Aysa Xuemo Fan
Evaluating the Quality of Code Comments Generated by Large Language Models for Novice Programmers
Sep 22, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise in generating code comments for novice programmers, but their educational effectiveness remains under-evaluated. This study assesses the instructional quality of code comments produced by GPT-4, GPT-3.5-Turbo, and Llama2, compared to expert-developed comments, focusing on their suitability for novices. Analyzing a dataset of ``easy'' level Java solutions from LeetCode, we find that GPT-4 exhibits comparable quality to expert comments in aspects critical for beginners, such as clarity, beginner-friendliness, concept elucidation, and step-by-step guidance. GPT-4 outperforms Llama2 in discussing complexity (chi-square = 11.40, p = 0.001) and is perceived as significantly more supportive for beginners than GPT-3.5 and Llama2 with Mann-Whitney U-statistics = 300.5 and 322.5, p = 0.0017 and 0.0003). This study highlights the potential of LLMs for generating code comments tailored to novice programmers.
Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models in Generating Code-Tracing Questions for Introductory Programming Courses
Oct 23, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we explore the application of large language models (LLMs) for generating code-tracing questions in introductory programming courses. We designed targeted prompts for GPT4, guiding it to generate code-tracing questions based on code snippets and descriptions. We established a set of human evaluation metrics to assess the quality of questions produced by the model compared to those created by human experts. Our analysis provides insights into the capabilities and potential of LLMs in generating diverse code-tracing questions. Additionally, we present a unique dataset of human and LLM-generated tracing questions, serving as a valuable resource for both the education and NLP research communities. This work contributes to the ongoing dialogue on the potential uses of LLMs in educational settings.
ConEntail: An Entailment-based Framework for Universal Zero and Few Shot Classification with Supervised Contrastive Pretraining
Oct 14, 2022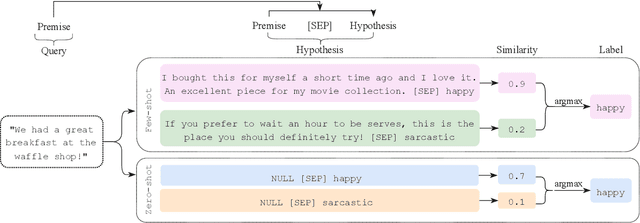
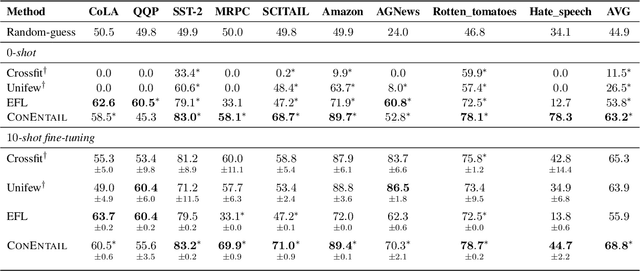
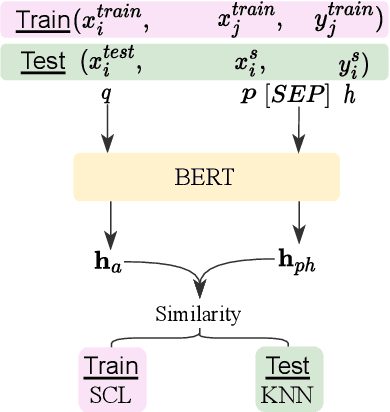
Abstract:A universal classification model aims to generalize to diverse classification tasks in both zero and few shot settings. A promising way toward universal classification is to cast heterogeneous data formats into a dataset-agnostic "meta-task" (e.g., textual entailment, question answering) then pretrain a model on the combined meta dataset. The existing work is either pretrained on specific subsets of classification tasks, or pretrained on both classification and generation data but the model could not fulfill its potential in universality and reliability. These also leave a massive amount of annotated data under-exploited. To fill these gaps, we propose ConEntail, a new framework for universal zero and few shot classification with supervised contrastive pretraining. Our unified meta-task for classification is based on nested entailment. It can be interpreted as "Does sentence a entails [sentence b entails label c]". This formulation enables us to make better use of 57 annotated classification datasets for supervised contrastive pretraining and universal evaluation. In this way, ConEntail helps the model (1) absorb knowledge from different datasets, and (2) gain consistent performance gain with more pretraining data. In experiments, we compare our model with discriminative and generative models pretrained on the same dataset. The results confirm that our framework effectively exploits existing annotated data and consistently outperforms baselines in both zero (9.4% average improvement) and few shot settings (3.5% average improvement).
Minimize Exposure Bias of Seq2Seq Models in Joint Entity and Relation Extraction
Oct 06, 2020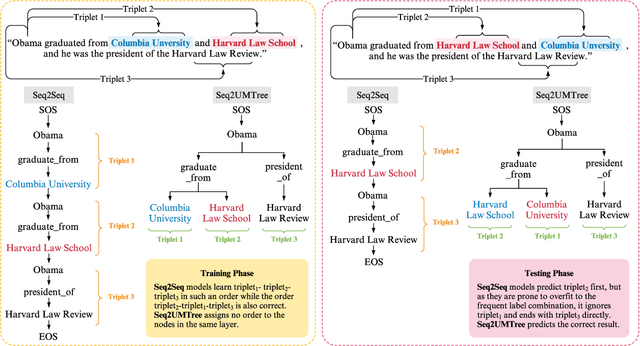
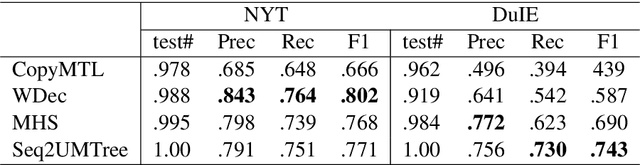
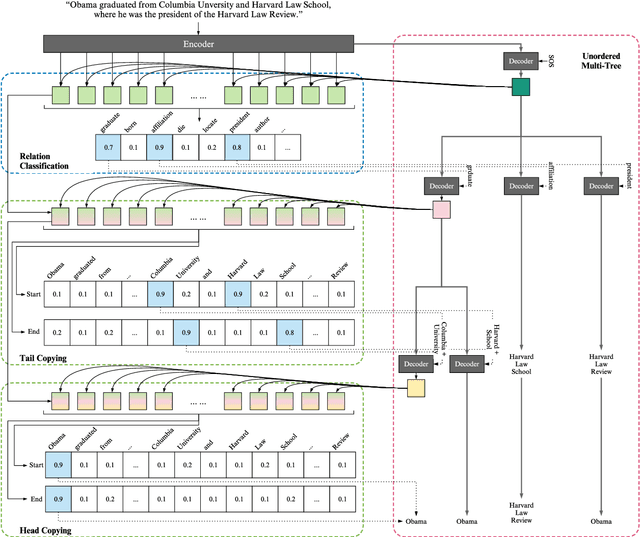
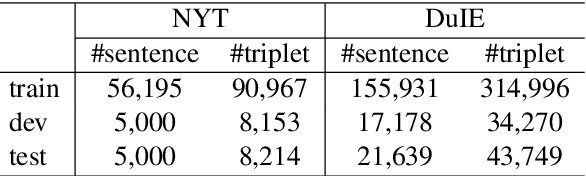
Abstract:Joint entity and relation extraction aims to extract relation triplets from plain text directly. Prior work leverages Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) models for triplet sequence generation. However, Seq2Seq enforces an unnecessary order on the unordered triplets and involves a large decoding length associated with error accumulation. These introduce exposure bias, which may cause the models overfit to the frequent label combination, thus deteriorating the generalization. We propose a novel Sequence-to-Unordered-Multi-Tree (Seq2UMTree) model to minimize the effects of exposure bias by limiting the decoding length to three within a triplet and removing the order among triplets. We evaluate our model on two datasets, DuIE and NYT, and systematically study how exposure bias alters the performance of Seq2Seq models. Experiments show that the state-of-the-art Seq2Seq model overfits to both datasets while Seq2UMTree shows significantly better generalization. Our code is available at https://github.com/WindChimeRan/OpenJERE .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge