Bao-Sinh Nguyen
Universal Graph Continual Learning
Aug 27, 2023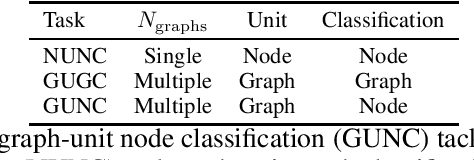
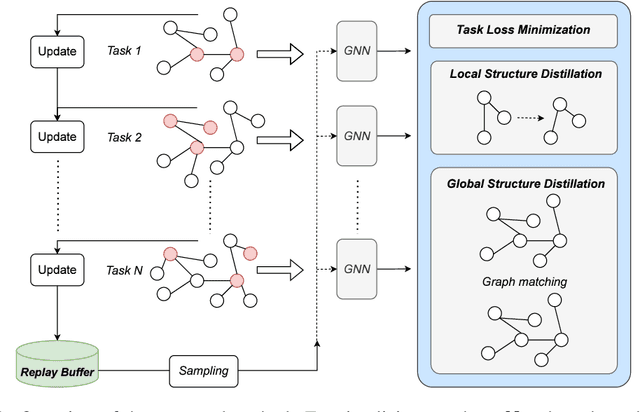
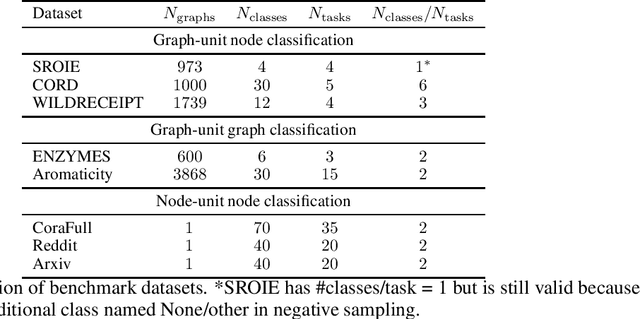
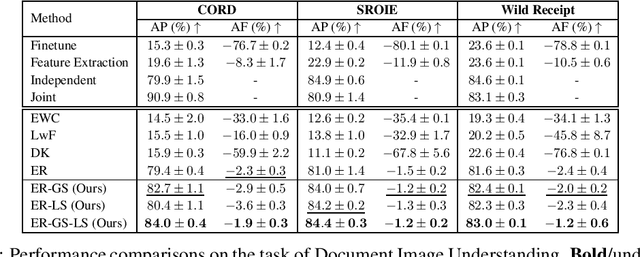
Abstract:We address catastrophic forgetting issues in graph learning as incoming data transits from one to another graph distribution. Whereas prior studies primarily tackle one setting of graph continual learning such as incremental node classification, we focus on a universal approach wherein each data point in a task can be a node or a graph, and the task varies from node to graph classification. We propose a novel method that enables graph neural networks to excel in this universal setting. Our approach perseveres knowledge about past tasks through a rehearsal mechanism that maintains local and global structure consistency across the graphs. We benchmark our method against various continual learning baselines in real-world graph datasets and achieve significant improvement in average performance and forgetting across tasks.
Improving Document Image Understanding with Reinforcement Finetuning
Sep 26, 2022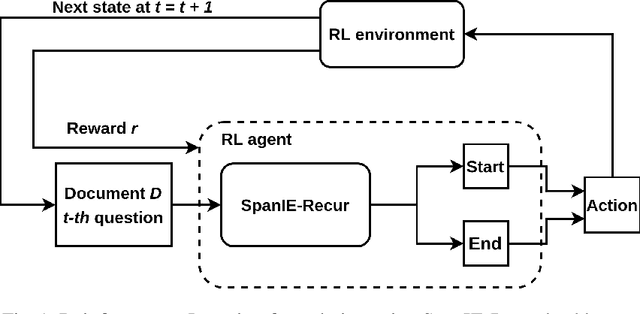
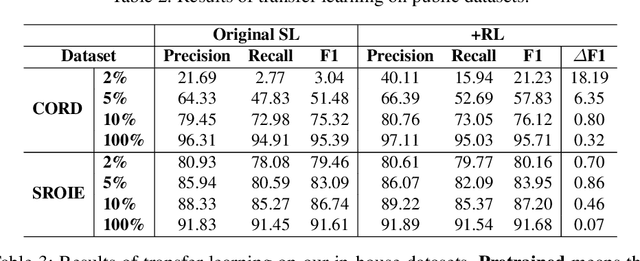
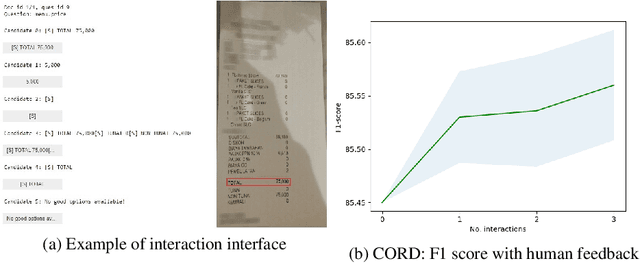
Abstract:Successful Artificial Intelligence systems often require numerous labeled data to extract information from document images. In this paper, we investigate the problem of improving the performance of Artificial Intelligence systems in understanding document images, especially in cases where training data is limited. We address the problem by proposing a novel finetuning method using reinforcement learning. Our approach treats the Information Extraction model as a policy network and uses policy gradient training to update the model to maximize combined reward functions that complement the traditional cross-entropy losses. Our experiments on four datasets using labels and expert feedback demonstrate that our finetuning mechanism consistently improves the performance of a state-of-the-art information extractor, especially in the small training data regime.
HYCEDIS: HYbrid Confidence Engine for Deep Document Intelligence System
Jun 01, 2022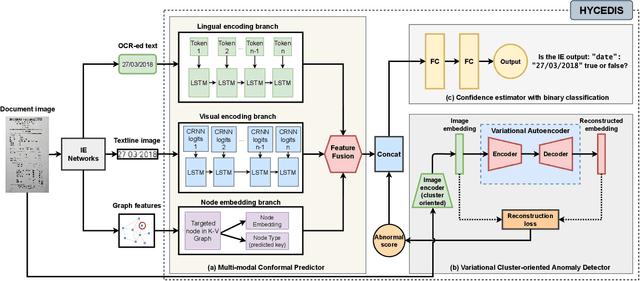
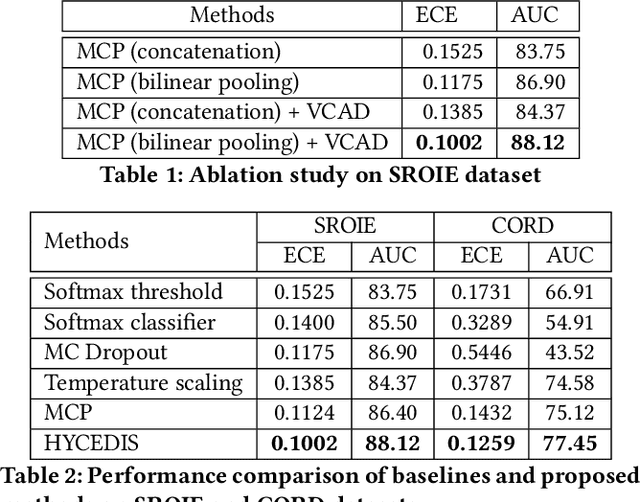
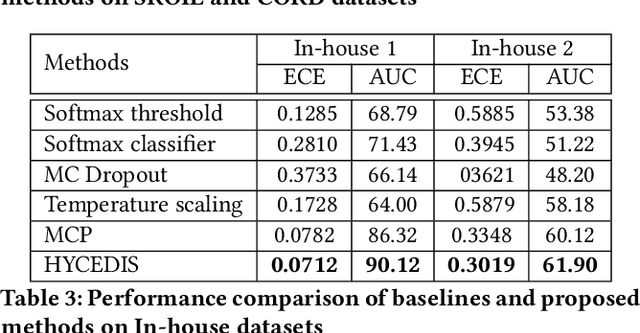
Abstract:Measuring the confidence of AI models is critical for safely deploying AI in real-world industrial systems. One important application of confidence measurement is information extraction from scanned documents. However, there exists no solution to provide reliable confidence score for current state-of-the-art deep-learning-based information extractors. In this paper, we propose a complete and novel architecture to measure confidence of current deep learning models in document information extraction task. Our architecture consists of a Multi-modal Conformal Predictor and a Variational Cluster-oriented Anomaly Detector, trained to faithfully estimate its confidence on its outputs without the need of host models modification. We evaluate our architecture on real-wold datasets, not only outperforming competing confidence estimators by a huge margin but also demonstrating generalization ability to out-of-distribution data.
Make The Most of Prior Data: A Solution for Interactive Text Summarization with Preference Feedback
Apr 12, 2022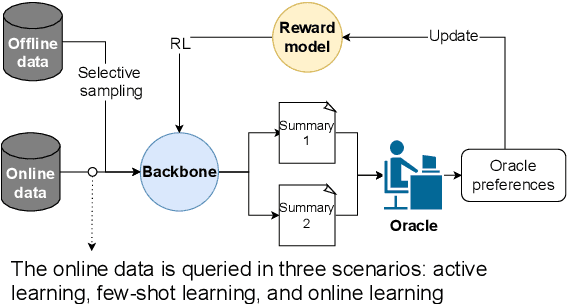

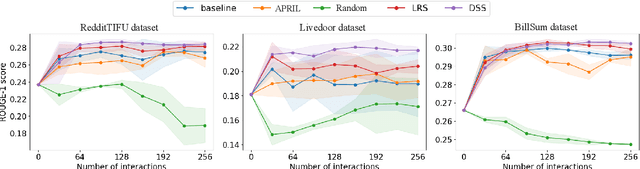

Abstract:For summarization, human preference is critical to tame outputs of the summarizer in favor of human interests, as ground-truth summaries are scarce and ambiguous. Practical settings require dynamic exchanges between human and AI agent wherein feedback is provided in an online manner, a few at a time. In this paper, we introduce a new framework to train summarization models with preference feedback interactively. By properly leveraging offline data and a novel reward model, we improve the performance regarding ROUGE scores and sample-efficiency. Our experiments on three various datasets confirm the benefit of the proposed framework in active, few-shot and online settings of preference learning.
Robust Deep Reinforcement Learning for Extractive Legal Summarization
Nov 23, 2021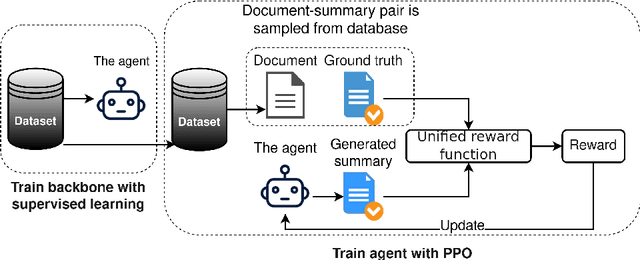
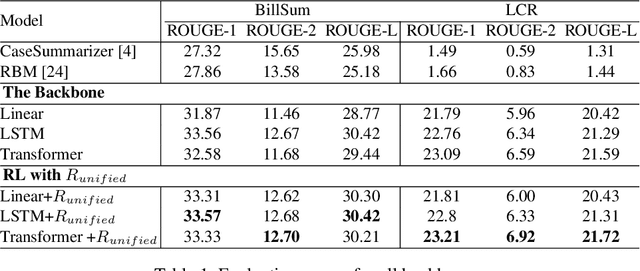


Abstract:Automatic summarization of legal texts is an important and still a challenging task since legal documents are often long and complicated with unusual structures and styles. Recent advances of deep models trained end-to-end with differentiable losses can well-summarize natural text, yet when applied to legal domain, they show limited results. In this paper, we propose to use reinforcement learning to train current deep summarization models to improve their performance on the legal domain. To this end, we adopt proximal policy optimization methods and introduce novel reward functions that encourage the generation of candidate summaries satisfying both lexical and semantic criteria. We apply our method to training different summarization backbones and observe a consistent and significant performance gain across 3 public legal datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge