Bertrand Cornélusse
Deep generative modeling for probabilistic forecasting in power systems
Jun 30, 2021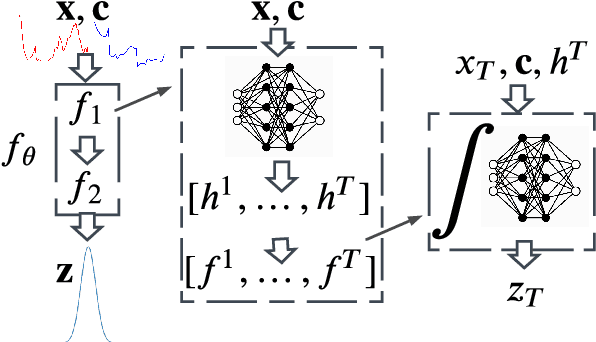
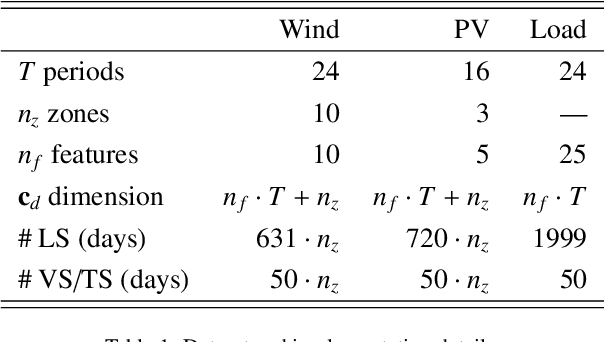
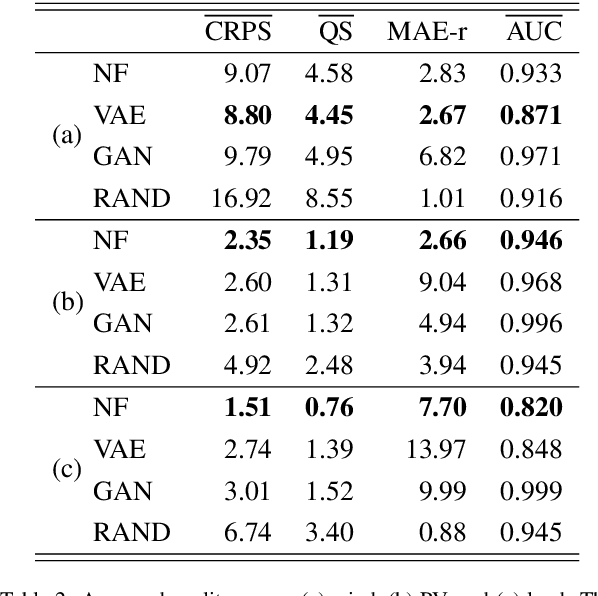
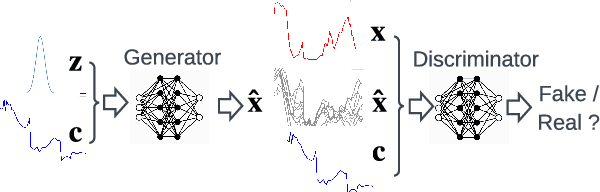
Abstract:Greater direct electrification of end-use sectors with a higher share of renewables is one of the pillars to power a carbon-neutral society by 2050. This study uses a recent deep learning technique, the normalizing flows, to produce accurate probabilistic forecasts that are crucial for decision-makers to face the new challenges in power systems applications. Through comprehensive empirical evaluations using the open data of the Global Energy Forecasting Competition 2014, we demonstrate that our methodology is competitive with other state-of-the-art deep learning generative models: generative adversarial networks and variational autoencoders. The models producing weather-based wind, solar power, and load scenarios are properly compared both in terms of forecast value, by considering the case study of an energy retailer, and quality using several complementary metrics.
A Probabilistic Forecast-Driven Strategy for a Risk-Aware Participation in the Capacity Firming Market
Jun 21, 2021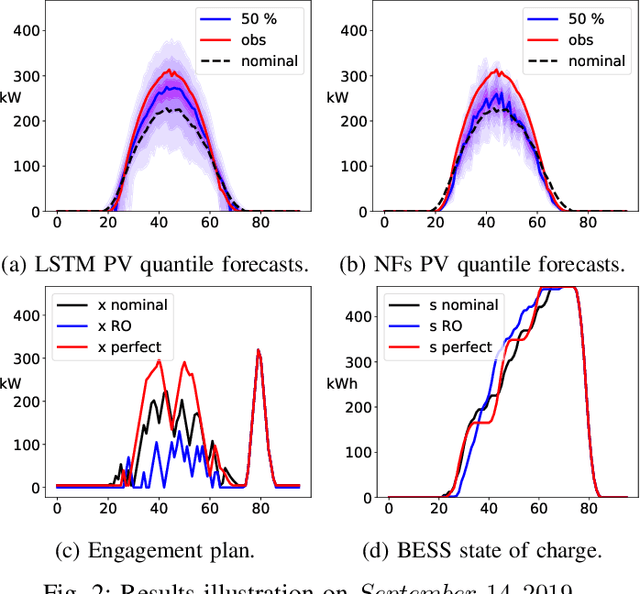
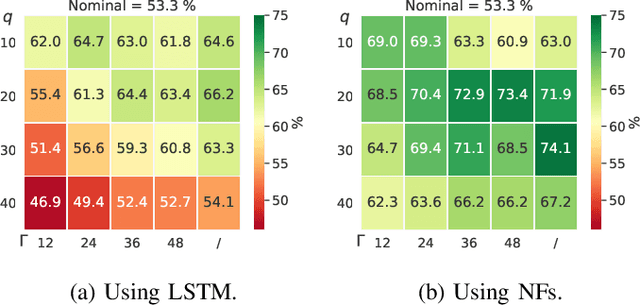
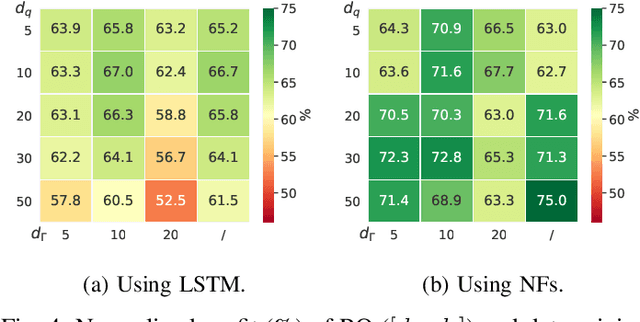
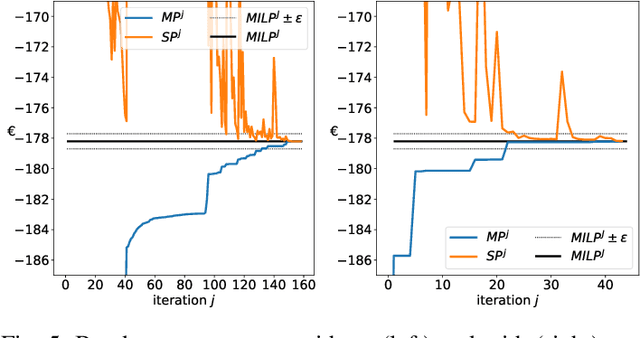
Abstract:The core contribution is to propose a probabilistic forecast-driven strategy, modeled as a min-max-min robust optimization problem with recourse, and solved using a Benders-dual cutting plane algorithm in a tractable manner. The convergence is improved by building an initial set of cuts. In addition, a dynamic risk-averse parameters selection strategy based on the quantile forecasts distribution is proposed. A secondary contribution is to use a recently developed deep learning model known as normalizing flows to generate quantile forecasts of renewable generation for the robust optimization problem. This technique provides a general mechanism for defining expressive probability distributions, only requiring the specification of a base distribution and a series of bijective transformations. Overall, the robust approach improves the results over a deterministic approach with nominal point forecasts by finding a trade-off between conservative and risk-seeking policies. The case study uses the photovoltaic generation monitored on-site at the University of Li\`ege (ULi\`ege), Belgium.
Probabilistic Forecasting of Imbalance Prices in the Belgian Context
Jun 09, 2021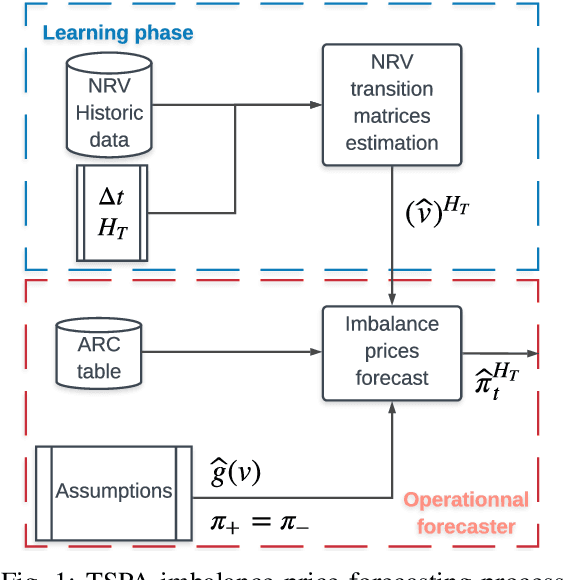
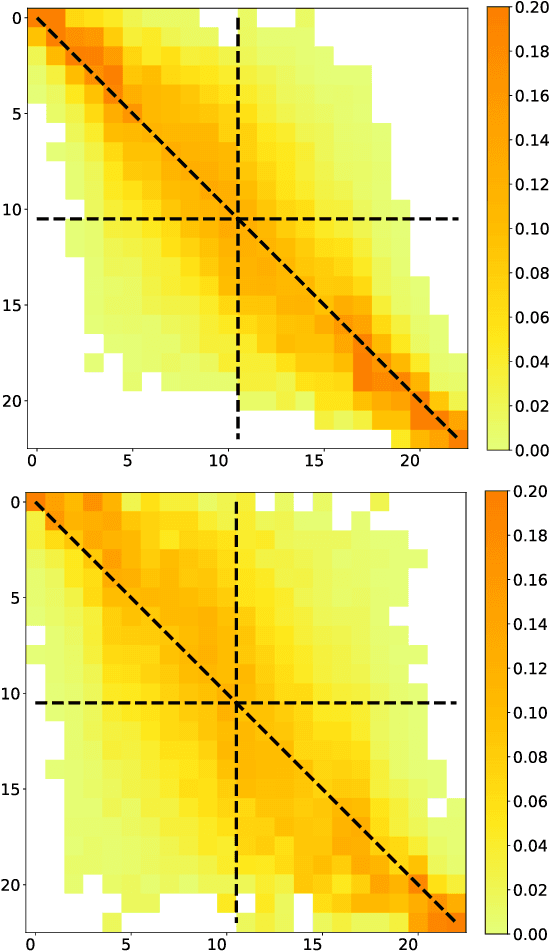


Abstract:Forecasting imbalance prices is essential for strategic participation in the short-term energy markets. A novel two-step probabilistic approach is proposed, with a particular focus on the Belgian case. The first step consists of computing the net regulation volume state transition probabilities. It is modeled as a matrix computed using historical data. This matrix is then used to infer the imbalance prices since the net regulation volume can be related to the level of reserves activated and the corresponding marginal prices for each activation level are published by the Belgian Transmission System Operator one day before electricity delivery. This approach is compared to a deterministic model, a multi-layer perceptron, and a widely used probabilistic technique, Gaussian Processes.
Deep learning-based multi-output quantile forecasting of PV generation
Jun 07, 2021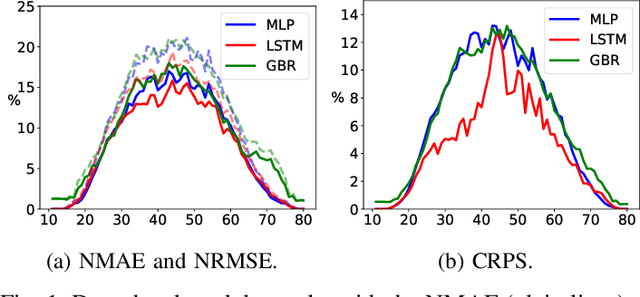

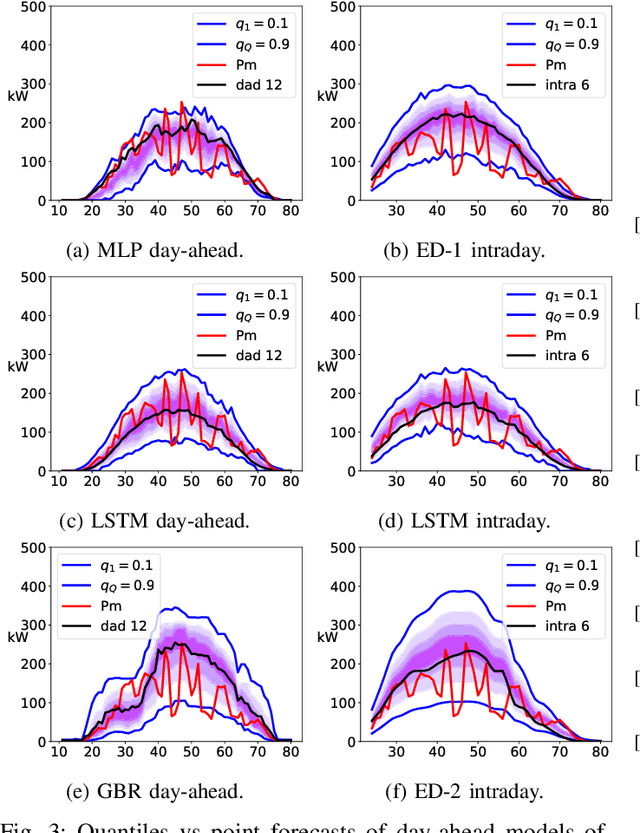
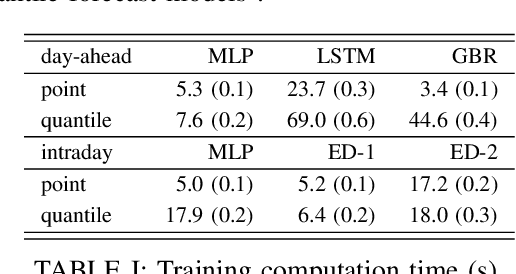
Abstract:This paper develops probabilistic PV forecasters by taking advantage of recent breakthroughs in deep learning. It tailored forecasting tool, named encoder-decoder, is implemented to compute intraday multi-output PV quantiles forecasts to efficiently capture the time correlation. The models are trained using quantile regression, a non-parametric approach that assumes no prior knowledge of the probabilistic forecasting distribution. The case study is composed of PV production monitored on-site at the University of Li\`ege (ULi\`ege), Belgium. The weather forecasts from the regional climate model provided by the Laboratory of Climatology are used as inputs of the deep learning models. The forecast quality is quantitatively assessed by the continuous ranked probability and interval scores. The results indicate this architecture improves the forecast quality and is computationally efficient to be incorporated in an intraday decision-making tool for robust optimization.
Lifelong Control of Off-grid Microgrid with Model Based Reinforcement Learning
May 16, 2020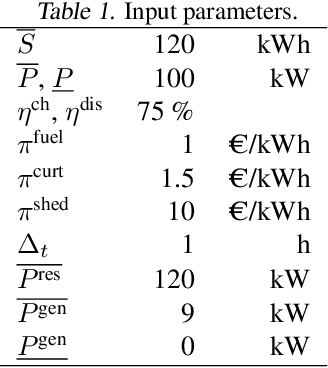
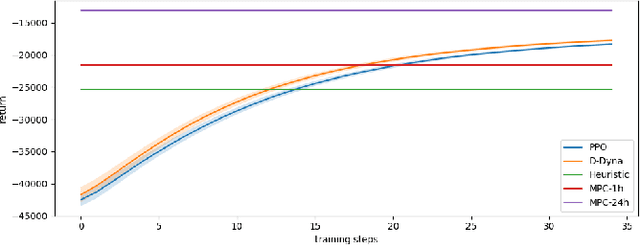
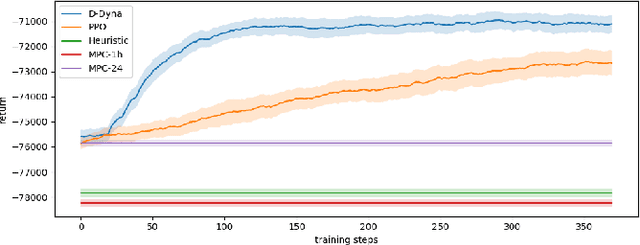
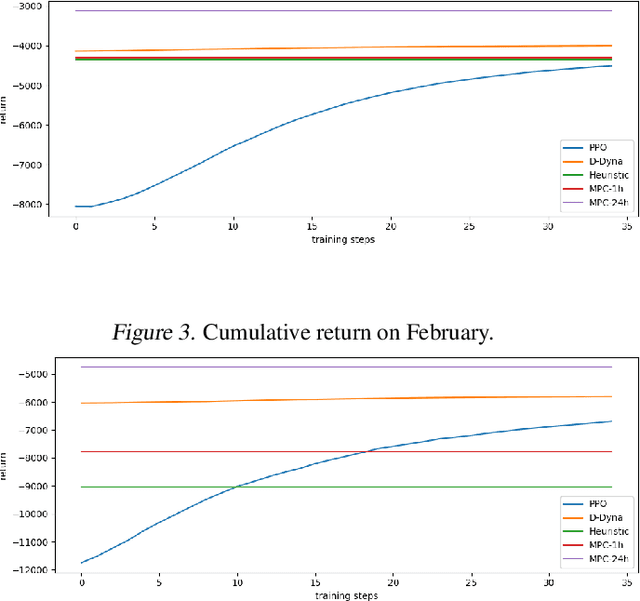
Abstract:The lifelong control problem of an off-grid microgrid is composed of two tasks, namely estimation of the condition of the microgrid devices and operational planning accounting for the uncertainties by forecasting the future consumption and the renewable production. The main challenge for the effective control arises from the various changes that take place over time. In this paper, we present an open-source reinforcement framework for the modeling of an off-grid microgrid for rural electrification. The lifelong control problem of an isolated microgrid is formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP). We categorize the set of changes that can occur in progressive and abrupt changes. We propose a novel model based reinforcement learning algorithm that is able to address both types of changes. In particular the proposed algorithm demonstrates generalisation properties, transfer capabilities and better robustness in case of fast-changing system dynamics. The proposed algorithm is compared against a rule-based policy and a model predictive controller with look-ahead. The results show that the trained agent is able to outperform both benchmarks in the lifelong setting where the system dynamics are changing over time.
A Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for Continuous Intraday Market Bidding
Apr 13, 2020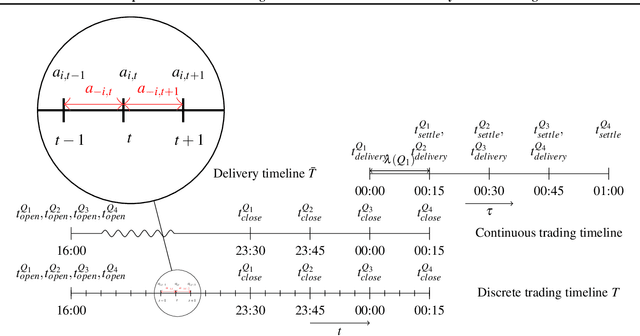
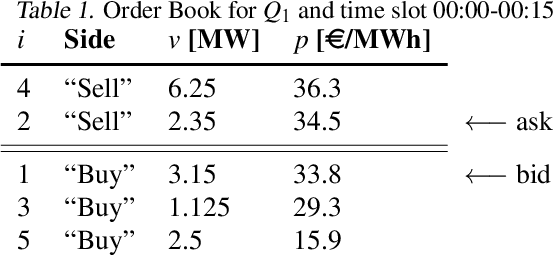
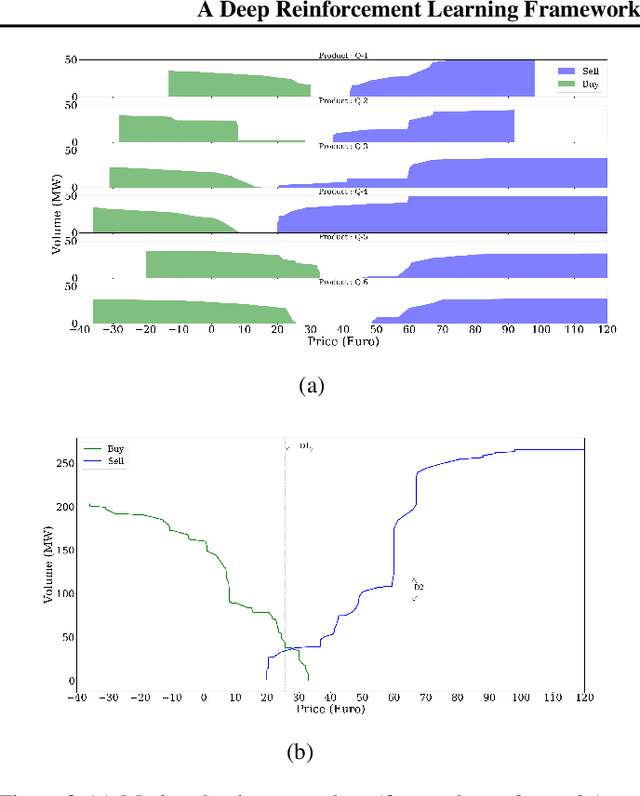

Abstract:The large integration of variable energy resources is expected to shift a large part of the energy exchanges closer to real-time, where more accurate forecasts are available. In this context, the short-term electricity markets and in particular the intraday market are considered a suitable trading floor for these exchanges to occur. A key component for the successful renewable energy sources integration is the usage of energy storage. In this paper, we propose a novel modelling framework for the strategic participation of energy storage in the European continuous intraday market where exchanges occur through a centralized order book. The goal of the storage device operator is the maximization of the profits received over the entire trading horizon, while taking into account the operational constraints of the unit. The sequential decision-making problem of trading in the intraday market is modelled as a Markov Decision Process. An asynchronous distributed version of the fitted Q iteration algorithm is chosen for solving this problem due to its sample efficiency. The large and variable number of the existing orders in the order book motivates the use of high-level actions and an alternative state representation. Historical data are used for the generation of a large number of artificial trajectories in order to address exploration issues during the learning process. The resulting policy is back-tested and compared against a benchmark strategy that is the current industrial standard. Results indicate that the agent converges to a policy that achieves in average higher total revenues than the benchmark strategy.
Classification of load forecasting studies by forecasting problem to select load forecasting techniques and methodologies
Dec 21, 2018



Abstract:This article proposes a two-dimensional classification methodology to select the relevant forecasting tools developed by the scientific community based on a classification of load forecasting studies. The inputs of the classifier are the articles of the literature and the outputs are articles classified into categories. The classification process relies on two couple of parameters that defines a forecasting problem. The temporal couple is the forecasting horizon and the forecasting resolution. The system couple is the system size and the load resolution. Each article is classified with key information about the dataset used and the forecasting tools implemented: the forecasting techniques (probabilistic or deterministic) and methodologies, the cleansing data techniques and the error metrics. This process is illustrated by reviewing and classifying thirty-four articles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge