Cagri Ozcaglar
Entity Personalized Talent Search Models with Tree Interaction Features
Feb 25, 2019



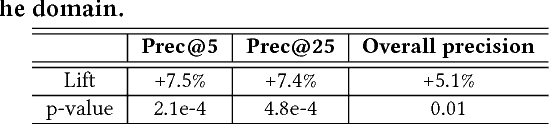
Abstract:Talent Search systems aim to recommend potential candidates who are a good match to the hiring needs of a recruiter expressed in terms of the recruiter's search query or job posting. Past work in this domain has focused on linear and nonlinear models which lack preference personalization in the user-level due to being trained only with globally collected recruiter activity data. In this paper, we propose an entity-personalized Talent Search model which utilizes a combination of generalized linear mixed (GLMix) models and gradient boosted decision tree (GBDT) models, and provides personalized talent recommendations using nonlinear tree interaction features generated by the GBDT. We also present the offline and online system architecture for the productionization of this hybrid model approach in our Talent Search systems. Finally, we provide offline and online experiment results benchmarking our entity-personalized model with tree interaction features, which demonstrate significant improvements in our precision metrics compared to globally trained non-personalized models.
Talent Search and Recommendation Systems at LinkedIn: Practical Challenges and Lessons Learned
Sep 18, 2018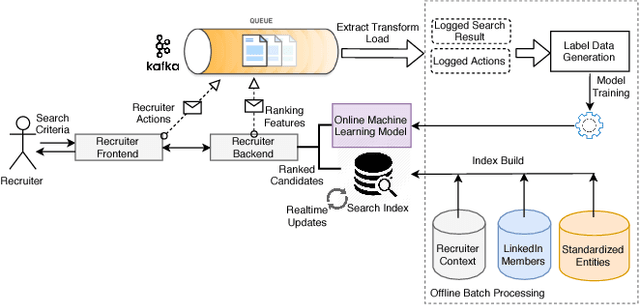
Abstract:LinkedIn Talent Solutions business contributes to around 65% of LinkedIn's annual revenue, and provides tools for job providers to reach out to potential candidates and for job seekers to find suitable career opportunities. LinkedIn's job ecosystem has been designed as a platform to connect job providers and job seekers, and to serve as a marketplace for efficient matching between potential candidates and job openings. A key mechanism to help achieve these goals is the LinkedIn Recruiter product, which enables recruiters to search for relevant candidates and obtain candidate recommendations for their job postings. In this work, we highlight a set of unique information retrieval, system, and modeling challenges associated with talent search and recommendation systems.
Towards Deep and Representation Learning for Talent Search at LinkedIn
Sep 17, 2018
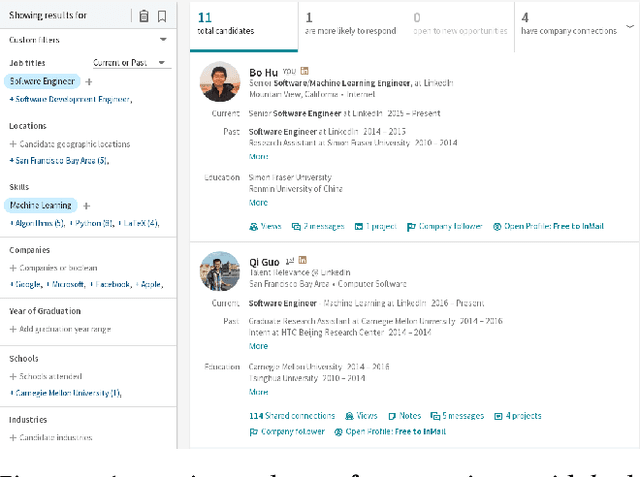
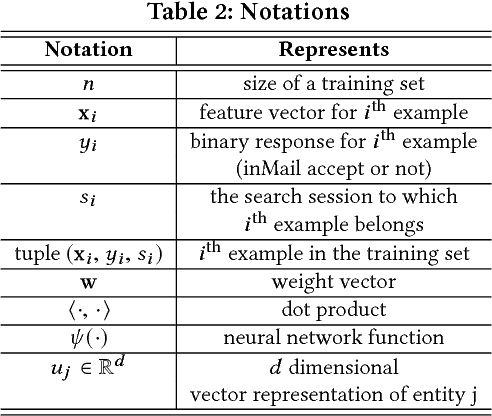
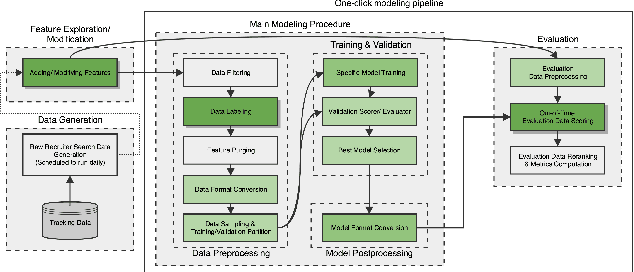
Abstract:Talent search and recommendation systems at LinkedIn strive to match the potential candidates to the hiring needs of a recruiter or a hiring manager expressed in terms of a search query or a job posting. Recent work in this domain has mainly focused on linear models, which do not take complex relationships between features into account, as well as ensemble tree models, which introduce non-linearity but are still insufficient for exploring all the potential feature interactions, and strictly separate feature generation from modeling. In this paper, we present the results of our application of deep and representation learning models on LinkedIn Recruiter. Our key contributions include: (i) Learning semantic representations of sparse entities within the talent search domain, such as recruiter ids, candidate ids, and skill entity ids, for which we utilize neural network models that take advantage of LinkedIn Economic Graph, and (ii) Deep models for learning recruiter engagement and candidate response in talent search applications. We also explore learning to rank approaches applied to deep models, and show the benefits for the talent search use case. Finally, we present offline and online evaluation results for LinkedIn talent search and recommendation systems, and discuss potential challenges along the path to a fully deep model architecture. The challenges and approaches discussed generalize to any multi-faceted search engine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge