Bojia Lin
Training A Multi-stage Deep Classifier with Feedback Signals
Nov 12, 2023Abstract:Multi-Stage Classifier (MSC) - several classifiers working sequentially in an arranged order and classification decision is partially made at each step - is widely used in industrial applications for various resource limitation reasons. The classifiers of a multi-stage process are usually Neural Network (NN) models trained independently or in their inference order without considering the signals from the latter stages. Aimed at two-stage binary classification process, the most common type of MSC, we propose a novel training framework, named Feedback Training. The classifiers are trained in an order reverse to their actual working order, and the classifier at the later stage is used to guide the training of initial-stage classifier via a sample weighting method. We experimentally show the efficacy of our proposed approach, and its great superiority under the scenario of few-shot training.
Rethinking the Value of Gazetteer in Chinese Named Entity Recognition
Jul 18, 2022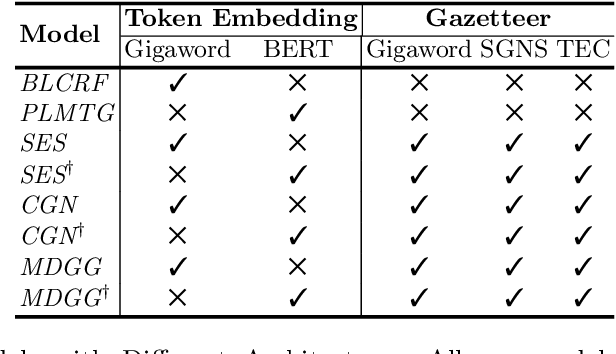

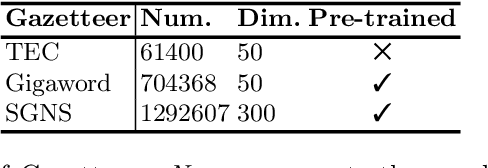

Abstract:Gazetteer is widely used in Chinese named entity recognition (NER) to enhance span boundary detection and type classification. However, to further understand the generalizability and effectiveness of gazetteers, the NLP community still lacks a systematic analysis of the gazetteer-enhanced NER model. In this paper, we first re-examine the effectiveness several common practices of the gazetteer-enhanced NER models and carry out a series of detailed analysis to evaluate the relationship between the model performance and the gazetteer characteristics, which can guide us to build a more suitable gazetteer. The findings of this paper are as follows: (1) the gazetteer improves most of the situations that the traditional NER model datasets are difficult to learn. (2) the performance of model greatly benefits from the high-quality pre-trained lexeme embeddings. (3) a good gazetteer should cover more entities that can be matched in both the training set and testing set.
Language Scaling for Universal Suggested Replies Model
Jun 04, 2021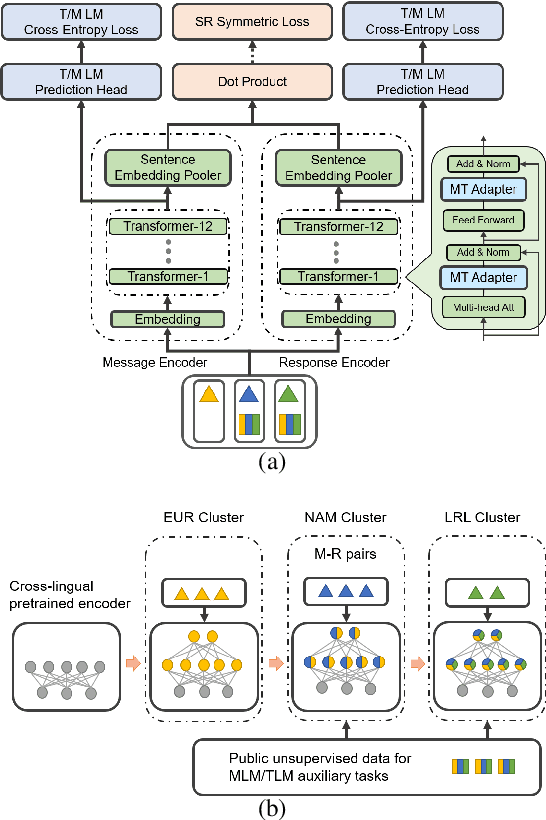
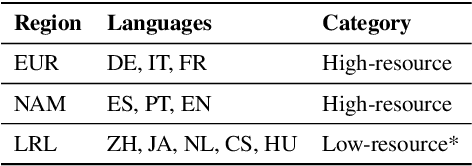
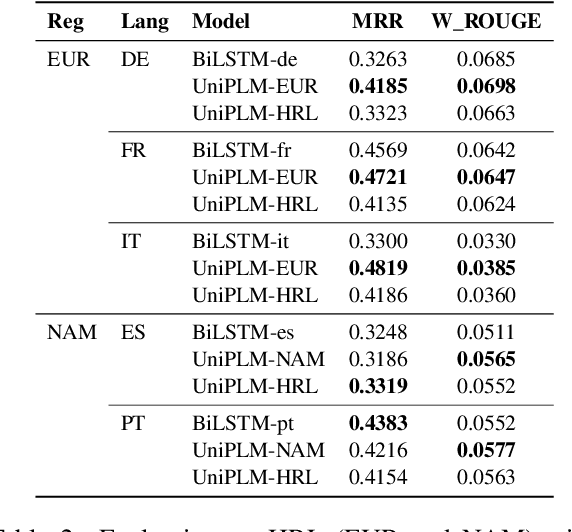
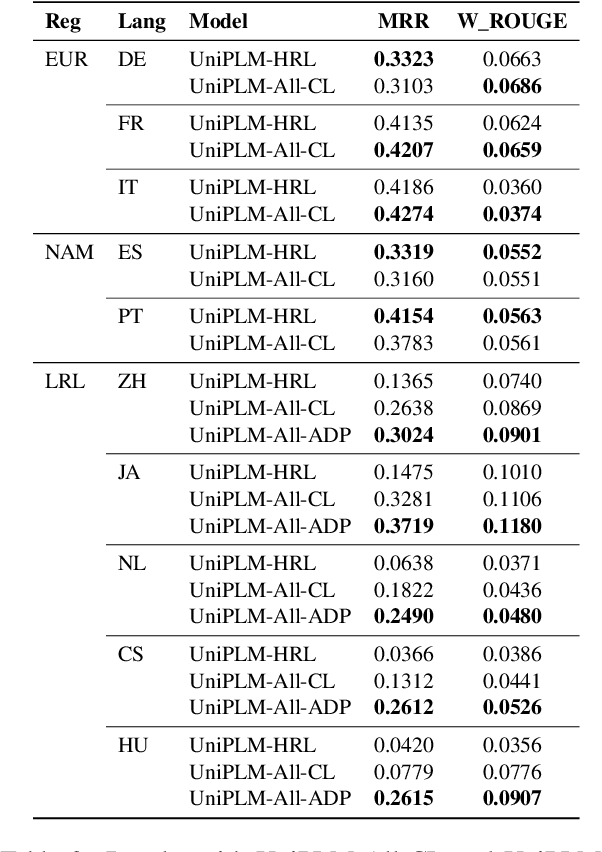
Abstract:We consider the problem of scaling automated suggested replies for Outlook email system to multiple languages. Faced with increased compute requirements and low resources for language expansion, we build a single universal model for improving the quality and reducing run-time costs of our production system. However, restricted data movement across regional centers prevents joint training across languages. To this end, we propose a multi-task continual learning framework, with auxiliary tasks and language adapters to learn universal language representation across regions. The experimental results show positive cross-lingual transfer across languages while reducing catastrophic forgetting across regions. Our online results on real user traffic show significant gains in CTR and characters saved, as well as 65% training cost reduction compared with per-language models. As a consequence, we have scaled the feature in multiple languages including low-resource markets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge