Tuan-Anh Nguyen Dang
HYCEDIS: HYbrid Confidence Engine for Deep Document Intelligence System
Jun 01, 2022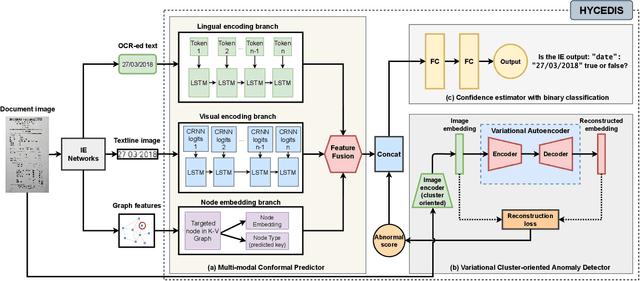
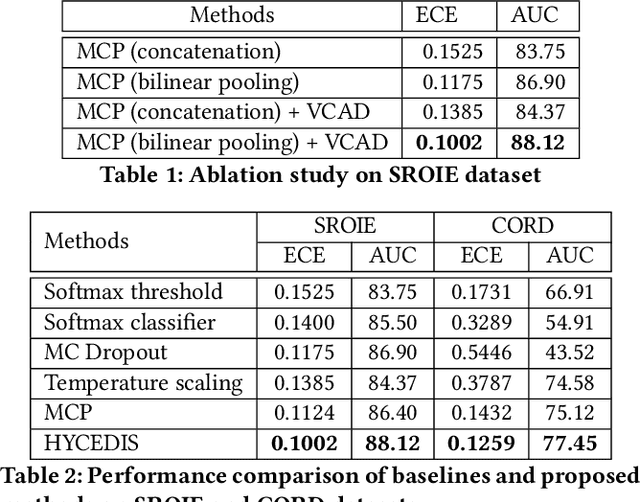
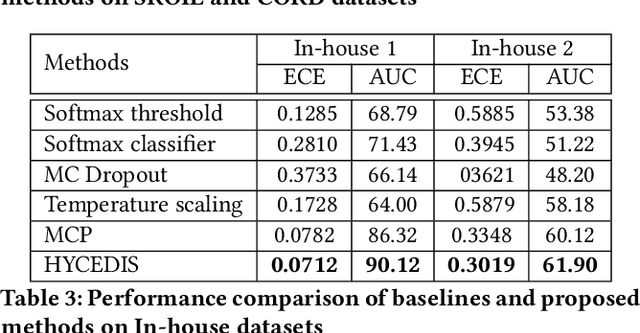
Abstract:Measuring the confidence of AI models is critical for safely deploying AI in real-world industrial systems. One important application of confidence measurement is information extraction from scanned documents. However, there exists no solution to provide reliable confidence score for current state-of-the-art deep-learning-based information extractors. In this paper, we propose a complete and novel architecture to measure confidence of current deep learning models in document information extraction task. Our architecture consists of a Multi-modal Conformal Predictor and a Variational Cluster-oriented Anomaly Detector, trained to faithfully estimate its confidence on its outputs without the need of host models modification. We evaluate our architecture on real-wold datasets, not only outperforming competing confidence estimators by a huge margin but also demonstrating generalization ability to out-of-distribution data.
End-to-End Hierarchical Relation Extraction for Generic Form Understanding
Jun 02, 2021

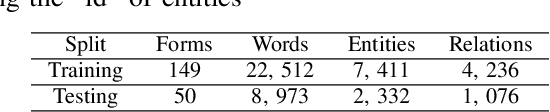
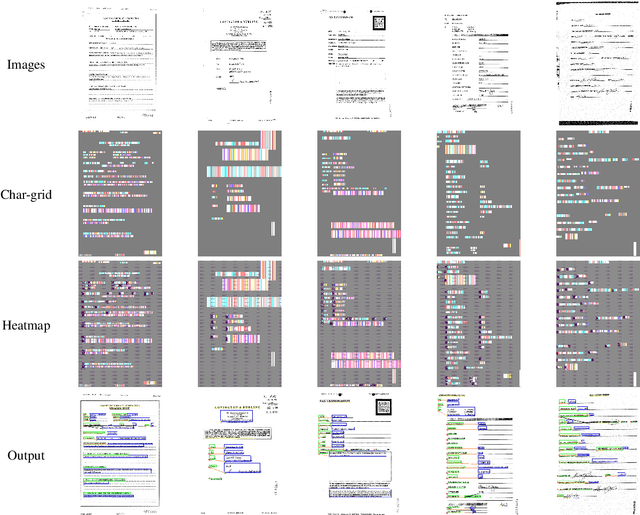
Abstract:Form understanding is a challenging problem which aims to recognize semantic entities from the input document and their hierarchical relations. Previous approaches face significant difficulty dealing with the complexity of the task, thus treat these objectives separately. To this end, we present a novel deep neural network to jointly perform both entity detection and link prediction in an end-to-end fashion. Our model extends the Multi-stage Attentional U-Net architecture with the Part-Intensity Fields and Part-Association Fields for link prediction, enriching the spatial information flow with the additional supervision from entity linking. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the model on the Form Understanding in Noisy Scanned Documents (FUNSD) dataset, where our method substantially outperforms the original model and state-of-the-art baselines in both Entity Labeling and Entity Linking task.
* Accepted to ICPR 2020
End-to-End Information Extraction by Character-Level Embedding and Multi-Stage Attentional U-Net
Jun 02, 2021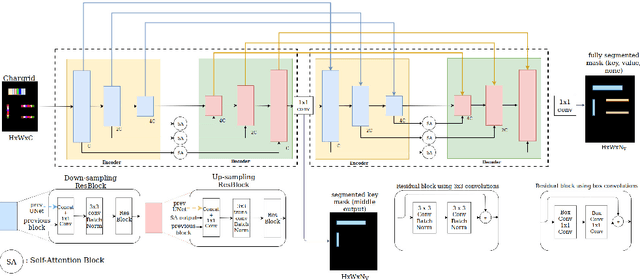
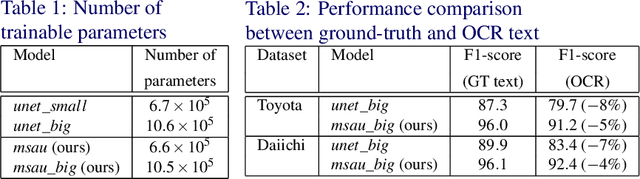
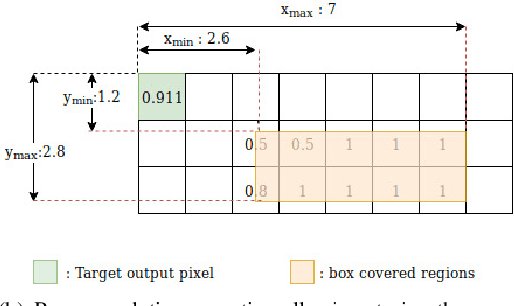
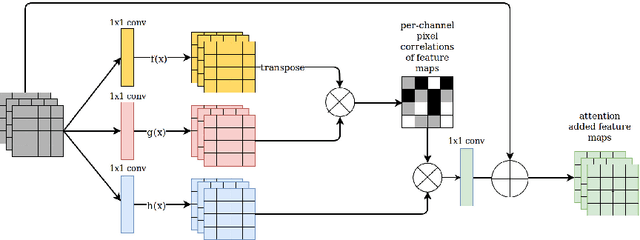
Abstract:Information extraction from document images has received a lot of attention recently, due to the need for digitizing a large volume of unstructured documents such as invoices, receipts, bank transfers, etc. In this paper, we propose a novel deep learning architecture for end-to-end information extraction on the 2D character-grid embedding of the document, namely the \textit{Multi-Stage Attentional U-Net}. To effectively capture the textual and spatial relations between 2D elements, our model leverages a specialized multi-stage encoder-decoders design, in conjunction with efficient uses of the self-attention mechanism and the box convolution. Experimental results on different datasets show that our model outperforms the baseline U-Net architecture by a large margin while using 40\% fewer parameters. Moreover, it also significantly improved the baseline in erroneous OCR and limited training data scenario, thus becomes practical for real-world applications.
* Accepted to BMVC 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge