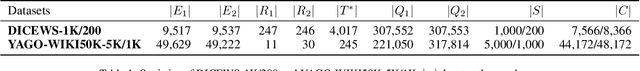
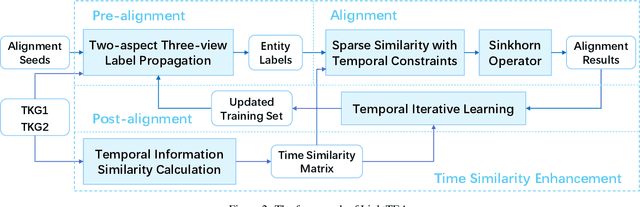
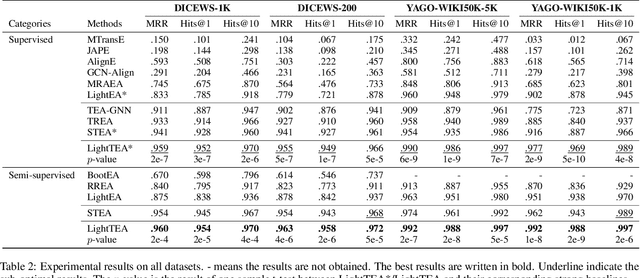
Abstract:Entity alignment (EA) aims to find the equivalent entity pairs between different knowledge graphs (KGs), which is crucial to promote knowledge fusion. With the wide use of temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs), time-aware EA (TEA) methods appear to enhance EA. Existing TEA models are based on Graph Neural Networks (GNN) and achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, but it is difficult to transfer them to large-scale TKGs due to the scalability issue of GNN. In this paper, we propose an effective and efficient non-neural EA framework between TKGs, namely LightTEA, which consists of four essential components: (1) Two-aspect Three-view Label Propagation, (2) Sparse Similarity with Temporal Constraints, (3) Sinkhorn Operator, and (4) Temporal Iterative Learning. All of these modules work together to improve the performance of EA while reducing the time consumption of the model. Extensive experiments on public datasets indicate that our proposed model significantly outperforms the SOTA methods for EA between TKGs, and the time consumed by LightTEA is only dozens of seconds at most, no more than 10% of the most efficient TEA method.
Vehicle-Human Interactive Behaviors in Emergency: Data Extraction from Traffic Accident Videos
Mar 02, 2020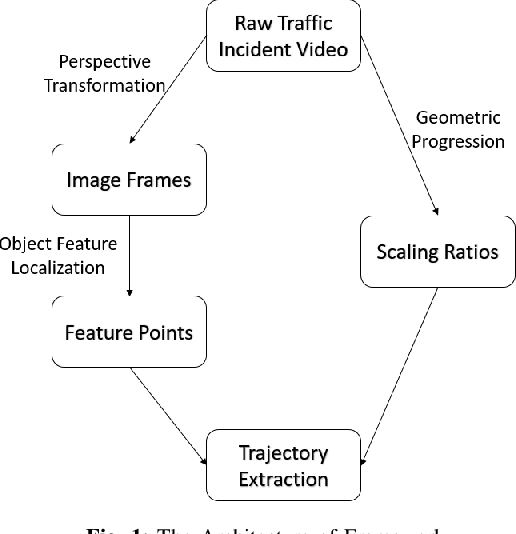


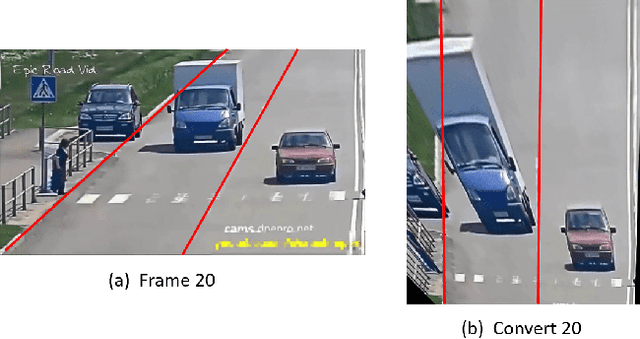
Abstract:Currently, studying the vehicle-human interactive behavior in the emergency needs a large amount of datasets in the actual emergent situations that are almost unavailable. Existing public data sources on autonomous vehicles (AVs) mainly focus either on the normal driving scenarios or on emergency situations without human involvement. To fill this gap and facilitate related research, this paper provides a new yet convenient way to extract the interactive behavior data (i.e., the trajectories of vehicles and humans) from actual accident videos that were captured by both the surveillance cameras and driving recorders. The main challenge for data extraction from real-time accident video lies in the fact that the recording cameras are un-calibrated and the angles of surveillance are unknown. The approach proposed in this paper employs image processing to obtain a new perspective which is different from the original video's perspective. Meanwhile, we manually detect and mark object feature points in each image frame. In order to acquire a gradient of reference ratios, a geometric model is implemented in the analysis of reference pixel value, and the feature points are then scaled to the object trajectory based on the gradient of ratios. The generated trajectories not only restore the object movements completely but also reflect changes in vehicle velocity and rotation based on the feature points distributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge