Bohui Fang
Dynamic Trip-Vehicle Dispatch with Scheduled and On-Demand Requests
Jul 20, 2019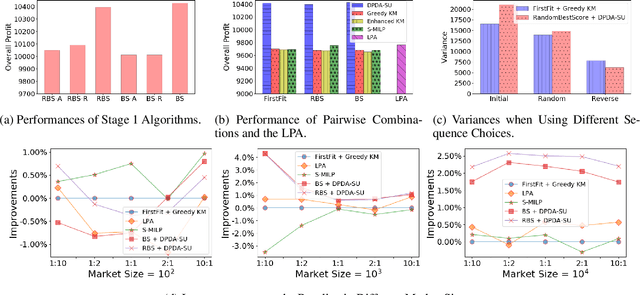
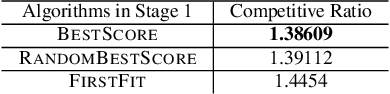
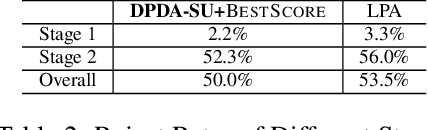
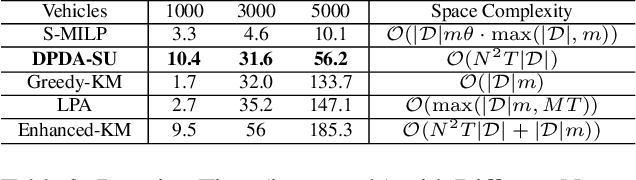
Abstract:Transportation service providers that dispatch drivers and vehicles to riders start to support both on-demand ride requests posted in real time and rides scheduled in advance, leading to new challenges which, to the best of our knowledge, have not been addressed by existing works. To fill the gap, we design novel trip-vehicle dispatch algorithms to handle both types of requests while taking into account an estimated request distribution of on-demand requests. At the core of the algorithms is the newly proposed Constrained Spatio-Temporal value function (CST-function), which is polynomial-time computable and represents the expected value a vehicle could gain with the constraint that it needs to arrive at a specific location at a given time. Built upon CST-function, we design a randomized best-fit algorithm for scheduled requests and an online planning algorithm for on-demand requests given the scheduled requests as constraints. We evaluate the algorithms through extensive experiments on a real-world dataset of an online ride-hailing platform.
Product-based Neural Networks for User Response Prediction over Multi-field Categorical Data
Jul 01, 2018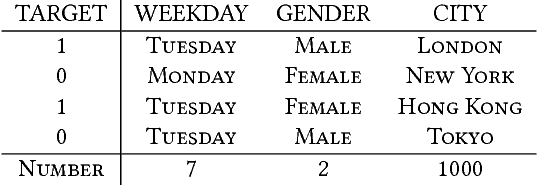
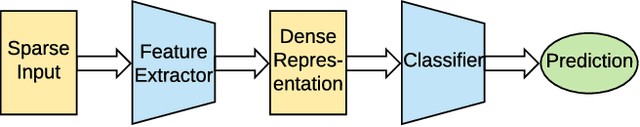
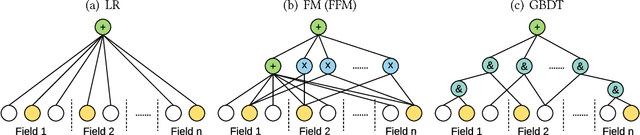
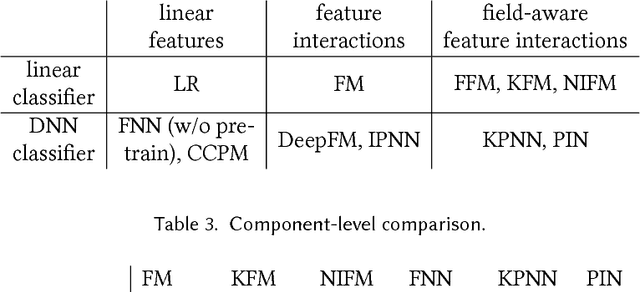
Abstract:User response prediction is a crucial component for personalized information retrieval and filtering scenarios, such as recommender system and web search. The data in user response prediction is mostly in a multi-field categorical format and transformed into sparse representations via one-hot encoding. Due to the sparsity problems in representation and optimization, most research focuses on feature engineering and shallow modeling. Recently, deep neural networks have attracted research attention on such a problem for their high capacity and end-to-end training scheme. In this paper, we study user response prediction in the scenario of click prediction. We first analyze a coupled gradient issue in latent vector-based models and propose kernel product to learn field-aware feature interactions. Then we discuss an insensitive gradient issue in DNN-based models and propose Product-based Neural Network (PNN) which adopts a feature extractor to explore feature interactions. Generalizing the kernel product to a net-in-net architecture, we further propose Product-network In Network (PIN) which can generalize previous models. Extensive experiments on 4 industrial datasets and 1 contest dataset demonstrate that our models consistently outperform 8 baselines on both AUC and log loss. Besides, PIN makes great CTR improvement (relatively 34.67%) in online A/B test.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge