Bihong Zhang
Seed-ASR: Understanding Diverse Speech and Contexts with LLM-based Speech Recognition
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:Modern automatic speech recognition (ASR) model is required to accurately transcribe diverse speech signals (from different domains, languages, accents, etc) given the specific contextual information in various application scenarios. Classic end-to-end models fused with extra language models perform well, but mainly in data matching scenarios and are gradually approaching a bottleneck. In this work, we introduce Seed-ASR, a large language model (LLM) based speech recognition model. Seed-ASR is developed based on the framework of audio conditioned LLM (AcLLM), leveraging the capabilities of LLMs by inputting continuous speech representations together with contextual information into the LLM. Through stage-wise large-scale training and the elicitation of context-aware capabilities in LLM, Seed-ASR demonstrates significant improvement over end-to-end models on comprehensive evaluation sets, including multiple domains, accents/dialects and languages. Additionally, Seed-ASR can be further deployed to support specific needs in various scenarios without requiring extra language models. Compared to recently released large ASR models, Seed-ASR achieves 10%-40% reduction in word (or character, for Chinese) error rates on Chinese and English public test sets, further demonstrating its powerful performance.
A meta learning scheme for fast accent domain expansion in Mandarin speech recognition
Jul 23, 2023Abstract:Spoken languages show significant variation across mandarin and accent. Despite the high performance of mandarin automatic speech recognition (ASR), accent ASR is still a challenge task. In this paper, we introduce meta-learning techniques for fast accent domain expansion in mandarin speech recognition, which expands the field of accents without deteriorating the performance of mandarin ASR. Meta-learning or learn-to-learn can learn general relation in multi domains not only for over-fitting a specific domain. So we select meta-learning in the domain expansion task. This more essential learning will cause improved performance on accent domain extension tasks. We combine the methods of meta learning and freeze of model parameters, which makes the recognition performance more stable in different cases and the training faster about 20%. Our approach significantly outperforms other methods about 3% relatively in the accent domain expansion task. Compared to the baseline model, it improves relatively 37% under the condition that the mandarin test set remains unchanged. In addition, it also proved this method to be effective on a large amount of data with a relative performance improvement of 4% on the accent test set.
Nextformer: A ConvNeXt Augmented Conformer For End-To-End Speech Recognition
Jun 30, 2022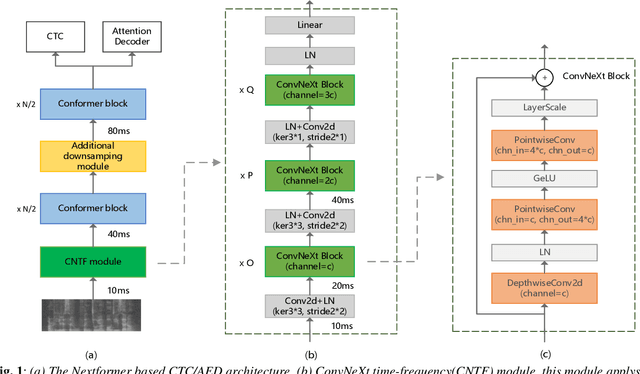
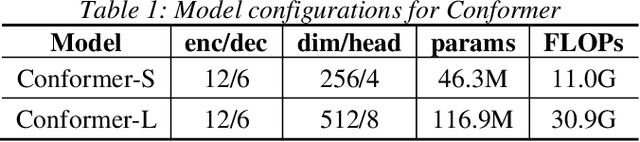
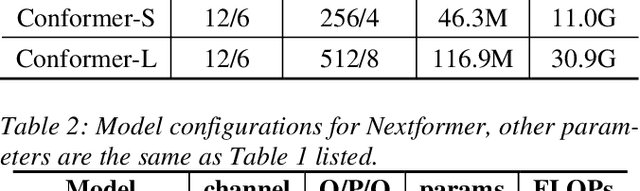
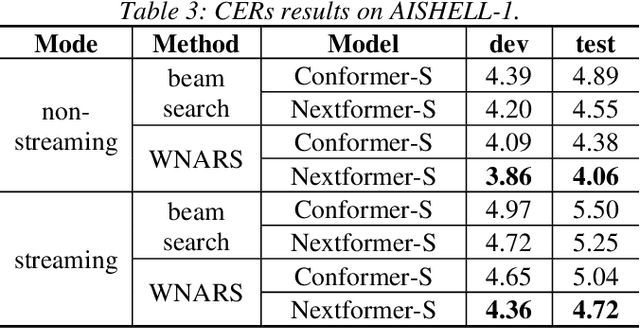
Abstract:Conformer models have achieved state-of-the-art(SOTA) results in end-to-end speech recognition. However Conformer mainly focuses on temporal modeling while pays less attention on time-frequency property of speech feature. In this paper we augment Conformer with ConvNeXt and propose Nextformer structure. We use stacks of ConvNeXt block to replace the commonly used subsampling module in Conformer for utilizing the information contained in time-frequency speech feature. Besides, we insert an additional downsampling module in middle of Conformer layers to make our model more efficient and accurate. We conduct experiments on two opening datasets, AISHELL-1 and WenetSpeech. On AISHELL-1, compared to Conformer baselines, Nextformer obtains 7.3% and 6.3% relative CER reduction in non-streaming and streaming mode respectively, and on a much larger WenetSpeech dataset, Nextformer gives 5.0%~6.5% and 7.5%~14.6% relative CER reduction in non-streaming and streaming mode, while keep the computational cost FLOPs comparable to Conformer. To the best of our knowledge, the proposed Nextformer model achieves SOTA results on AISHELL-1(CER 4.06%) and WenetSpeech(CER 7.56%/11.29%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge