Bing-Fei Wu
Boosting Online 3D Multi-Object Tracking through Camera-Radar Cross Check
Jul 18, 2024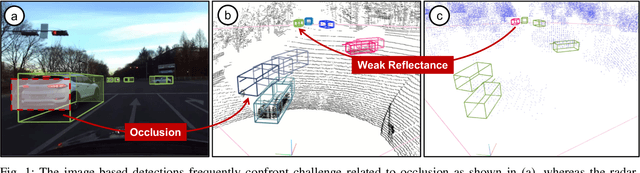
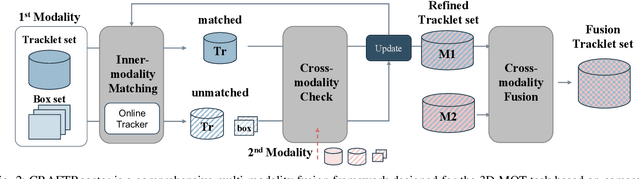
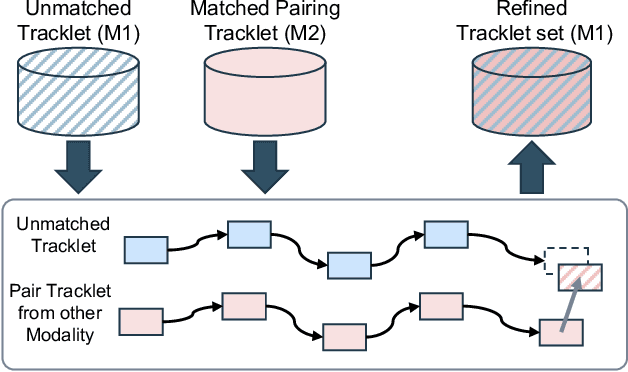
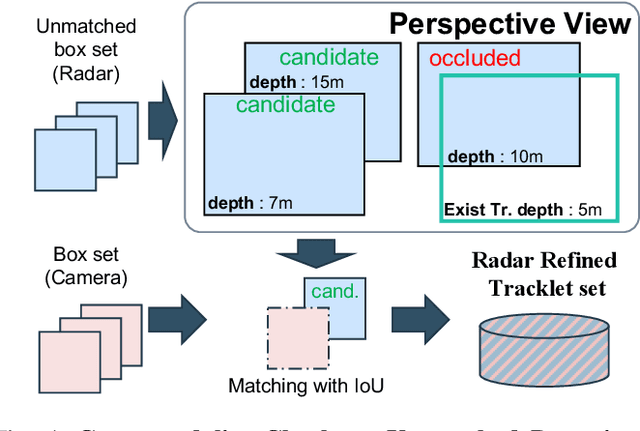
Abstract:In the domain of autonomous driving, the integration of multi-modal perception techniques based on data from diverse sensors has demonstrated substantial progress. Effectively surpassing the capabilities of state-of-the-art single-modality detectors through sensor fusion remains an active challenge. This work leverages the respective advantages of cameras in perspective view and radars in Bird's Eye View (BEV) to greatly enhance overall detection and tracking performance. Our approach, Camera-Radar Associated Fusion Tracking Booster (CRAFTBooster), represents a pioneering effort to enhance radar-camera fusion in the tracking stage, contributing to improved 3D MOT accuracy. The superior experimental results on the K-Radaar dataset, which exhibit 5-6% on IDF1 tracking performance gain, validate the potential of effective sensor fusion in advancing autonomous driving.
Mitigating Domain Mismatch in Face Recognition Using Style Matching
Feb 26, 2021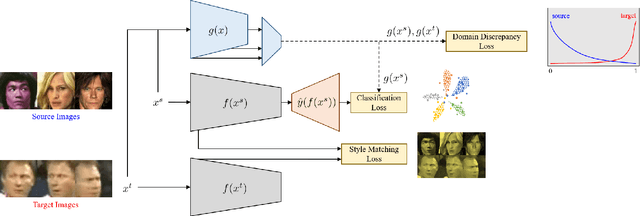
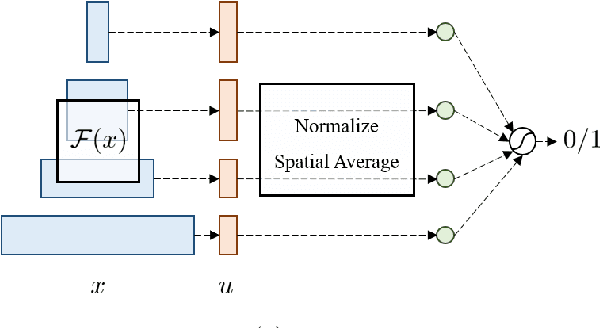

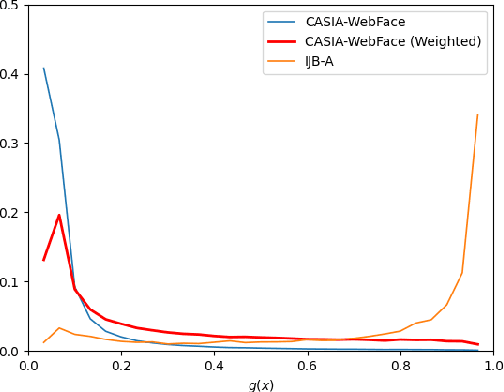
Abstract:Despite outstanding performance on public benchmarks, face recognition still suffers due to domain mismatch between training (source) and testing (target) data. Furthermore, these domains are not shared classes, which complicates domain adaptation. Since this is also a fine-grained classification problem which does not strictly follow the low-density separation principle, conventional domain adaptation approaches do not resolve these problems. In this paper, we formulate domain mismatch in face recognition as a style mismatch problem for which we propose two methods. First, we design a domain discriminator with human-level judgment to mine target-like images in the training data to mitigate the domain gap. Second, we extract style representations in low-level feature maps of the backbone model, and match the style distributions of the two domains to find a common style representation. Evaluations on verification and open-set and closed-set identification protocols show that both methods yield good improvements, and that performance is more robust if they are combined. Our approach is competitive with related work, and its effectiveness is verified in a practical application.
Domain Adapting Ability of Self-Supervised Learning for Face Recognition
Feb 26, 2021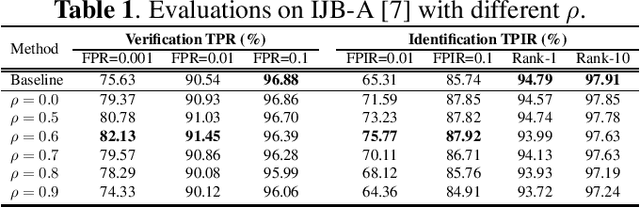
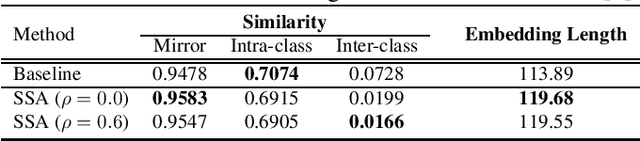

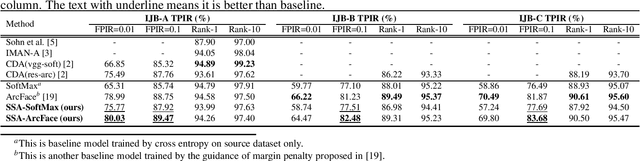
Abstract:Although deep convolutional networks have achieved great performance in face recognition tasks, the challenge of domain discrepancy still exists in real world applications. Lack of domain coverage of training data (source domain) makes the learned models degenerate in a testing scenario (target domain). In face recognition tasks, classes in two domains are usually different, so classical domain adaptation approaches, assuming there are shared classes in domains, may not be reasonable solutions for this problem. In this paper, self-supervised learning is adopted to learn a better embedding space where the subjects in target domain are more distinguishable. The learning goal is maximizing the similarity between the embeddings of each image and its mirror in both domains. The experiments show its competitive results compared with prior works. To know the reason why it can achieve such performance, we further discuss how this approach affects the learning of embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge